Acquisition Lesson Plan
Name: L Etheridge
Topic: A Divided Nation
Essential Question:
How did westward expansion cause growing north-south divisions? How did key events, issues, and
individuals contribute to the causes, course, and consequences of the Civil War? Why did Reconstruction
cause political and social issues in the United States?
What do students need to learn to be able to answer the Essential Question?
Assessment Prompts:
1. How did the issue of slavery intensify the differences between the northern and southern economy,
social structure, and culture?
2. Why did the idea of states’ rights continue to be one of the main issues of the first half of the 19 th
century?
3. How did western expansion in the 1840s make conflict between the north and south inevitable?
4. How were the key battles (Antietam, Vicksburg, Gettysburg, Atlanta) examples of successful or failed
national war strategies?
5. How did the actions of Nat Turner, John C. Calhoun, and John Brown contribute to the Civil War?
6. What effect did free blacks have on the cause of abolition?
7. What is the connection between abolitionism and women’s suffrage?
8. How did the military and political leadership of the North compare with that of the South?
9. To what extent can society regulate morals and ethics with laws?
10. How was Reconstruction a struggle between the executive and legislative branches of government?
Activating Strategy:
KWL
Key vocabulary to preview:
Conflict,
Teaching Strategies:
Mind Map, Cause and Effect, Notes, Wordles
Assignment and/or Extending Thinking Activity:
The South (or North) is on trial for starting the Civil War. As with any trial, there will be a defense team,
prosecution/plaintiff team, witnesses, judge, and a jury.
The lawyers for the prosecution will research and prepare an indictment of the North/South. Your
indictment needs to include MULTIPLE reasons why the North or South is at fault. The overlying theme of the
trial is “conflict causes change.” What you are expected to do is prepare an opening and closing statement
citing SPECIFIC conflicts that led to the Civil War. Your goal is to prove that the way the North/South handled
these conflicts is what caused the war.
The lawyers for the defense will research and prepare a “not-guilty” defense of the charges given by
the prosecution. The overlying theme of the case is “conflict causes change.” In your opening and closing,
you need to used MULTIPLE, SPECIFIC examples of conflicts leading up to the Civil War and state how you
were NOT at fault in each of your examples. Remember, you do not have to prove that the other side caused
the war, just that you DIDN’T cause the war.
Each side will be allowed to call witnesses to testify on their behalf. Witnesses can include civilians,
soldiers, politicians, slaves, business owners, immigrants, etc. There should be at least one or two witnesses
called for each example of conflict that is used in the case. For example, if the prosecution claims that the
South is guilty because they kept pushing the issue of slavery, the prosecution should have a couple of
witnesses testify about WHAT the conflict over slavery was about, and why the South handled it incorrectly.
You must prepare a written biography of your witness prior to taking the stand.
Summarizing Strategy:
Review using CPS clickers, Test Study Guide
©2010 LEARNING-FOCUSED. All Rights Reserved.
Acquisition Lesson Pacing Guide
Name: L Etheridge
Topic: A Divided Nation
Essential Question: How did westward expansion cause
growing north-south divisions? How did key
events, issues, and individuals contribute to the causes, course, and consequences of the Civil War? Why did
Reconstruction cause political, and social issues in the United States?
Day 25/Session 1
Day 26/Session 2
Day 27/Session 3
Activating Strategy:
Activating Strategy:
Activating Strategy:
Daily 10
Daily 10
Daily 10
Key Vocabulary and Strategy:
Key Vocabulary and Strategy:
Key Vocabulary and Strategy:
The Alamo, annexation of Texas, war
on Mexico, Gadsden purchase, gold
rush of 1849
slavery, state’s rights, John C
Calhoun, doctrine of nullification,
secede, South Carolina nullification
crisis, sectionalism, Second Middle
Passage, mulattos, William Lloyd
Garrison, Grimke sisters, Nat
Turner’s Rebellion, Missouri
Compromise, Wilmot Proviso,
Compromise of 1850, Popular
sovereignty, Fugitive Slave law,
Kansas-Nebraska Act, Dred Scott
decision, John Brown’s Raid
slavery, state’s rights, John C
Calhoun, doctrine of nullification,
secede, South Carolina nullification
crisis, sectionalism, Second Middle
Passage, mulattos, William Lloyd
Garrison, Grimke sisters, Nat
Turner’s Rebellion, Missouri
Compromise, Wilmot Proviso,
Compromise of 1850, Popular
sovereignty, Fugitive Slave law,
Kansas-Nebraska Act, Dred Scott
decision, John Brown’s Raid
Students copy and define in the
vocabulary section of their
notebook by folding paper in half
with one side having definition
and other the term/phrase
Students copy and define in the
vocabulary section of their
notebook by folding paper in half
with one side having definition
and other the term/phrase
Teaching Strategies:
Teaching Strategies:
Students copy and define in the
vocabulary section of their
notebook by folding paper in half
with one side having definition
and other the term/phrase
Teaching Strategies:
Notes on Westward Expansion
and the issue of slavery in
western states including Texas
and California
Students create a mindmap
using their knowledge of
westward expansion and
Manifest Destiny
Assessment Prompt
Read chapter 10
Students will be given a map of
the United States at the time of
the Civil War. This will lead to a
class discussion regarding the
states and territories involved
and what events caused that area
to become a part of the war.
Using the map study as a
beginning point, students will
then create a time line to
visualize how unrelated events
can lead to war. These events
include Compromise of 1850,
publication of Uncle Tom’s Cabin,
the Kansas-Nebraska Act, John
Brown’s raid, and the election of
Abraham Lincoln as President.
Assessment Prompt
11. How did western expansion in 12. How did western expansion in
the 1840s make conflict
the 1840s make conflict
Read Chapter 10
Notes on causes of the civil
war
Students will use wordle along
with powerpoint to create a
collage representing the
causes of the Civil War
Assessment Prompt
How did the actions of Nat Turner,
John C. Calhoun, and John Brown
between the north and south
inevitable?
between the north and south
inevitable?
contribute to the Civil War?
What effect did free blacks have
on the cause of abolition?
What is the connection between
abolitionism and women’s suffrage?
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
©2010 LEARNING-FOCUSED. All Rights Reserved.
Day 28/Session 4
Day 29/Session 5
Day 30/Session 6
Activating Strategy:
Activating Strategy:
Activating Strategy:
Daily 10
Daily 10
Daily 10
Key Vocabulary and Strategy
Key Vocabulary and Strategy
Key Vocabulary and Strategy:
Republican Party, Abraham Lincoln,
presidential election of 1860,
Jefferson Davis, Fort Sumter, Ulysses
s Grant, William Y Sherman, Robert E
Lee, Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson,
writ of habeus corpus, draft,
Emancipation Proclamation, second
inaugural address, Antiem
Gettysburg, Gettysburg Address,
Vicksburg, Atlanta campaign, march
to the sea, Appomattox Courthouse,
Union advantages (population,
railroads industry)
Republican Party, Abraham Lincoln,
presidential election of 1860,
Jefferson Davis, Fort Sumter, Ulysses
s Grant, William Y Sherman, Robert E
Lee, Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson,
writ of habeus corpus, draft,
Emancipation Proclamation, second
inaugural address, Antiem
Gettysburg, Gettysburg Address,
Vicksburg, Atlanta campaign, march
to the sea, Appomattox Courthouse,
Union advantages (population,
railroads industry)
Students copy and define in the
vocabulary section of their
notebook by folding paper in half
with one side having definition
and other the term/phrase
Students copy and define in the
vocabulary section of their
notebook by folding paper in half
with one side having definition
and other the term/phrase
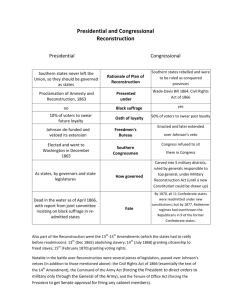
Andrew Johnson, presidential
Reconstruction, black codes, Radical
Republicans, Radical Reconstruction,
Thirteenth Amendment, Fourteenth
Amendment, Johnson’s
impeachment, sharecropping, tenant
farming, Freedman’s Bureau, role of
African American Churches, postwar
African American education,
Morehouse College, role of African
American in politics during
Reconstruction, Ku Klux Klan, Jim
Crow laws, literacy tests, poll taxes,
grandfather clauseStudents copy
Teaching Strategies:
Teaching Strategies:
Read Chapter 11
Finish Wordles
Key individuals of the Civil War
Read chapter 11
The Civil War – Major battles
Students will write a letter
from the perspective of a
Union or Confederate soldier
during the war. Students are
to include specific battles,
conditions of a soldier’s life,
and personal events.
and define in the vocabulary
section of their notebook by
folding paper in half with one side
having definition and other the
term/phrase
Teaching Strategies:
Read chapter 12
Complete Notes on the Civil
War
The Civil War in 10 minutes
video
Assessment Prompt
Assessment Prompt
Assessment Prompt
How did the military and political
leadership of the North compare
with that of the South?
How were the key battles
(Antietam, Vicksburg, Gettysburg,
Atlanta) examples of successful or
failed national war strategies?
How was Reconstruction a
struggle between the executive
and legislative branches of
government?
To what extent can society regulate
morals and ethics with laws?
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
Day 31/Session 7
Day32/Session 8
Activating Strategy:
Activating Strategy:
Daily 10
Daily 10
Key Vocabulary and Strategy:
Key Vocabulary and Strategy:
Andrew Johnson, presidential
Reconstruction, black codes, Radical
Republicans, Radical Reconstruction,
Thirteenth Amendment, Fourteenth
Amendment, Johnson’s
impeachment, sharecropping, tenant
farming, Freedman’s Bureau, role of
African American Churches, postwar
African American education,
Morehouse College, role of African
American in politics during
Reconstruction, Ku Klux Klan, Jim
Crow laws, literacy tests, poll taxes,
Andrew Johnson, presidential
Reconstruction, black codes, Radical
Republicans, Radical Reconstruction,
Thirteenth Amendment, Fourteenth
Amendment, Johnson’s
impeachment, sharecropping, tenant
farming, Freedman’s Bureau, role of
African American Churches, postwar
African American education,
Morehouse College, role of African
American in politics during
Reconstruction, Ku Klux Klan, Jim
Crow laws, literacy tests, poll taxes,
Students copy and define in the
vocabulary section of their
notebook by folding paper in half
with one side having definition
and other the term/phrase
Students copy and define in the
vocabulary section of their
notebook by folding paper in half
with one side having definition
and other the term/phrase
Teaching Strategies:
Teaching Strategies:
Students will examine primary
source documents from the
Reconstruction era.
www.enotes.com/reconstructi
on-era-primary-sources
www.thenagain.info/WebChro
n/USA/ReconstructionEra.html
These may include
photographs, letters, and
other visuals. These may
include photographs, letters,
and other visuals. Students, in
small groups, will break down
the historical background and
events addressed in the
document.
Review chapter 10-12
Review for test
Read chapter 12
Using the textbook and
working with a partner
Assessment Prompt
Assessment Prompt
How was Reconstruction a
struggle between the executive
and legislative branches of
government?
How was Reconstruction a
struggle between the executive
and legislative branches of
government?
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
Summarizing Strategy:
Understanding checks
Day 33/Session 9
Activating Strategy:
Test Review
Key Vocabulary and Strategy:
The Alamo, annexation of Texas, war on Mexico, Gadsden purchase, gold rush of 1849, slavery, state’s rights, John C
Calhoun, doctrine of nullification, secede, South Carolina nullification crisis, sectionalism, Second Middle Passage,
mulattos, William Lloyd Garrison, Grimke sisters, Nat Turner’s Rebellion, Missouri Compromise, Wilmot Proviso,
Compromise of 1850, Popular sovereignty, Fugitive Slave law, Kansas-Nebraska Act, Dred Scott decision, John Brown’s
Raid, Republican Party, Abraham Lincoln, presidential election of 1860, Jefferson Davis, Fort Sumter, Ulysses s Grant,
William Y Sherman, Robert E Lee, Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson, writ of habeus corpus, draft, Emancipation Proclamation,
second inaugural address, Antiem Gettysburg, Gettysburg Address, Vicksburg, Atlanta campaign, march to the sea,
Appomattox Courthouse, Union advantages (population, railroads industry), Andrew Johnson, presidential
Reconstruction, black codes, Radical Republicans, Radical Reconstruction, Thirteenth Amendment, Fourteenth
Amendment, Johnson’s impeachment, sharecropping, tenant farming, Freedman’s Bureau, role of African American
Churches, postwar African American education, Morehouse College, role of African American in politics during
Reconstruction, Ku Klux Klan, Jim Crow laws, literacy tests, poll taxes,
Teaching Strategies:
Unit Test
Summarizing Strategy:
Unit Test
Know-Understand-Do Organizer
Name: Lorrie Etheridge
Course/Subject: US History
Topic: A Divided Nation
Which Standards are students learning in this unit?
SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing north-south divisions and westward
expansion.
a. Explain how slavery became a significant issue in American politics, include the slave rebellion of Nat Turner
and the rise of abolitionism (William Lloyd Garrison, Frederick Douglass, and the Grimke sisters).
b. Explain the Missouri Compromise and the issue of slavery in western states and territories.
c. Describe the Nullification Crisis and the emergence of states’ rights ideology, including the role of John C.
Calhoun and development of sectionalism.
d. Describe war with Mexico and the Wilmot Proviso,
e. Explain how the Compromise of 1850 arose out of territorial expansion and population growth.
SSUSH9 The student will identify key events, issues, and individuals relating to the causes, course, and
consequences of the Civil War.
a. Explain the Kansas-Nebraska Act, the failure of popular sovereignty, Dred Scott case, and John Brown’s raid.
b. Describe President Lincoln’s efforts to preserve the Union as seen in his second inaugural address and the
Gettysburg speech and in his use of emergency powers, such as his decision to suspend habeas corpus.
c. Describe the role of Ulysses S. Grant, Robert E. Lee, “Stonewall Jackson,” William Tecumseh Sherman, and
Jefferson Davis.
d. Explain the importance of Fort Sumter, Antietam, Vicksburg, Gettysburg, and the Battle for Atlanta and the
impact of geography on these battles.
e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation.
f. Explain the importance of the growing economic disparity between the North and the South through an
examination of population, functioning railroads, and industrial output.
SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction.
a. Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Republican Reconstruction.
b. Explain efforts to redistribute land in the South among the former slaves and provide advanced education
such as (Morehouse College) and describe the role the Freedmen’s Bureau.
c. Describe the significance of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments.
d. Explain Black Codes, the Ku Klux Klan, and other forms of resistance to racial equality during Reconstruction.
e. Explain the impeachment of Andrew Johnson in relationship to Reconstruction.
f. Analyze how the presidential election of 1876 and the subsequent compromise of 1877 marked the end of
Reconstruction.
By the end of this unit, students will be able to…
KNOW:
UNDERSTAND
Vocabulary:
gradualism, American Colonization
Society, abolition, David Walker,
William Lloyd Garrison, emancipation,
Sojourner Truth, Tejano,
DO:
The failure to follow the principles
of compromise and consensus
often leads to conflict and
division.
Fighting a war involves planning
and sacrifice.
How did the issue of slavery
intensify the differences
between the northern and
southern economy, social
structure, and culture? (USH8a,
b; USH9a)
Why did the idea of states’ rights
empresario, Antonio Lopez de
Santa Anna, Sam Houston, Alamo,
William B. Travis, annexation, ,
John Tyler, James K. Polk, "54-40'
or Fight", envoy, Zachary Taylor,
John C. Fremont, Bear Flag
Republic, Winfield Scott, Treaty of
Guadalupe Hidalgo, cede, , Wilmot
Proviso, popular sovereignty,
secession, , Compromise of 1850,
Uncle Tom's Cabin, Harriet Beecher
Stowe, Fugitive Slave Act,
Underground Railroad, Harriet
Tubman, transcontinental railroad,
Gadsden Purchase, KansasNebraska Act, "Bleeding Kansas",
Charles Sumner, Preston Brooks,,
Republican Party, Know-Nothings,
Election of 1856, Dred Scott v.
Sanford, referendum, Lecompton
constitution, Lincoln-Douglas
Debates, John Brown's Raid,
Election of 1860, South Carolina's
Secession, Crittenden's
Compromise, Confederate States
of America, Jefferson Davis, Fort
Sumter, Identify the Border States,
, Robert E. Lee, Tredegar Iron
Works, Copperheads, conscription,
habeas corpus, attrition, Anaconda
Plan, Thomas "Stonewall" Jackson,
Irwin McDowell, blockade runner,
Ulysses S. Grant, Battle of Shiloh,
Battle of Murfreesboro, George B.
McClellan, Seven Days' Battle,
Second Battle of Bull Run, Battle of
Antietam, Emancipation
Proclamation, 54th Massachusetts
regiment, hardtack, Florence
Nightingale, Clara Burton,
Andersonville, Ga., Battle of
Vicksburg, Battle of
Fredericksburg, Battle of
Chancellorsville, Battle of
Individuals play a role in creating
a nation.
The federal government plays a
role in mandating political and
social change.
continue to be one of the main
issues of the first half of the 19th
century? (USH8c)
How did western expansion in
the 1840s make conflict between
the north and south inevitable?
(USH8b, d; USH9a)
How were the key battles
(Antietam, Vicksburg,
Gettysburg, Atlanta) examples of
successful or failed national war
strategies? (USH9d)
How did the actions of Nat
Turner, John C. Calhoun, and
John Brown contribute to the
Civil War? (USH8a, c; USH9a)
What effect did free blacks have
on the cause of abolition?
(USH8a)
What is the connection between
abolitionism and women’s
suffrage? (USH8a)
How did the military and political
leadership of the North compare
with that of the South? (USH9b)
To what extent can society
regulate morals and ethics with
laws? (USH9a; USH10c)
How was Reconstruction a
struggle between the executive
and legislative branches of
government? (USH10a
Gettysburg, Gettysburg Address,
Battle of Chattanooga, William
Tecumseh Sherman, Wilderness to
Cold Harbor, Siege of Petersburg,
Fall of Atlanta, Sherman's march to
the Sea, Appomattox Courthouse,
Election of 1864, Lincoln's
Assassination, John Wilkes Booth, ,
Reconstruction, Lincoln's Plan,
amnesty, Thaddeus Stevens,
Radical Republicans, Wade-Davis
Bill, Freedmen's Bureau, Andrew
Johnson, Johnson's Plan, black
codes, Civil Rights Act of 1866,
14th Amendment, Election of
1866, Military Reconstruction Act,
Tenure of Office Act, Johnson's
Impeachment, 15th Amendment,
carpetbaggers, scalawags, Ku Klux
Klan, "sin taxes", Horace Greely,
"Whiskey Ring", Election of 1876,
Compromise of 1877, "New
South", tenant farmers,
sharecroppers, furnishing
merchants, crop liens, debt
peonage, ,
Facts: