Physical Properties of Minerals—Lab Review
advertisement

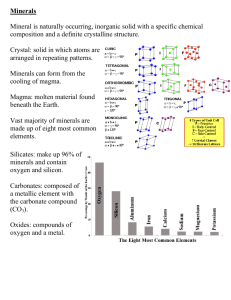
Name: Science 9: Mineral Review Questions 1. What is the purpose of investigating the physical properties of minerals? What do they tell us? 2. If topaz scratches fluorite, what can you tell about the hardness of each mineral? 3. How do the physical properties of minerals relate to what we use them for? Explain using an example. 4. What is the hardness of a streak plate? Minerals leave a powder streak on the tile because the tile scratches the minerals. Which mineral(s) on Mohs Scale will not leave a powder streak on the tile? 5. The strength of the bond holding atoms together determines the hardness of a mineral. Which has stronger bonds, your fingernail or a water glass? Explain. 6. Which object could scratch a glass tabletop—a copper staple, a scrap of iron, or a steel wire? 7. Soapstone is frequently used to make sinks. Soapstone is largely composed of talc. What special care would you take in cleaning sinks made of soapstone? 8. A mineral is found to have a mass of 5 g and a volume of 12 mL. What is the minerals density? Show your work and include units. 9. Kim has an opal that fell out of an old ring. She plans to keep the opal, which has a hardness of 5 or 6, with her mineral samples. She knows the opal will be safe. How is that possible? 10. Give examples of three minerals that can be identified using their unique or distinctive property. Be sure to also describe that property. 11. If both quartz and mica are in the silicate group, both would contain the silicon-oxygen tetrahedron. Why then does mica cleave easily, while quartz fractures instead of cleaves? 12. Read each statement below. Decide if they are true or false and explain your reasoning a. The streak test is a reliable test for mineral identification b. Fluorescent minerals glow while being subjected to ultraviolet light c. Cleavage is important in identifying some minerals d. All minerals have the same basic crystal shape 13. Although color is the most obvious property of a mineral, it is difficult to identify a mineral by color alone. Explain. 14. Diamonds and graphite are both made of the element carbon, but they are not considered the same mineral. Explain. 15. What five characteristics do all minerals share? 16. Explain the displacement method for determining the volume of a solid object. 17. Determine to what mineral group the following minerals belong: Bauxite: Al(OH)3 Fluorite: CaF2 Halite: NaCl Magnetite: Fe3O4 Graphite: C Calcite: CaCO3 Galena: PbS Talc: Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 Olivine: Fe2SiO4 Orthoclase: KAlSi3O8 18. Go to page 63 of your text. Look at the graph on p. 63 and answer questions #4-6 below.