6.P.2 (by Melanie Smith, Jennifer Tiso, Charlene - NHCS
advertisement

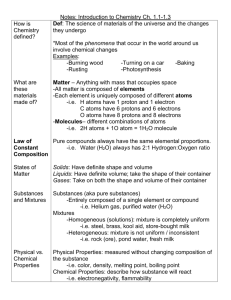
Science Essential Standards Unit Development Unit Topic Matter Essential Standards Goals and Objectives Standard 6.P.2 Understand the structure, classifications and physical properties of matter. Object. 6. P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements. 6. P.2.2 Explain the effect of heat on the motion of atoms through a description of what happens to particles during a change in phase. 6. P.2.3 Compare the physical properties of pure substances that are independent of the amount of matter present including density, boiling point, melting point and solubility to properties that are dependent on the amount of matter present to include volume, mass and weight. Concepts Being Studied 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements Properties shared by particles of all matter. Describe the Three states of matter. State Differences between the three states of matter. Identify physical properties of matter. 6. P.2.2 Explain the effect of heat on the motion of atoms through a description of what happens to particles during a change in phase. How temperature relates to kinetic energy. Compare temperatures on different temperature scales. Describe how energy is involved in changing state. 6. P.2.3 Compare the physical properties of pure substances that are independent of the amount of matter present including density, boiling point, melting point and solubility to properties that are dependent on the amount of matter present to include volume, mass and weight. Describe a pure substance. Describe the characteristics of pure substances: boiling point, melting point, density. Essential Questions 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements Describe the four states of Matter? How are they different? What are some examples of matter? What are atoms? 6. P.2.2 Explain the effect of heat on the motion of atoms through a description of what happens to particles during a change in phase. In terms of particle movement explain how increasing temperature changes water in the solid state. 6. P.2.3 Compare the physical properties of pure substances that are independent of the amount of matter present including density, boiling point, melting point and solubility to properties that are dependent on the amount of matter present to include volume, mass and weight. What is density? What are physical properties? Essential Information 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements What branch of science studies of matter? What are atoms Atoms and molecules make up the three common states of matter on Earth—solids, liquids, and gases. 6. P.2.2 Explain the effect of heat on the motion of atoms through a description of what happens to particles during a change in phase. The particles of a liquid are attracted to one another, are in motion, and are able to move past one another. 6. P.2.3 Compare the physical properties of pure substances that are independent of the amount of matter present including density, boiling point, melting point and solubility to properties that are dependent on the amount of matter present to include volume, mass and weight. Vocabulary- density, melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation, mass, volume. Essay Questions Being a solid, liquid or gas is a property of a substance. 6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements Why does matter change states? 6. P.2.2 Explain the effect of heat on the motion of atoms through a description of what happens to particles during a change in phase. How does temperature affect the movement of particles in matter? 6. P.2.3 Compare the physical properties of pure substances that are independent of the amount of matter present including density, boiling point, melting point and solubility to properties that are dependent on the amount of matter present to include volume, mass and weight. How are physical properties used to describe pure substances? Project Ideas Web quest,Tic-Tac-Toe, Models Technology Web learning –Techtopics- Matter Interactive smart lesson on states of matter, Ipads, data projectors, and all other resources within the school. Labs, Experiments, Activities, etc. ·6.P.2.1 Recognize that all matter is made up of atoms and atoms of the same element are all alike, but are different from the atoms of other elements Explore states of matter (i.e., solids, liquids, gases, and plasma) through experimenting, modeling, and interpreting. ·6.P.2.3 Compare the physical properties of pure substances that are independent of the amount of matter present including density, boiling point, melting point and solubility to properties that are dependent on the amount of matter present to include volume, mass and weight. Analyze and explore the states of matter and model the molecular differences in states (e.g., lots of molecules Resources Assessment moving slowly/solid). What is Density? Finding Volume—The Water Displacement Method Density of Water Density—Sink and Float for Solids Density—Sink and Float for Liquids Temperature and Density Cornstarch experiment Brain Pop – States of matter United Streaming -Properties of Matter Internet, textbooks Bill Nye video matter. Matter Magazine (Discovery Ed) American Physical Society National Geographic NASA Education American Geological Institute National Association of Biology Teachers Weekly Quiz, Test , classscapes, and Teacher made test.