Arabidopsis mutants point to pathways of microtubule
advertisement

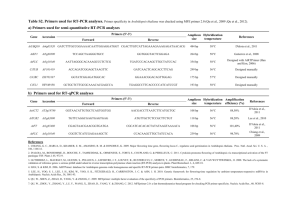
Table 1. Arabidopsis mutations of genes with microtubule-associated functions. Only mutants for which the genetic lesion has been reported are presented. This list contains sensu strictu MAP mutants, mutants of the tubulin folding machinery as well as further mutants for which distinctive microtubule-related phenotypes have been reported. Homology AGI number Mutant angustifolia1 similar to CtBP- an1 Bars At1g01510 Main morphological and sub- Miscellaneous Reference cellular phenotype - reduced trichome branching (Kim et al., 2002) - microtubule density (Folkers et al., - elongated leaves 2002) - microtubule orientation arl2 ARF-like (titan5, GTPase family, hallimasch) tubulin folding armadillo-repeat kinesin (plant- containing specific class) At2g18390 - mutants arrest during (Steinborn et al., embryogenesis At1g01950 2002) - helical root growth (Sakai et al., 2008) kinesin ark2 atk1 kinesin 14 At4g21270 class - atk1-1 mutant male meiotic (Chen et al., spindles (metaphase1) were 2002; Marcus et broad, unfocused and multi- al., 2003) axial atk5 kinesin 14 At4g05190 class - plants appear (Ambrose et al., morphologically normal 2005; Ambrose - involved in early mitotic and Cyr, 2007) spindle formation champignon tubulin-folding (titan1) co-factor D clasp-1 CLASP At3g60740 - mutants arrest during (Steinborn et al., embryogenesis At2g20190 homologue 2002) - plants are dwarfed (Ambrose et al., - less populated cortical 2007; Kirik et al., microtubules array 2007) - mitotic arrays are aberrant eb1-a End Binding1 At3g47690 - helical growth double and (Bisgrove et al., eb1-b homologue At5g62500 - some alleles oryzalin triple mutants 2008) eb1-c At5g67270 hypersensitive reveal phenotype endosperm plant MAP At2g44190 defective1 - endosperm does not (Pignocchi et al., cellularize ede1 2009) - cytokinesis defects in embryo fass phosphatase fs1 PP2A (ton2) regulatory and cortical microtubules are Camilleri et al., subunit B” misaligned 2002) fragile fiber1 kinesin 4 class At5g18580 At5g47820 fra1 - no division plane alignment (Torres-Ruiz and - lacks pre-prophase bands Jurgens, 1994; - reduced mechanical (Zhong et al., strength of fibers 2002; Zhou et al., - abnormal orientation of 2007) cellulose microfibrils fragile fiber2 katanin p60 fra2 subunit At1g80350 (bot1, lue1, erh3) - stunted growth (Bichet et al., - ectopic root hairs 2001; Burk et al., - delayed establishment of 2001; Webb et the cortical microtubule array al., 2002; Bouquin et al., 2003) hinkel kinesin 14 (nack1) class At1g18370 - cytokinesis defects (Nishihama et al., - phragmoplast microtubules 2002; Strompen do not re-organize ibo1 NIMA-related (nek6) protein kinase At3g44200 - epidermal outgrowth et al., 2002) GFP fusions (Motose et al., label 2008; Sakai et microtubules; al., 2008) interaction with ARK kinesins. kiesel tubulin-folding kis co-factor A At2g30410 - shape defect in trichomes (Kirik et al., - cell defect in etiolated 2002b; Steinborn hypocotyls et al., 2002) - microtubule orientation abnormal kinesin13a kinesin 13 At3g16630 class map18 microtubule binding motif of MAP1B - overbranched trichome (Lu et al., 2005) - Golgi stacks clustered At5g44610 - cell shape defects based on RNAi (Wang et al., - microtubule orientation data 2007) defective map70-5 plant MAP At4g17220 - reduced inflorescence growth based on RNAi (Korolev et al., data 2007) temperature- (Whittington et - helical organ growth in overexpressors microtubule XMAP215 / organization1 TOGp swelling, stunted organs and sensitive alleles al., 2001; Twell et mor1 homologue cytokinesis defects present al., 2002) At2g35630 (gem1) - helical organ growth, cell - reduced microtubule length morphogenesis kinesin (plant- of root-hairs specific class) At3g54870 - split root hairs (Jones et al., - root hair microtubules with 2006; Yang et al., mrh2 ectopic localization in 2007; Sakai et (ark1) endoplasm al., 2008) nedd1 WD40 repeat At5g05970 protein pfifferling tubulin-folding tubulin folding plp3 (Zeng et al., development At1g71440 co-factor E phosducin 3 - mitotic defects during pollen 2009) - mutants arrest during (Steinborn et al., embryogenesis At3g50960 At5g66410 - disoriented cell growth and cytokinesis defects - disrupted microtubule arrays 2002) includes RNAi (Castellano and data, double Sablowski, 2008) knock-down reveals phenotype phragmoplast- kinesin 12 At3g17360 orienting class At3g19050 kinesin kinesin 12 At4g14150 associated class At3g23670 pakrp2 double mutants (Müller et al., reveal 2006) phenotype and misplaced cell walls phramoplast- pakrp1 and cytokinesis - misoriented mitotic arrays pok1 and pok2 kinesin - abnormal plane of - defects in the first post- double mutants meiotic division of the male reveal gametophyte1 phenotype - phragmoplasts of the microspore become disorganized (Lee et al., 2007) pleiade PRC1 / Ase1 / (map65-3) MAP65 At5g51600 homologue - cytokinesis defects in roots (Müller et al., - the cytokinetic phragmoplast 2002; Müller et is distorted al., 2004; Caillaud et al., 2008) porcino tubulin-folding por co-factor C At4g39920 - mutants arrest early during (Kirik et al., embryogenesis 2002a; Steinborn - strong mutants have no et al., 2002) detectable microtubules propyzamide- similar to hypersensitive1 MAPK phs1 phosphatase prefoldin6 prefoldin At5g23720 At1g29990 homologue - helical growth dominant- (Naoi and - cortical microtubules less negative allele, Hashimoto, 2004) ordered and more knock-out is fragmented embryo-lethal - shorter roots and etiolated (Gu et al., 2008) hypocotyls ran-gap mutants RanGAP At3g63130 - oblique cell walls in roots based on a rg1 homologue At5g19320 - cell wall stubs combination of rg2 (Xu et al., 2008) RNAi with TDNA insertion root swelling7 kinesin 5 class At2g28620 rsw7 - swollen roots temperature- (Bannigan et al., - cortical and spindle sensitive allele 2007) microtubules misoriented rop-interacting1 CRIB motif At2g33460 ric1 - misformed leaf epidermal (Fu et al., 2005) cells - fewer, shorter and less organized microtubules runkel kinase domain ruk and HEAT organization and arrested (emb3013) repeats cell plate expansion spira1-like 2 plant MAP At5g18700 At1g69230 - abnormal phragmoplast - enhanced helical organ spira1-like 3 At3g02180 growth when analyzed in spira1-like 4 At5g15600 spr1 background (Krupnova et al., 2009) (Nakajima et al., 2006) spiral1 plant MAP At2g03680 spr1 - helical growth and swollen cells (sku6) - helical microtubule arrays (Furutani et al., 2000; Nakajima et al., 2004; Sedbrook et al., 2004) spiral3 GCP2 spr3 homologue through recessive missense with grip motif mutation At5g17410 (SPC98-like) - right-handed helical growth (Nakamura and Hashimoto, 2009) - knock-outs have gametophytic defects stud1 kinesin 14 std1 class At3g43210 (tetraspore, (Hülskamp et al., abnormal pollen shape 1997; Spielman - male meiotic microtubule nack2) tangled1 - meiosis defects lead to array fails to form plant MAP At3g05330 tan1 - abnormal plane of cytokinesis et al., 1997; Yang et al., 2003) (Walker et al., 2007) - PPB alignment and phragmoplast attraction impaired tonneau1 LisH domain ton1 TOF motif At3g55000 - no division plane alignment (Traas et al., - no PPB formed 1995; Nacry et PLL motif al., 1998; Azimzadeh et al., 2008) tortifolia1 plant MAP At4g27060 tor1 (spr2, cn) - helical organ growth (Bürger, 1971; - cortical microtubules Buschmann et misaligned and later helical - altered microtubule dynamics tortifolia1-like (spr2-like) plant MAP At1g50890 - enhances twisting in tor1 background al., 2004; Shoji et al., 2004; Yao et al., 2008) (Yao et al., 2008) tua2 -tubulin At1g50010 tua3 GTP binding At5g19770 tua4 At1g04820 tua5 At5g19780 tua6 At4g14960 (lefty1+2, tor2) tua6cys213 is a (Bao et al., 2001; helical microtubule arrays in temperature Thitamadee et dominant-negative mutants sensitive allele; al., 2002; Ishida antisense data and Hashimoto, available. 2007; Ishida et - helical organ twisting and - altered microtubule dynamics in helical growth background al., 2007; - stunted growth in -tubulin Buschmann et al., 2009) antisense plants tub1 -tubulin At1g75780 - helical organ twisting dominant- (Ishida et al., tub2 GTPase At5g62690 - helical microtubule arrays negative tubulin 2007) tub3 At5g62700 tub4 At5g44340 mutations tug1 -tubulin tug2 At3g61650 At5g05620 - gametophytic or seedling lethal - aberrant cytokinetic microtubule arrays double mutants (Binarova et al., reveal 2006; Pastuglia phenotype, et al., 2006) RNAi data also available ungud9 plant MAP At2g34680 (air9) - embryo lethal and (Lalanne et al., gametophyte defective 2004; Buschmann et al., 2006; Buschmann et al., 2007) wave- TPX2 domain dampened2 homology At5g28646 - helical growth and impaired root waving wvd2 overexpression (Yuen et al., and RNAi 2003; Perrin et - helical microtubule arrays wave- TPX2 domain dampened-like homology At3g04630 - helical growth and impaired root waving al., 2007) overexpression (Yuen et al., and RNAi 2003; Perrin et wdl1 al., 2007) zwichel Ca2+ / zwi (kcbp) - fewer trichome branches zwi mutants (Oppenheimer et calmodulin – and impaired branch may be al., 1997; regulated class elongation hypomorphic Krishnakumar 14 kinesin At5g65930 and Oppenheimer, 1999; Reddy et al., 2004) Supplemental References Ambrose, J.C., and Cyr, R. (2007). The kinesin ATK5 functions in early spindle assembly in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 226-236. Ambrose, J.C., Li, W., Marcus, A., Ma, H., and Cyr, R. (2005). A minus-end-directed kinesin with plusend tracking protein activity is involved in spindle morphogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 1584-1592. Ambrose, J.C., Shoji, T., Kotzer, A.M., Pighin, J.A., and Wasteneys, G.O. (2007). The Arabidopsis CLASP gene encodes a microtubule-associated protein involved in cell expansion and division. Plant Cell 19, 2763-2775. Azimzadeh, J., Nacry, P., Christodoulidou, A., Drevensek, S., Camilleri, C., Amiour, N., Parcy, F., Pastuglia, M., and Bouchez, D. (2008). Arabidopsis TONNEAU1 Proteins Are Essential for Preprophase Band Formation and Interact with Centrin. Plant Cell 20, 2146-2159. Bannigan, A., Scheible, W.R., Lukowitz, W., Fagerstrom, C., Wadsworth, P., Somerville, C., and Baskin, T.I. (2007). A conserved role for kinesin-5 in plant mitosis. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2819-2827. Bao, Y., Kost, B., and Chua, N.H. (2001). Reduced expression of alpha-tubulin genes in Arabidopsis thaliana specifically affects root growth and morphology, root hair development and root gravitropism. Plant J. 28, 145-157. Bichet, A., Desnos, T., Turner, S., Grandjean, O., and Hofte, H. (2001). BOTERO1 is required for normal orientation of cortical microtubules and anisotropic cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 25, 137-148. Binarova, P., Cenklova, V., Prochazkova, J., Doskocilova, A., Volc, J., Vrlik, M., and Bogre, L. (2006). Gamma-tubulin is essential for acentrosomal microtubule nucleation and coordination of late mitotic events in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18, 1199-1212. Bisgrove, S.R., Lee, Y.R., Liu, B., Peters, N.T., and Kropf, D.L. (2008). The microtubule plus-end binding protein EB1 functions in root responses to touch and gravity signals in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20, 396-410. Bouquin, T., Mattsson, O., Naested, H., Foster, R., and Mundy, J. (2003). The Arabidopsis lue1 mutant defines a katanin p60 ortholog involved in hormonal control of microtubule orientation during cell growth. J. Cell Sci. 116, 791-801. Bürger, D. (1971). Die morphologischen Mutanten des Göttinger Arabidopsis-Sortiments, einschließlich der Mutanten mit abweichender Samenfarbe. Arabidopsis Inf. Serv. 8, 36-42. Burk, D.H., Liu, B., Zhong, R., Morrison, W.H., and Ye, Z.H. (2001). A katanin-like protein regulates normal cell wall biosynthesis and cell elongation. Plant Cell 13, 807-827. Buschmann, H., Sanchez-Pulido, L., Andrade-Navarro, M.A., and Lloyd, C.W. (2007). Homologues of Arabidopsis Microtubule-Associated AIR9 in Trypanosomatid Parasites: Hints on Evolution and Function. Plant Signal. Behav. 2, 296-299. Buschmann, H., Hauptmann, M., Niessing, D., Lloyd, C.W., and Schäffner, A.R. (2009). Helical Growth of the Arabidopsis Mutant tortifolia2 Does Not Depend on Cell Division Patterns but Involves Handed Twisting of Isolated Cells. Plant Cell 21, 2090-2106. Buschmann, H., Chan, J., Sanchez-Pulido, L., Andrade-Navarro, M.A., Doonan, J.H., and Lloyd, C.W. (2006). Microtubule-Associated AIR9 Recognizes the Cortical Division Site at Preprophase and Cell-Plate Insertion. Curr. Biol. 16, 1938-1943. Buschmann, H., Fabri, C.O., Hauptmann, M., Hutzler, P., Laux, T., Lloyd, C.W., and Schäffner, A.R. (2004). Helical growth of the Arabidopsis mutant tortifolia1 reveals a plant-specific microtubuleassociated protein. Curr. Biol. 14, 1515-1521. Caillaud, M.C., Lecomte, P., Jammes, F., Quentin, M., Pagnotta, S., Andrio, E., de Almeida Engler, J., Marfaing, N., Gounon, P., Abad, P., and Favery, B. (2008). MAP65-3 microtubuleassociated protein is essential for nematode-induced giant cell ontogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20, 423-437. Camilleri, C., Azimzadeh, J., Pastuglia, M., Bellini, C., Grandjean, O., and Bouchez, D. (2002). The Arabidopsis TONNEAU2 gene encodes a putative novel protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit essential for the control of the cortical cytoskeleton. Plant Cell 14, 833-845. Castellano, M.M., and Sablowski, R. (2008). Phosducin-like protein 3 is required for microtubuledependent steps of cell division but not for meristem growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20, 969981. Chen, C., Marcus, A., Li, W., Hu, Y., Calzada, J.P., Grossniklaus, U., Cyr, R.J., and Ma, H. (2002). The Arabidopsis ATK1 gene is required for spindle morphogenesis in male meiosis. Development 129, 2401-2409. Folkers, U., Kirik, V., Schobinger, U., Falk, S., Krishnakumar, S., Pollock, M.A., Oppenheimer, D.G., Day, I., Reddy, A.S., Jurgens, G., and Hulskamp, M. (2002). The cell morphogenesis gene ANGUSTIFOLIA encodes a CtBP/BARS-like protein and is involved in the control of the microtubule cytoskeleton. Embo J. 21, 1280-1288. Fu, Y., Gu, Y., Zheng, Z., Wasteneys, G., and Yang, Z. (2005). Arabidopsis interdigitating cell growth requires two antagonistic pathways with opposing action on cell morphogenesis. Cell 120, 687700. Furutani, I., Watanabe, Y., Prieto, R., Masukawa, M., Suzuki, K., Naoi, K., Thitamadee, S., Shikanai, T., and Hashimoto, T. (2000). The SPIRAL genes are required for directional control of cell elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 127, 4443-4453. Gu, Y., Deng, Z., Paredez, A.R., Debolt, S., Wang, Z.Y., and Somerville, C. (2008). Prefoldin 6 is required for normal microtubule dynamics and organization in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. Hülskamp, M., Parekh, N.S., Grini, P., Schneitz, K., Zimmermann, I., Lolle, S.J., and Pruitt, R.E. (1997). The STUD gene is required for male-specific cytokinesis after telophase II of meiosis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Dev. Biol. 187, 114-124. Ishida, T., and Hashimoto, T. (2007). An Arabidopsis thaliana tubulin mutant with conditional rootskewing phenotype. J. Plant Res. 120, 635-640. Ishida, T., Kaneko, Y., Iwano, M., and Hashimoto, T. (2007). Helical microtubule arrays in a collection of twisting tubulin mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 8544-8549. Jones, M.A., Raymond, M.J., and Smirnoff, N. (2006). Analysis of the root-hair morphogenesis transcriptome reveals the molecular identity of six genes with roles in root-hair development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 45, 83-100. Kim, G.T., Shoda, K., Tsuge, T., Cho, K.H., Uchimiya, H., Yokoyama, R., Nishitani, K., and Tsukaya, H. (2002). The ANGUSTIFOLIA gene of Arabidopsis, a plant CtBP gene, regulates leaf-cell expansion, the arrangement of cortical microtubules in leaf cells and expression of a gene involved in cell-wall formation. Embo J. 21, 1267-1279. Kirik, V., Herrmann, U., Parupalli, C., Sedbrook, J.C., Ehrhardt, D.W., and Hulskamp, M. (2007). CLASP localizes in two discrete patterns on cortical microtubules and is required for cell morphogenesis and cell division in Arabidopsis. J. Cell Sci. 120, 4416-4425. Kirik, V., Mathur, J., Grini, P.E., Klinkhammer, I., Adler, K., Bechtold, N., Herzog, M., Bonneville, J.M., and Hulskamp, M. (2002a). Functional analysis of the tubulin-folding cofactor C in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 12, 1519-1523. Kirik, V., Grini, P.E., Mathur, J., Klinkhammer, I., Adler, K., Bechtold, N., Herzog, M., Bonneville, J.M., and Hulskamp, M. (2002b). The Arabidopsis TUBULIN-FOLDING COFACTOR A gene is involved in the control of the alpha/beta-tubulin monomer balance. Plant Cell 14, 2265-2276. Korolev, A.V., Buschmann, H., Doonan, J.H., and Lloyd, C.W. (2007). AtMAP70-5, a divergent member of the MAP70 family of microtubule-associated proteins, is required for anisotropic cell growth in Arabidopsis. J. Cell Sci. 120, 2241-2247. Krishnakumar, S., and Oppenheimer, D.G. (1999). Extragenic suppressors of the Arabidopsis zwi-3 mutation identify new genes that function in trichome branch formation and pollen tube growth. Development 126, 3079-3088. Krupnova, T., Sasabe, M., Ghebreghiorghis, L., Gruber, C.W., Hamada, T., Dehmel, V., Strompen, G., Stierhof, Y.D., Lukowitz, W., Kemmerling, B., Machida, Y., Hashimoto, T., Mayer, U., and Jurgens, G. (2009). Microtubule-Associated Kinase-like Protein RUNKEL for Cell Plate Expansion in Arabidopsis Cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 19, 6 pages. Lalanne, E., Michaelidis, C., Moore, J.M., Gagliano, W., Johnson, A., Patel, R., Howden, R., VielleCalzada, J.P., Grossniklaus, U., and Twell, D. (2004). Analysis of transposon insertion mutants highlights the diversity of mechanisms underlying male progamic development in Arabidopsis. Genetics 167, 1975-1986. Lee, Y.R., Li, Y., and Liu, B. (2007). Two Arabidopsis phragmoplast-associated kinesins play a critical role in cytokinesis during male gametogenesis. Plant Cell 19, 2595-2605. Lu, L., Lee, Y.R., Pan, R., Maloof, J.N., and Liu, B. (2005). An internal motor kinesin is associated with the Golgi apparatus and plays a role in trichome morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Cell 16, 811-823. Marcus, A.I., Li, W., Ma, H., and Cyr, R.J. (2003). A kinesin mutant with an atypical bipolar spindle undergoes normal mitosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 1717-1726. Motose, H., Tominaga, R., Wada, T., Sugiyama, M., and Watanabe, Y. (2008). A NIMA-related protein kinase suppresses ectopic outgrowth of epidermal cells through its kinase activity and the association with microtubules. Plant J. 54, 829-844. Müller, S., Han, S., and Smith, L.G. (2006). Two kinesins are involved in the spatial control of cytokinesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 16, 888-894. Müller, S., Fuchs, E., Ovecka, M., Wysocka-Diller, J., Benfey, P.N., and Hauser, M.T. (2002). Two new loci, PLEIADE and HYADE, implicate organ-specific regulation of cytokinesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 130, 312-324. Müller, S., Smertenko, A., Wagner, V., Heinrich, M., Hussey, P.J., and Hauser, M.T. (2004). The plant microtubule-associated protein AtMAP65-3/PLE is essential for cytokinetic phragmoplast function. Curr. Biol. 14, 412-417. Nacry, P., Camilleri, C., Courtial, B., Caboche, M., and Bouchez, D. (1998). Major chromosomal rearrangements induced by T-DNA transformation in Arabidopsis. Genetics 149, 641-650. Nakajima, K., Kawamura, T., and Hashimoto, T. (2006). Role of the SPIRAL1 gene family in anisotropic growth of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 47, 513-522. Nakajima, K., Furutani, I., Tachimoto, H., Matsubara, H., and Hashimoto, T. (2004). SPIRAL1 encodes a plant-specific microtubule-localized protein required for directional control of rapidly expanding Arabidopsis cells. Plant Cell 16, 1178-1190. Nakamura, M., and Hashimoto, T. (2009). A mutation in the Arabidopsis -tubulin-containing complex causes helical growth and abnormal microtubule branching. J. Cell Sci. 122, 2208-2217. Naoi, K., and Hashimoto, T. (2004). A semidominant mutation in an Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-like gene compromises cortical microtubule organization. Plant Cell 16, 1841-1853. Nishihama, R., Soyano, T., Ishikawa, M., Araki, S., Tanaka, H., Asada, T., Irie, K., Ito, M., Terada, M., Banno, H., Yamazaki, Y., and Machida, Y. (2002). Expansion of the cell plate in plant cytokinesis requires a kinesin-like protein/MAPKKK complex. Cell 109, 87-99. Oppenheimer, D.G., Pollock, M.A., Vacik, J., Szymanski, D.B., Ericson, B., Feldmann, K., and Marks, M.D. (1997). Essential role of a kinesin-like protein in Arabidopsis trichome morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 6261-6266. Pastuglia, M., Azimzadeh, J., Goussot, M., Camilleri, C., Belcram, K., Evrard, J.L., Schmit, A.C., Guerche, P., and Bouchez, D. (2006). Gamma-tubulin is essential for microtubule organization and development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18, 1412-1425. Perrin, R.M., Wang, Y., Yuen, C.Y., Will, J., and Masson, P.H. (2007). WVD2 is a novel microtubuleassociated protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 49, 961-971. Pignocchi, C., Minns, G.E., Nesi, N., Koumproglou, R., Kitsios, G., Benning, C., Lloyd, C.W., Doonan, J.H., and Hills, M.J. (2009). ENDOSPERM DEFECTIVE1 Is a Novel MicrotubuleAssociated Protein Essential for Seed Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. Reddy, V.S., Day, I.S., Thomas, T., and Reddy, A.S. (2004). KIC, a novel Ca2+ binding protein with one EF-hand motif, interacts with a microtubule motor protein and regulates trichome morphogenesis. Plant Cell 16, 185-200. Sakai, T., Honing, H., Nishioka, M., Uehara, Y., Takahashi, M., Fujisawa, N., Saji, K., Seki, M., Shinozaki, K., Jones, M.A., Smirnoff, N., Okada, K., and Wasteneys, G.O. (2008). Armadillo repeat-containing kinesins and a NIMA-related kinase are required for epidermal-cell morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 53, 157-171. Sedbrook, J.C., Ehrhardt, D.W., Fisher, S.E., Scheible, W.R., and Somerville, C.R. (2004). The Arabidopsis SKU6/SPIRAL1 Gene Encodes a Plus End-Localized Microtubule-Interacting Protein Involved in Directional Cell Expansion. Plant Cell 16, 1506-1520. Shoji, T., Narita, N.N., Hayashi, K., Asada, J., Hamada, T., Sonobe, S., Nakajima, K., and Hashimoto, T. (2004). Plant-specific microtubule-associated protein SPIRAL2 is required for anisotropic growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 136, 3933-3944. Spielman, M., Preuss, D., Li, F.L., Browne, W.E., Scott, R.J., and Dickinson, H.G. (1997). TETRASPORE is required for male meiotic cytokinesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 124, 2645-2657. Steinborn, K., Maulbetsch, C., Priester, B., Trautmann, S., Pacher, T., Geiges, B., Kuttner, F., Lepiniec, L., Stierhof, Y.D., Schwarz, H., Jurgens, G., and Mayer, U. (2002). The Arabidopsis PILZ group genes encode tubulin-folding cofactor orthologs required for cell division but not cell growth. Genes Dev 16, 959-971. Strompen, G., El Kasmi, F., Richter, S., Lukowitz, W., Assaad, F.F., Jurgens, G., and Mayer, U. (2002). The Arabidopsis HINKEL gene encodes a kinesin-related protein involved in cytokinesis and is expressed in a cell cycle-dependent manner. Curr. Biol. 12, 153-158. Thitamadee, S., Tuchihara, K., and Hashimoto, T. (2002). Microtubule basis for left-handed helical growth in Arabidopsis. Nature 417, 193-196. Torres-Ruiz, R.A., and Jurgens, G. (1994). Mutations in the FASS gene uncouple pattern formation and morphogenesis in Arabidopsis development. Development 120, 2967-2978. Traas, J., Bellini, C., Nacry, P., Kronenberger, J., Bouchez, D., and Caboche, M. (1995). Normal differentiation patterns in plants lacking microtubular preprophase bands. Nature 375, 676–677. Twell, D., Park, S.K., Hawkins, T.J., Schubert, D., Schmidt, R., Smertenko, A., and Hussey, P.J. (2002). MOR1/GEM1 has an essential role in the plant-specific cytokinetic phragmoplast. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 711-714. Walker, K.L., Muller, S., Moss, D., Ehrhardt, D.W., and Smith, L.G. (2007). Arabidopsis TANGLED identifies the division plane throughout mitosis and cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 17, 1827-1836. Wang, X., Zhu, L., Liu, B., Wang, C., Jin, L., Zhao, Q., and Yuan, M. (2007). Arabidopsis MICROTUBULE-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN18 functions in directional cell growth by destabilizing cortical microtubules. Plant Cell 19, 877-889. Webb, M., Jouannic, S., Foreman, J., Linstead, P., and Dolan, L. (2002). Cell specification in the Arabidopsis root epidermis requires the activity of ECTOPIC ROOT HAIR 3 - a katanin-p60 protein. Development 129, 123-131. Whittington, A.T., Vugrek, O., Wei, K.J., Hasenbein, N.G., Sugimoto, K., Rashbrooke, M.C., and Wasteneys, G.O. (2001). MOR1 is essential for organizing cortical microtubules in plants. Nature 411, 610-613. Xu, X.M., Zhao, Q., Rodrigo-Peiris, T., Brkljacic, J., He, C.S., Muller, S., and Meier, I. (2008). RanGAP1 is a continuous marker of the Arabidopsis cell division plane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 18637-18642. Yang, C.Y., Spielman, M., Coles, J.P., Li, Y., Ghelani, S., Bourdon, V., Brown, R.C., Lemmon, B.E., Scott, R.J., and Dickinson, H.G. (2003). TETRASPORE encodes a kinesin required for male meiotic cytokinesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 34, 229-240. Yang, G., Gao, P., Zhang, H., Huang, S., and Zheng, Z.L. (2007). A mutation in MRH2 kinesin enhances the root hair tip growth defect caused by constitutively activated ROP2 small GTPase in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2, e1074. Yao, M., Wakamatsu, Y., Itoh, T.J., Shoji, T., and Hashimoto, T. (2008). Arabidopsis SPIRAL2 promotes uninterrupted microtubule growth by suppressing the pause state of microtubule dynamics. J. Cell Sci. 121, 2372-2381. Yuen, C.Y., Pearlman, R.S., Silo-Suh, L., Hilson, P., Carroll, K.L., and Masson, P.H. (2003). WVD2 and WDL1 modulate helical organ growth and anisotropic cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 131, 493-506. Zeng, C.J., Lee, Y.R., and Liu, B. (2009). The WD40 repeat protein NEDD1 functions in microtubule organization during cell division in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21, 1129-1140. Zhong, R., Burk, D.H., Morrison, W.H., 3rd, and Ye, Z.H. (2002). A kinesin-like protein is essential for oriented deposition of cellulose microfibrils and cell wall strength. Plant Cell 14, 3101-3117. Zhou, J., Qiu, J., and Ye, Z.-H. (2007). Alteration in secondary wall deposition by overexpression of the fragile fiber1 kinesin-like protein in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 49, 1235–1243.