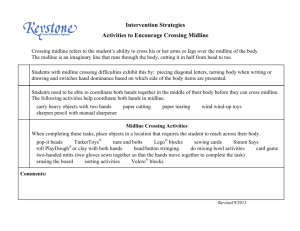
Basic Terminology
advertisement

Basic Terminology I. Introduction 1. Anatomy: Studies shape and structure of the body a. Gross anatomy: large structures studied looking at their shape and external features b. Microscopic anatomy: use of microscopes to study fine details (histology: tissues, cytology: cells) 2. Physiology: studies the function of each body part and how the functions coordinate to form a complete organism II. Terminology 1. anatomical position: position used when referencing all other movements and directions: head forward, arms at side, palms forward 2. sagital: the plane that runs longitudinally and divides the body or organ into right and left portions 3. midsagital (median): the plane that runs longitudinally and divides the body or organ into EQUAL right and left portions 4. frontal (coronal): the plane that runs longitudinally and divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior portions 5. transverse: the plane that runs horizontally across the long axis of the body or organ and divides it into superior and inferior parts III. Directional and Positional Terms 6. anterior: situated at or directed toward the front of the body 7. Posterior: situated at or directed toward the back of the body 8. Cranial: towards the head 9. Caudal: toward the tail 10. Superior: situated towards the head 11. Inferior: situated towards the feet 12. Medial: pertaining to or directed toward the midline (medial plane) 13. Lateral: pertaining to or directed away from the midline 14. proximal: used when describing a point on an appendage: nearest the point of reference or to the point of attachment 15. distal: used when describing a point on an appendage: farthest from the point of reference or to the point of attachment 16. Superficial: pertaining to the surface of the body 17. Deep: away from the surface of the body, more internal IV. Terms of Basic Anatomy 18. ligament: a band of tough connective tissue connecting bone to bone 19. tendon: fibrous cord of connective tissue continuous with the fibers of a muscle; connect muscle to bone 20. joint: the junction or union between two or more bones 21. cartilage: the gristle or white elastic substance attached to articular bone surfaces and forming parts of the skeleton 22. bone: the hard, tough, elastic material that forms the skeleton; composed primarily of calcium salts 23. muscle: type ot tissue containing fibers that contract; when working together they can move a body part or organ 24. fascia: band or sheath of connective tissue the encases muscle and/or tendons 25. bursa: a sack or sack-like cavity in the vicinity of a join which acts to reduce friction around a joint 26. extremity: a limb or appendage V. Terms of Movement 27. range of motion (ROM): the amount of normal movement of a particular joint of the body 28. abduction: to move away from the center or midline 29. adduction: to move towards the center or midline 30. flexion: to decrease the angle of a joint: to bend a limb 31. 32. extension: to increase the angle of a joint: to straighten a limb 33. rotation: to move a limb around a joint axis 34. circumduction: to move joint in a circle 35. plantarflexion: to point the toes/foot down (stand on tip-toes) 36. dorsiflexion: to pull the toes/foot up 37. inversion: to rotate foot so that sole of the foot is facing in 38. eversion: to rotate foot so that the sole of the foot is facing out 39. pronation: to rotate palms/forearm so that they are facing posteriorly (when in anatomical position) 40. supination: to rotate palms/foream so that they are facing anteriorly (when in anatomical position) 41. valgus: force directed towards the midline of the body 42. varus: force directed away from the midline of the body VI. Injury Terms 1. acute: having sudden onset and short duration 2. chronic: having a gradual onset and long duration: showing little change or extremely slow progression over a long period of time 3. Sprain: injury to a ligament 4. Strain: injury to a muscle or tendon 5. sign: objective evidence of an abnormal situation within the body 6. symptom: subjective evidence of an abnormal situation within the body