Unit 6 Bacteria nd Viruses Review Sheet_honors answer key
advertisement

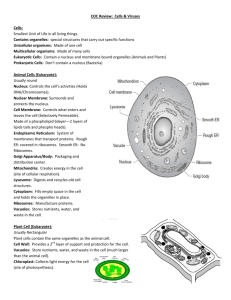
HK Biology Unit 6: Bacteria and Viruses Test/Midterm Review Packet Name______________________________________________ Date___________________ Class__________ 1. Most bacteria are ________________________ (autotroph / heterotroph) because they must get food from an outside source. However, cyano-bacteria can use the sun to produce food, therefore are called ___autotrophic______. Some perform ___chemosynthesis____, getting food from chemical compounds. 2. The three shapes of bacteria are __cocci_____ (which is round/spherical), _____bacilli______ (which is rod-shaped), and ___spirilla___, (which is spiralshaped). 3. Some bacteria also have a tail, called a ___flagellum_____. 4. In what ways are bacteria beneficial to us? ___can produce food (i.e. yogurt), serve to prptect against harmful bacteria, clean up oil spill__ 5. To fight (treat) bacterial infections, ____antibiotic_____ may be taken. 6. Some ways to prevent bacterial infection are (list several ways) 1.wash hands and surfaces 2. use of disinfectants on surfaces 3. use refrigerator to slow growth on food 7. True / False: Disinfectants are used to destroy bacteria on nonliving inanimate objects. 8. True / False: A pathogen is harmful to living organisms because it causes disease. 9. Antibiotics are effective against __bacteria____but not __viruses___. 10. The process by which a dead or disabled pathogen (or proteins from that pathogen) is introduced into the body so that an immune response results without an actual infection is called? A) Vaccination/Vaccine B) Antibiotics C) Bacteriophage D) Pathogenics Matching __B__Photoautotrophs A. Feed on organic matter. __C__Chemolithotrophs B. Use energy from the sunlight to produce glucose __A__Chemoorganotrophs C. Feed on inorganic matter D. Feed on food already prepared for them 11. Viruses are (living, nonliving). They are composed of an outer __protein coat___, with ___DNA or RNA____ inside. 12. When a virus injects its DNA into the host cell, it hijacks the host, forcing it to ___replicate/make copies___the viral DNA. Once the viral proteins are assembled, the cell __assembles the viruses___, releasing the viruses. This is referred to as the ________lytic_____ cycle. 13. If the viral DNA is not immediately copied, it becomes integrated within the host's __DNA______. When the host cell divides, the daughter cells produced will also contain copies of the _viral DNA____. The virus may be __dormant/inactive___ for several years in this state, but it is being spread. This is called the __lysogenic___ cycle. Once it becomes active again, the lytic cycle will take over. 14. __Pathogenic___means disease causing, either from a bacteria or virus. 15. Viruses do not respond to ___antibiotics_____. The body produces interferons to help fight viruses. Humans can receive immunity from viruses through _vaccines____, which is when we are injected with dead or weakened viruses so that __immunity/antibodies___ will be produced against it. 16. The __________________ (lytic / lysogenic) cycle is a cycle of viral infection, replication, and cell destruction. 17. Is the host cell destroyed during the lysogenic cycle? Yes or no? 18. The protective outer coat of a VIRUS is called a __capsid___. 19. A typical ________________ (Bacteria / Virus) consists of a protein coat and a nucleic acid core of DNA or RNA. . 20. Viruses are surrounded by a _________________ coat called a capsid. A) polysaccharide B) Protein C) Lipid D) Carbohydrate 21. Tell some reasons why viruses are NOT considered LIVING. (Short-answer). Some reasons viruses are NOT considered living is due to the fact that virus need a host cell to reproduce, as well as obtain and use energy. While virus do show some characteristics of life, such as change over time, contain genetic information, since not all characteristics are present a virus is considered non-living. 22. Label the parts of the bacteria and virus below: 1. flagellum 2. Pili 3. DNA 4. Cell membrane 5. Ribosomes 6. Cell wall- (peptidoglycan) 7. Cell wall Surface Protein DNA/RNA Capsid Matching 23. __E___Viruses that invade bacteria A. Lytic cycle 24. __G____When a bacterium grows to twice its normal size and replicates its DNA and divides is called 25. ___F___In this type of viral infection, the DNA of the virus B. Archae C. Conjunction enters the host cell and is inserted into its DNA 26. __D___Cells that do not have a nucleus D. Prokaryotes 27. __B___The smaller group of prokaryotes that tend to live in harsh/ extreme environments 28. __C___The process by which bacteria exchange genetic E. Bacteriophage F. Lysogenic Infection information through a “bridge like” structure 29. __A___This type of virus invades a cell, reproduces and is G. Binary Fission scattered when the cell lyses and breaks 30. __H___A non-cellular particle made up of genetic material H. Virus and protein that can invade living cells 31. What is a plasmid and describe unique characteristics of a plasmid. a. Small circular segment of DNA found in a bacteria that often carries the genetic information for antibiotic resistance 32. Label and describe the various stages of the lytic and lysogenic cycle. (see #40) 33. Discuss why it is important to take an antibiotic through the whole course of treatment. a. Due to the fact that the bacteria remaining after the first few days of treatment of more resistant to antibiotics, if the treatment is not taken for the full course of treatment antibiotic resistant bacteria survive and are able to reproduce. This contributes to the increase of antibiotic resistant bacteria 34. What is a “retrovirus”? a. A virus containing RNA. This type of virus will use reverse transcriptase to create DNA which can be inserted into the host cell DNA. 35. Explain the difference between DNA and RNA containing viruses and why one type can change quickly and the other cannot. a. DNA has a mechanism which will check for errors during replication, therefore DNA containing virus do not change quickly and can be treated effectively. RNA does not have the mechanism which will check for errors. As a result, the virus changes very quickly and is very difficult to treat. 36. What is a glycoprotein and what is its function. a. determine what host species the virus can infect and which tissues of the host the virus can enter. 37. List and describe: conjugation, transduction and transformation a. b. c. 38. Discuss how bacteria are able to resist an antibiotic. a. pump an antibiotic out of their cells as fast as it enters so it never reaches a lethal concentration inside the bacterial cell. b. Other bacteria have proteins that bind to the antibiotic molecule and block its lethal effect. c. have enzymes that break down the antibiotic molecules which are then used as fuel to help the bacteria grow faster! 39. How is the pig involved in a bird infecting a human with a virus? a. a pig that was infected with the bird virus was also infected with a human virus, and if the viruses are not careful when they pack new RNA into the capsid, then the pig cell could contain RNA from both humans and birds, and some of the new viruses could contain a mixture of RNA from the human and the bird viruses. These mixtures might produce a new form of the virus that carries the genes that make the bird flu lethal to humans AND the gene that codes for the host-entry glycoprotein. This virus would infect human cells and spread easily from person to person. 40. Label/describe each stage in the diagram below. Assembly of new virus Cell Lyses releasing new virus Virus injects DNA/RNA Incorporated into Synthesis of viral proteins from DNA bacterial DNA Cell copies DNA, along with viral DNA codes during Cell division replication Cell begins division with newly replicated viral DNA