Cellular Structures Table (Ansewer Key)
advertisement

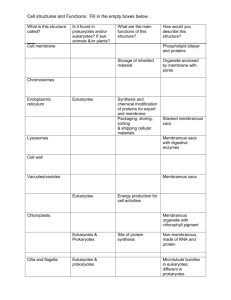
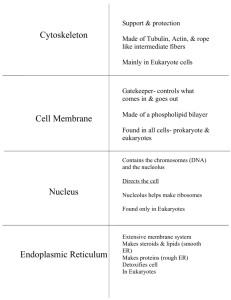
Name _________________________ Ch. 6 - Cellular Structures Table Cell Structure or Organelle Structure Function Gel-like substance Cytoplasm (pg. 98) Plasma Membrane (pg. 99) Metabolic activities such as glycolysis (sugar splitting) occur here. Membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. Found in Plants Animals. or Prokaryotes Animals Plants (Eukaryotes) Prokaryotes Animals Plants Prokaryotes Nucleus (pg. 102) Contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins (i.e. histones) to form chromosomes. Plants Animals (Eukaryotes) Function—transcription occurs here (mRNA is transcribed from DNA) Chromosome (pg. 102) Nucleolus (pg. 102) Organized structure of DNA and protein (histones) found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Non-membrane bound structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids found within the nucleus of cells. Its function is to transcribe ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and assemble it within the nucleolus. Ribosomes are created here. Plants Animals (Eukaryotes) Plants Animals (Eukaryotes) Cell Structure or Organelle Ribosomes (pg. 102) Structure Function Complex of rRNA and protein which catalyzes protein translation, the formation of proteins from individual amino acids using messenger RNA as a template. This process is known as translation. Ribosomes are found in all living cells. Protein synthesis occurs here ** No membrane around this ‘organelle’ Prokaryotes—70S Eukaryotes—80S Found in Plants Animals or Prokaryotes ALL Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (pg. 104) Synthesis of lipids, including oils, phospholipids and steroids, metabolism of carbohydrates, regulation of calcium concentration and detoxification of drugs and poisons. Think of a body builder—smooth (shave), put oil on them in competitions, take steroids to get big, metabolize lots of food. Help detoxify all the drugs (steroids) that they take Plants and Animals (Eukaryotes) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (pg. 104-105) Plants and forms an Animals interconnected (Eukaryotes) network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae. Rough endoplasmic reticulum are involved in the synthesis of proteins and is also a membrane factory for the cell. Proteins made here are sorted according to their destination. Proteins made here either are secreted out of the cell or are destined for the plasma membrane, golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Golgi apparatus (pg. 105) Lysosomes (pg. 107) Integral in modifying, sorting, and packaging macromolecules for cell secretion (exocytosis) or use within the cell. Primarily modifies proteins delivered from the rough endoplasmic reticulum but is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell, and the creation of lysosomes Contain acid hydrolase enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris. These are non-specific. Plants and Animals (Eukaryotes) Animals Maintains the turgor pressure of a plant cell. It stores food for the cell. Vacuoles a membrane-enclosed cell vacuole with a digestive function, containing material taken up in by the process of phagocytosis. Cell Structure or Organelle Structure Function Central vacuole in Plants only (large) Tonoplast surrounds the central vacuole Sap vacuole (plants only) Food vacuoles (animals and plantssmall) Found in Plants Animals or Prokaryotes Mitochondria (pg. 109-110) “cellular power plants"--Generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. Other processes-signaling, cellular differentiation, cell death, as well as the control of the cell cycle and cell growth. **Cellular respiration occurs here. Has own DNA Has own Ribosomes Can replicate on its own. Double membrane Plants and animals (Eukaryotes) Chloroplast (pg. 110) Manufacture and storage site of important chemical compounds used by the cell. Contain pigments used in photosynthesis, and the types of pigments present can change or determine the cell's color Chromoplasts aid in pigment synthesis and storage. Has own DNA Has own Ribosomes Can replicate on its own. Double membrane Plants only!!! Peroxisome Cytoskeleton Break down (catabolism) of fatty acid chains Plants and animals (Eukaryotes) Within the cytoplasm. Is located throughout the entire cell Structure, support, transport Plants and animals (Eukaryotes) Also forms flagella and pili in prokaryotes Microtubules Centrioles & Centrosomes Component of the cytoskeleton. Help with cell structure Intracellular transport Plants and animals (Eukaryotes) Involved in the organization of the mitotic spindle and in the completion of cytokinesis (cell splitting) Centrioles are a very important part of centrosomes (MTOC), which are involved in filing, organizing microtubules in the cytoplasm Animals Prokaryotes have microtubule like structures **creates spindle apparatus used for cell division. Cell Structure or Organelle Structure Function Movement of cell Move fluid along the cell Cilia Found in Plants Animals or Prokaryotes Animal Flagella Flagella are used by cells and unicellular organisms for movement, sensation and signal transduction. They can be described as long slender extensions of the cell or organism. The singular form of flagella is flagellum. Animal Prokaryotes Cytokinesis (cell splitting) Plants and Changing shape of cell animals Microfilaments Intermediate Filaments Make up cytoskeleton (support, transport) Plants and animals Cell Wall Plasmodesmata Structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing overexpansion when water enters the cell. Plants Tunnels between the cell wall and the plasma membrane Plant Intercellular transport Prokaryotes Fungi Protist





![Cell Game Board [10/16/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007063627_1-08082c134bbc8d8b7ad536470fbed9dc-300x300.png)
