Final Exam Review Packet
advertisement

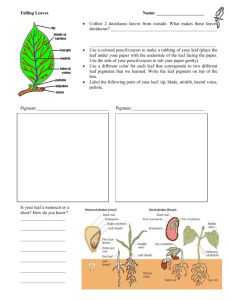
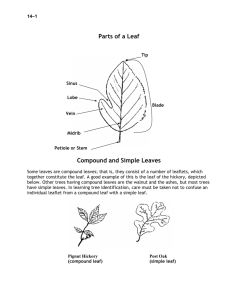
HL Ecology: Final Exam Review Packet Mr. Distasio /Mr Liscinski Name_____________________________________ per ____ date __________ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. Opossum Mammal known for its prehensile tail. Eastern Hemlock Tannic acid comes from this type of tree. Tannersville PA town known named for its tanneries. Biomonitoring Using biological data to examine water quality. Calcium & Magnesium The two minerals responsible for hard water. Opposite Leaf arrangement: two leaves per node. Alternate Leaf arrangement: one leaf per node. Pinnate Leaf venation: veins branch from a central midrib. Palmate Leaf venation: veins branch from a central point at the leaf base. Parallel Leaf venation: veins run side-by-side. Compound Leaf composition: blade divided into leaflets. Simple Leaf composition: blade all in one piece. Lobed Leaf margin: leaf edge has lobes and sinuses. Toothed Leaf margin: leaf edge has small, regular serrations. Entire/Smooth Leaf margin: leaf edge has no lobes, sinuses or serrations. Eastern Hemlock PA State Tree. White Pine Only five-needled pine in PA. American Chestnut Once valuable tree – now affected by a blight. Sugar Maple Used to make bowling pins, floors, furniture, cabinets & cue sticks American Beech Smooth gray bark, big, pointy bud, edible nuts Black Cherry Valuable tree found along PA’s northern tier. PA supplies 75% of the world’s supply. Oak This type of tree produces acorns. Aspen Flat petioles cause leaves of this tree to move in the slightest breeze. Cedar Wood from this aromatic tree is used to make moth-resistant closets. Witch Hazel This tree’s extract is used as an astringent. Sassafras Three distinct leaf shapes. Teas, soaps & flavoring. Catalpa Easily identified by its “bean”. Hickory Compound leaf, often used for smoking meats. Eg. Shagbark Locust Compound leaves, protective thorns. Eg. Black, Honey White Ash Baseball bats, oars, tennis racquets. Compound, opposite. Poison Ivy All parts of this plant are poisonous. “Leaves of three let them be” Pulpwood This classification of wood is used to make paper. Chlorine Greenish-yellow gas. Enters streams through paper mills, pools and bleaches. Aspen When it comes to succession, this tree is a “pioneer”. Increment Borer Tool used to obtain a core sample form a tree. Clinometer, Hypsometer Tool(s) used to estimate the height of a tree. DBH Measured at 41/2 feet of the ground by foresters. 1930 Year that Hawk Mountain was purchased. Rosalie Edge Woman who purchased Hawk Mountain. Xylem Plant cells that carry water up a plant. Phloem Plant cells that carry food down. Cambium Region of cell division where an annual ring is added. Pith The center “core” of a tree cross-section. Sapwood The lighter colored ring of wood found just under the bark of a tree. Heartwood The darker colored ring of wood that gives support to a tree. Boardfoot A piece of wood 12”X12”X1” Veneer A thin sheet of wood used to cover inexpensive wood. 48. Nitrates & Phosphates The presence of these compounds in a stream may result in algae blooms.(2) 49. Delaware The streams of Monroe County are part of this watershed. 50. Dendrology The study of trees. 51. Dendrochronology The study of tree rings. 52. Silviculture The human management of forest resources. 53. Succession The natural progression from bare soil to climax community. 54. 35 -40 The average annual rainfall in PA (in inches) 55. Deer “The most serious problem” faced by PA’s lumber industry. 56. Pellet The regurgitated fur, bones, teeth etc. of a raptor. 57. South This slope of a hill usually contains hardwood trees & fertile soil. 58. North This slope of a hill usually contains softwoods & acidic, sterile soil. 59. Osprey The “fish hawk”. 60. Saw Whet The smallest PA owl. 61. American Kestrel Small falcon with the ability to hover. 62. Barred Dark-eyed owl, “who-cooks-for-you” call. 63. Great Horned Largest PA owl, “tiger of the sky”, 1200 psi. 64. Gyr Falcon owned by noblemen. 65. Peregrine Falcon reintroduced into urban areas. 66. Accipiters Forest hawks, flap-flap-flap glide flight, i.e. Coopers & Sharpshin 67. Buteos Soaring flight, Redtail, Broadwing, Red-shouldered for example. 68. Golgen Midwestern eagle who hunts jackrabbits. 69. Turkey Vulture Carrion eater, sense of smell, dihedral pattern, rocking flight. 70. Owl Raptor group: silent flight, facial disk, ear tufts, asymmetrical ears. 71. Asynchronous Eggs don’t hatch at the same time. 72. DDT Pesticide banned in the 1970’s. Still made & sold by the US. 73. Nictitating Clear membrane on the eye for protection. 74. Supraorbital Ridge above the eye on buteos & eagles used to shield from sun. 75. Talons The claws of a raptor. 76. Eyas Baby raptors. 77. 80-90% Mortality rate of young raptors (%). 78. Eyrie Name given to a Bald Eagle’s nest. 79. Sexual Dimorphism Males & females differ in body form & structure. 80. Habitat Loss #1 problem faced by the California Condor. 81. Beaver Largest PA rodent. 82. 6.5-8.5 pH range preferred by trout 83. Plankton Microscopic plants & animals that serve as the basis for many aquatic food chains. 84. Gary Alt PGC biologist famous for his bear research. 85. pH Potential for Hydrogen ions; measured on a scale from 1-14. 86. Carrying Capacity The number of organisms an area can support indefinitely. 87. Thermal Rising heated air masses. 88. Cold Which water usually has a higher D.O., warm or cold? 89. Carnivore Eats meat exclusively. 90. Herbivore Eats vegetation exclusively. 91. Omnivore Eats both plant and animal matter. 92. Class I Which class of aquatic organisms is very pollution sensitive, I,II or III? 93. Non-point Agricultural & stormwater runoff, acid mine drainage: Point or Nonpoint pollution? 94. Quills Spines on a porcupine. 95. Susquehanna Large, central PA river that empties into the Chesapeake Bay. 96. Lead Toxin associated with neurological & developmental damage in children. 97. Harrier Marsh Hawk” with a white rump patch. 98. Photoperiodism The response of organisms to varying period of light. 99. Elk & Cameron The two PA counties where you might find elk. 100.750-850 The approximate # of elk in PA. 101.Spring The season when most animals give birth, 102.1.5 years Before antler restrictions, the average age of a whitetail deer when it was harvested in PA. 103.Chipmunk Smallest PA squirrel, cheek pouches, stripes. 104.Raccoon Masked bandit who “washes” its food. 105.Cottontail Rabbit PA’s #1 small game animal. 106.Malocclusion The abnormal growth of incisors. 107.Diurnal This means “active during the day”. 108.Nocturnal This means “active at night” 109.Scrape A patch on the ground where a whitetail buck paws away the leaves. 110.Rub A mark on a tree created by a whitetail’s antlers. 111.Age, Diet & Genetics The three factors that determine how large a whitetail’s antlers will grow. 112.Rut Another name for the mating season for some animals. 113.Black Bear Pa mammal with the largest home range. 114.Rodents Mammal group: squirrels, beaver, muskrat, porcupine. 115.Weasel Mammal group: river otter, skunk, mink, ermine. 116.Limestone Stream with a higher buffering capacity: Freestone or Limestone? 117.Freestone Most common stream type in PA: Freestone or Limestone? 118.Decrease As you move up the food chain, does the amount of available energy increase or decrease? 119.AMD The #1 source of water pollution in PA. 120.Opossum North America’s only marsupial. 121.Fisher Reintroduced to PA in 1995, preys on porcupines, weasel family. 122.Opossum Displays catatonic shock, more teeth than any other mammal. 123.Delayed Implantation Putting pregnancy “on hold” 124.Red Fox, Gray Fox, Coyote The three canine predators in PA. 125.Bobcat PA’s largest feline predator, protected from 1972 -2000. Now limited trapping 126. River Otter Protected, reintroduced, fish-eating weasel. 127.R-selective High # of young, little parental care, high infant mortality. 128.K-selective Low # of young, high parental care, low infant mortality. 129. Pole Timber Classification of trees ranging from 4-12 inches at DBH. 130.Sawlog Classification of trees with a diameter greater than 12” 131.Deciduous Term for trees who lose their leaves. 132.Pruning The process of trimming the terminal buds from trees. 133.Diameter Limit Cut The most commonly used non-silvicultural technique in PA. 134.Detritus Dead & decomposing organic matter. 135.Pelagic “free swimming” 136.Pathogenic disease causing 137. Imago another name for the adult stage of an insect 138. Lotic pertaining to flowing water 139. Lentic pertaining to non-flowing water 140. Littoral the “near-shore” zone of bodies of water 141. Limnetic the “open water” zone of ponds, lakes, etc... 142. Instar the developmental stage between two molting events 143. Brackish describes freshwater with a high salt content 144. Catadromous migrates from freshwater to saltwater to spawn 145. Anadromous migrates from saltwater to freshwater to spawn 146. Plankton microscopic, aquatic plants & animals 147. Eutrophication aquatic succession; the enrichment of an aquatic environment with nutrients & organic matter 148.Benthic means “bottom dwelling” 149. D 150. F 151. A 152. H 153. C 154 E 155 G 156 B 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 Tsuga canadensis Pinus strobus Quercus rubra Populus tremuloides Acer saccharum Populus grandidentata Fagus grandifolia Betula populifolia A. Red Oak B. White Birch C. Sugar Maple D. Eastern Hemlock E. Bigtooth Aspen F. White Pine G. Beech H. Quaking Aspen C Ursus americanus E F G A B D H A. Woodchuck B. Whitetail Deer C. Black Bear D. Chipmunk E. Raccoon F. Beaver G. Red Fox H. Cottontail Rabbit Procyon lotor Castor canadensis Vulpes vulpes Marmota monax Odocoileus virginiana Tamias striatus Sylivagus floridanus 165. - 170. Identify the PA watershed 165. Erie 166. Genessee 167. Ohio 165. 168. Susquehanna 169. Delaware 170. Potomac 166. 168. 167. 169. 170.