Cells: Structure and Function Chapter 6
advertisement

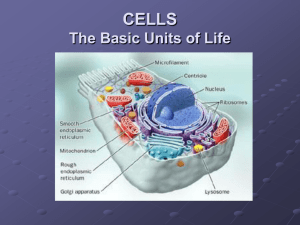
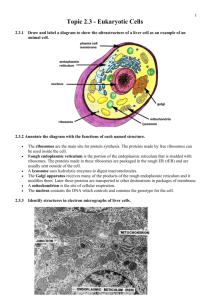
Cells: Structure and Function Chapter 6 2 Types of Cells • Prokaryotic cells – bacteria • Eukaryotic cells – Animals – Plants – Fungi – Protists [single cell organisms] The People • Jansen made the first microscope. • Anton van Leewenhoek discovered microorganisms. • Hooke discovered cells. • Virchow and Schleiden developed the cell theory. Cell Theory • All living things are: – Cells – Or are made of cells • All cells come from pre-existing cells First cells were Prokaryotes Prokaryotes • Appeared about 3.5 billion years ago. Layers of bacteria growing on top of each other. Prokaryotes, bacteria • • • • • • • • • No nucleus or organelles. Nucleoid region is where DNA is located. Ribosomes change genetic info. into proteins. Flagella for movement Cell wall, support and protection. Plasma membrane control entry/exit. Capsule protection, may cause disease. Pili allow attachment to host or surfaces. Biofilms optional report Prokaryotic cells needed to do all life functions. • • • • • • • Eat/Digest Remove wastes Reproduce Move Make organic molecules Make ATP Single cells must do it all. Eukaryotic cells Eukaryotes • Arose from existing prokaryotes 2.1 billion years ago. • Cells contain organelles doing specific tasks. • Endosymbiotic theory. [When an organism was eaten by a cell (phagocytosis) it was not digested but instead became an organelle in the cell that ate it. Mitochondria and Chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes] Nucleus, contains DNA and nucleolus Nucleolus, creates new ribosomes Mitochondria, makes ATP Chloroplast, make sugar by photosynthesis Ribosome, joins amino acids into proteins Golgi, modifies and packages chemicals Smooth E.R. production fats and steriods Rough E.R. makes/packages proteins Plasma Membrane, controls movement of materials in/out of cell Lysosome, intracellular digestion Cytoskeleton, maintain cell shape & internal organization Vacuoles, compartment for storing wastes or water or starch, etc. Cell Wall, support and protection Cytoplasm, liquid part of cell interior (water, salt, proteins, etc.) Centrioles, allow DNA to separate during cell division Flagella, cell movement Plant cells vs Animal cells • Plant Animal • Chloroplasts • Cell Wall • Central Vacuole Centrioles Single Eukaryotic cell Cooperation • Cells living together may gaining some survival advantage. • Cells specialize. • Example, Colonial Volvox Volvox Colony Volvox • Many cells living as a single organism Size = protection • Offspring protected within. • No specialized cells. Reproduction Multicellular organisms Made from many cells that have specialized functions. Some cells digest food. Some cells allow for movement. Division of Labor More Specialization • • • • Specialized cells for different tasks. Do not do everything. More Efficient Cells specialize into Tissues, layers of cells. Tissues, cell layers [in a sponge] Levels of structure • • • • Cells Tissue, Similar cells with a common function. Organs, Heart-different tissues working together. Heart. Organ Systems, Circulatory system-Heart, Veins, arteries, capillaries. • Organisms, Human, different organ systems working together-digestive sistem, nervous system, circulatory system, etc. Organ Organ System, excretory system Organism Levels of Structure • Population, members of the same Species. • Community, the different species living in the same environment. • Ecosystem, the biotic (living organisms) and the abiotic factors (light, oxygen level, temperature, etc.) in the same area. • Biomes, regions of the world with similar climate (weather, temperature) animals and plants. There are terrestrial biomes (land) and aquatic biomes, both freshwater and marine. Population Community Ecosystem Biomes