ITUC/Indonesia - Roni Febrianto
advertisement

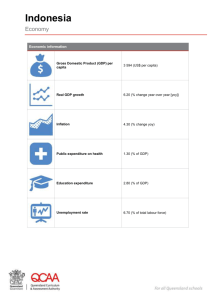
Country Report Trade Union Training on Information Technology ITC OF ILO Turin 8 November – 10 December 2004 General Information - OVERVIEW CAPITAL CITY: Jakarta LONG NAME: Republic of Indonesia INDEPENDENCE DAY: 17 August 1945 (proclaimed independence; on 27 December 1949, Indonesia became legally independent from the Netherlands) GOVERNMENT TYPE: Republic TOTAL AREA: 1,919,440 sq km POPULATION: 238,452,952 LANGUAGES: Bahasa Indonesia (official, modified form of Malay), English, Dutch, local dialects, the most widely spoken of which is Javanese RELIGION: Muslim 88%, Protestant 5%, Roman Catholic 3%, Hindu 2%, Buddhist 1%, other 1% (1998) LIFE EXPECTANCY: 69.26 INFANT MORTALITY: 36.82 CURRENCY: Indonesian Rupiah (IDR) GDP(PER CAPITA) : 3200 LABOR FORCE BY OCCUPATION: INDUSTRIES: petroleum and natural gas, textiles, apparel, footwear, mining, cement, chemical fertilizers, plywood, rubber, food, tourism EXPORTS: oil and gas, electrical appliances, plywood, textiles, rubber IMPORT machinery and equipment, chemicals, fuels, foodstuffs POLITICAL STRUCTURE 2004 is an important year. This is the year that Indonesia democracy either opens its doors to a new wave of consolidation and reform retreats along the historically familiar path towards a new kind of authoritarianism .In 2004 elections will decide whether Indonesia democracy will experience a rebirth or continue suffer slow suffocation for second time in fifty years.. 1 People worry about job and not income statistics. Unemployment matters. It is commonplace to hear that Indonesia is too poor to have an unemployment problem Open unemployment remains higher than many industrial counties and wide prevalence of underemployment means the people cannot end meet even when willing to work long hour at low wage. Public euphoria at the fall of an autocracy can easily turn to public disgust .Even worse it can to nostalgia for the past. Part of the problem is the inability on unwillingness of post- new order political to spell out what democracy actually means to lives or ordinary citizens. These is no attempt to explain to the ordinary citizen the rights and rituals of democracy ,no spelling out of claims and responsibilities, no evaluation of damage done by the kleptocracy that pass as orderly governments of the new order .Democracy is equated with chaos and dictatorship with leadership and stability. This is the inevitable consequence of political parties who jockey for parliamentary and government seats without any defined political positions .Civil society organizations carp and complain at the margins of political life, contents to safeguard their image and chastity from the depredation of the state and large business .The elevation of the importance of macroeconomic recovery ,the absence of any transparent plan of political reform and ambivalent attitude to corruption in high places has created a deep seated cynicism in public mind. This has bred a number of other anxieties : separatism and disintegration of the nation state ,the capture of political power by a resurgent business elite ,and the lack of any serious leadership which can give the country a sense of will and direction .But things are not bad as that .The political and constitution change already undertaken, thought often flawed,, make an effortless retreat to authoritarian structures of the past unlikely .Decentralization, parliamentary reform ,the establishment of independent institution such as the Constitution Court ,The Audit Commission and Central Bank and the initial steps in military reform. As has been the experience of many countries in transition to democracy, the political pendulum is likely to swing back by 2009.The extent to which it does so will on the engines of democratic reform its self: Political parties, media, civil-social organization .It will depend on creating a new kind of leadership which can work collectively toward working out the steps of second wave of reformism. To understand what needs to be including in the agenda of the second wave they must go to the people. Democracy is about representing the people. ECONOMIC STRUCTURE The collapse of the rupiah in late 1997 and early 1998 caused GDP to contract by an estimated 13.7% in 1998 because of Indonesian firms' reliance on short-term dollar-denominated debt and high levels of no performing loans in the banking sector. To solve the problem, the government announced a bank re-capitalization program in late 1998, but by early 1999 the plan faced growing challenges over its reliance on public funds. However, following the sharp contraction and high inflation of 1998, the Indonesian economy stabilized in 1999 and following tight monetary policy, the government reduced inflation from over 70% in 1998 to 2% in 1999. Although interest rates spiked as high as 70% in response to the monetary contraction, they fell rapidly to the 10% to 15% range. The economy stopped its free-fall as GDP showed some growth in the second half of 1999, although GDP for the year as a whole showed no growth. With the commitment of the government to maintaining fundamentally sound macro economic and investors continued to face a host of the ground microeconomic problem and an inadequate judicial system.Keys to future growth remain internal reform, building up confidence of international and domestic investors and strong global economic growth. 2 In 2003, gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 4.1%, a modest improvement over 3.7% the previous year, even though the country was hit by another terrorist attack and faced the regional problems caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and the conflict in Iraq. Inflation slowed to 5.1% at the end of the year, the reference interest rate fell, and the rupiah firmed against the dollar. Fueled by growth in private and government consumption, Indonesia's economy is expected to expand by 4.5% in 2004 and 2005 . The key challenge facing policy makers now is to achieve and sustain higher levels of economic growth, especially through greater domestic and foreign direct investment.Indonesia offers some comparatives advantages to investors, with an attractive range and combination such as: o o o o o o A vast, fertile country endowed with rich and diversified natural resources. A large population of about 202 million and dynamically adaptive to progress, constituting a huge potential market as well as a competitive workforce. A strategic location, on the cross road of two great continents and oceans controlling vital international sea communities lines A more democratic country An open market oriented economy, with free foreign currency exchange rule. A favorable business and investment climate. Export as one of major economic indicator at last two years start to increase it can see on below table : 3 Table 2. EXPORT GROWTH Petroleum * Crude oil * Gas * Others Non Petroleum 2003 9.230,5 3.754,4 4.309,4 1.166,7 31.517,4 2004 9.963,7 4.086,7 4.773,7 1.103,3 33,126,2 Total Export 40.747,9 43.089,9 ( Million U$ ) Source : Central Bureau of Statistic SOCIAL AND LABOR STRUCTURE . As development county with population 238,452,952 , labor force 100,316,00 ( Male 64,837,000 Female 35,479,00 ) and who are working 90,785.000 ( Male 59,909,000 Female 30,876,000) is potential for economic activities for growth of country . Working population by main industries and labor force and non labor force by education can see as below table : Table 3 Working population by Industries Sector Male Female Total Agriculture &Foresty 27,385,000 14,616,000 42,001,000 Manufacture Industry 6,539,000 4,388,000 10,927,000 Construction Wholesale trade,Retail,Restaurant &Hotel Transportation,Storage &Communication 3,977,000 130,000 4,107,000 9,303,000 7,534,000 16,837,000 4,814,000 163,000 4,977,000 Source : ILO /USA declaration project in Indonesia Table 4 Labor Force Base on Education Educational Attainment Not complated elementry school Junior High School Senior High School Diploma I - III University Grand Total Male 37,391,000 18,689,000 16,753,000 1,235,000 1,916,000 75,984,000 Female 45,307,000 16,594,000 12,529,000 1,128,000 1,108,000 76,666,000 Total 82,698,000 35,283,000 29,282,000 2,363,000 3,024,000 152,650,000 Source : ILO /USA declaration project in Indonesia 4 STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION OF TRADE UNION. A brief summary of the major trade union groupings in Indonesia is below : Konfederation Serikat Pekerja Seluruh Indonesia ( KSPSI –formerly FSPSI ) Following a split in 1998,the former FSPSI restructured it self in 2002 .It is now a confederation known as KSPSI ( Konfederasi Serikat Pekerja Seluruh Indonesia ).Some commentators still regard this organization as single union grouping in Indonesia .The Ministry of Man Power takes this view and presently allocates 50 % of the seats on any tripartite structures to KSPSI. Konfederasi Serikat Pekerja Indonesia ( KSPI ). A number of unions broke away from FSPSI in 1998 to Reform the Union. Since than most of the Reformation have become associated with a new grouping. KSPI which had its founding Congress early in 2003.Most of the 11 unions in this grouping are industry based unions many of which cooperate with Global Union Federation. KSPI has a working relationship with the International Confederation of Free Trade Union ( ICFTU ) ,although not yet a member. The Confederation’s founding met under a banner proclaiming KSPI as “Building a Free, Independent and Democratic union movement” .In the period ahead the new organization will be seeking to develop its organization and administrative structures and to develop a work program aimed at supporting the development of the Confederation and its affiliated unions. The Federation has affiliated to KSPI : PB PGRI ( Teachers ),FSPTSK ( Textile, Garment& Leather ),FSP Kahutindo ( Wood & Building ), FSPKEP ( Chemical ,Energy &Mining ), ASPEK Indonesia ( Economic & Finance ) FSPMI ( Metal ) ,SP PPMI ( Press & Printed ), FSPISI ( Indo Cement ), FSP Farkes – Ref ( Pharmacy & Health ), Gasbindo Konfederasi Serikat Buruh Seluruh Indonesia ( KSBSI ). KSBSI was outlawed during the new order period and now organization now operation openly ,but complains of continuing harassment in its activities. FSBSI is a member of the World Confederation Labor .It gas received significant international support ,most recently securing assistance from European Union backed project for building of a training center on outskirts of Jakarta. For the membership of Three Labor Confederation can see an below table : Table 5 . Membership of Labor Confederation Confederation Affiliated Federation Total Membership KSPSI KSBSI 18 11 5,100,000 1,753,000 KSPI 11 2,908,047 * the data is based on information provided directly by relavant confederation INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY & TRADE UNION In Indonesia with population more than 238 million , user of internet around 2.5 million. It is increase year by year cause economic condition growing up. Information and technology is quiet expensive and new knowledge. At trade union only a view persons use computer especially 5 at white color worker and worker at industrial with high technology .Some trade union just use computer only for administration .For trade union which is affiliate with international trade they quiet familiar with information and technology .Some also already have web side such as ASPEK Indonesia, FSPMI ,KSBSI Trade union movement also can fast running by use information of technology .Labor information and some rally also can see at internet .International solidarity also step by step can build by use internet. By international support trade union movement and freedom of association in Indonesia rise up at 1998 . Now also rally of Mayday in Indonesia and worker /union demonstrating are common and easy to see at internet .At special industrial area worker have high education and work in multinational company communication between worker starting to organize & communication use internet or e-mail .For example at Batam Industrial area some link make by workers before settle union than by support from Union in Jakarta they start make Union .With Internet or e-mail some info from Batam can easy know & fast to others outside. So during 6 months 17 plan unions can establish with members around 5,000 under FSPMI. International support from IMF ( affiliate of FSPMI ) , ACILS ( Jakarta Office ) and ILO/USA declaration project make Batam Union branch establish. By special support from International trade union affiliate Aspek Indonesia and KSBSI can set up training center with full computerize .By spirit of solidarity some trade union can borrow and make short course about basic know how of Information and Technology. ILO/Usa declaration project in Indonesia also support training for some trade union which program include Information & Technology .During the course trainer get basic computer such as Microsoft word, excel and power point also basic use of internet .With practical trainer can make small presentation by power point and make communication by e-mail. ACILS with international link make special training to build strong solidarity for trade union in Asia region by held IT training at Taiwan Confederation Trade Union Training Center .With participant from Japan, Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Thailand, Bangladesh and Indonesia all participant make strategy to settle Global Union .With instructor from ACILS USA learning about important think of Global Union in Globalization era . For economical issue than make Indonesia almost bank croup Indonesia Trade Union have networking that focus on reforming the IFIs namely Asia Labor Networking on the IFIs – ALNI establish on 2003. For Labor advocated some NGO make special web side namely BenHill ( Location name of Organization at Bendungan Hilir Jakarta ) on 2004 .They give advocate and information for Industrial Labor dispute in Indonesia . MAJOR PROBLEM &ISSUE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY . them use University Archipelago with more than 13.000 islands for Indonesia it is quite difficult to build communication now day .Only less than 5 % of population have telephone line.In Java , Bali and Sumatra also in Big City have good telephone line and infrastructure of communication now there are about 10 million telephone line . Even in big City student familiar with Information & Technology only a few have personal computer some of, School or Course Computer .In big city they can rent computer or internet in Indonesia call by Warung Internet ( Internet Shop ). 6 Such as development country computer as hardware of information & technology still too expensive for Indonesia Worker as general .With Minimum wage it is impossible for worker to buy computer them self .Some lucky worker work in the office can use company computer and get basic know how of computer but it is less than 10 % of Indonesia Workers .Some union by Check Of System ( Membership ) can buy computer usually for administration and make communication with affiliate international union . Generally there is no special budget for IT development from Organization so become can not make special IT training /course and set up hard ware(Computerand LAN ).There still not enough awareness the important point of IT at Union to solve their problems. Some union at Federation level such as ASPEK Indonesia have IT facility but still can not shearing know how of IT to others federation due not enough budget . PRIORITY AGENDA FOR TRADE UNION IN AREA OF IT . In global era and to build global solidarity IT is the starting point. The fast information and networking is the key of global solidarity. Agenda for set up IT in trade union area such as : 1.Development IT Department and support by enough budget and human resource . 2.Make special training for workers who will handle IT at Union and set up Task Force IT at Federation /National level .Use long term education system so PIC will always learning last version of software and have new knowledge of IT . 3.Make networking between union at Federation/national level and connect with affiliation union ( Confederation and International ). 4.For quick and effective cost for use internet there must change from dial up system to Server System . 5.Up grading software with effective. new version to make communication and work more quick and 6.Supporting from affiliation international organization and Foundation or Labor organization such as ACILS ,ILO ,FES etc . 7