Anatomy & Physiology
advertisement

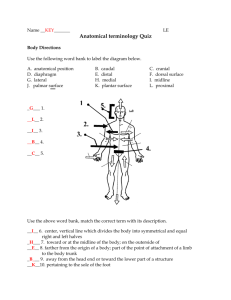
Anatomy & Physiology Lab #1- Part A Anatomical Position, Terminology, Directional & Regional Terms, Landmarks, Planes, Sections & Cavities Complete the following exercises: 1. Describe & stand to demonstrate the anatomical position: 2. Describe & demonstrate the following orientation & directional terms: superior - toward the head, above inferior - toward the lower part of a structure, below anterior (ventral) - toward the front posterior (dorsal) - toward the back medial - toward the midline lateral - away from the midline intermediate - between a medial & lateral structure proximal - closest to the origin, closest to trunk distal - furthest from origin, furthest from trunk superficial (peripheral) - toward (closest) to body surface deep - furthest from body surface 3. Describe, & locate on diagram A, the following body landmarks: (for answers see diagram in book) Anterior: o abdominal o cervical o orbital o antecubital o digital o pubic o axillary o femoral o sternal o brachial o inguinal o tarsal o buccal o nasal o thoracic o carpal o oral o umbilical Posterior: o cephalic o deltoid o gluteal o lumbar o occipital o popliteal o scapular o sural (calf) o vertebral 4. Describe & locate on a diagram the following terms used to describe planes & sections: sagittal - divides body or organ into right and left sides midsagittal - divides body or organ equally into right and left sides median - same as above frontal (coronal) - divides body or and organ into anterior (front and posterior (back) portions transverse - divides the body or organ into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions oblique - passes through the body or organ at an angle cross section - same as above 5. Name the plane in relation to the brain: transverse (cross-sectional) ______________________ frontal plane ______________________ midsagittal plane ______________________ 6. Locate the major body cavities & list the chief organs in each: (answers see diagram) Dorsal Body Cavity - cranial cavity-spinal (or ventral) cavityVentral Body Cavity - thoracic cavity- abdominopelvic- 7. Fill in the blanks: The _thoracic_ cavity is above the diaphragm and the _abdominopelvic_ cavity is below. The _diaphragm_ is a large, domeshaped muscle. Another name for organ is _viscera_. The organs are covered with _serous_ membrane. 8. What encircles the following cavities? ABDOMINOPELVIC CAVITY abdominal wall bones of pelvis muscles of pelvis THORACIC CAVITY ribs sternum vertebral column muscle 9. Fill in the blanks: The thoracic cavity is divided into __2 pleural cavities__ by the __mediastinum__. The __mediastinum__ contains all thoracic organs except the __lungs__. 10. What does the mediastinum contain? heart great vessels esophagus trachea thymus 11. What is the visceral peritoneum? -serous membrane that covers the abdominal viscera parietal peritoneum? -serous membrane that lines the abdominal wall 12. Draw a diagram of the following regions and quantrants: (for answers see diagram) a) Regions of the abdomen: epigastric umbilical hypogastric left & right hypochondriac left & right lumbar left & right iliac b) Quadrants of the abdomen:right upper right lower left upper left lower CHEMISTRY - PART B 1. What is the order of the chemical level of organization? a. b. c. d. e. f. matter chemical bonds chemical energy chemical reactions inorganic compounds organic compounds 2. What are the chemical symbols for the following elements? oxygen - O calcium - Ca hydrogen - H sodium - Na carbon - C potassium - K nitrogen - N 3. Fill in the blanks: (in relation to the 4 types of chemical bonds.) Positively and negatively charged ions attract each other to form _ionic______ bonds. These __ionic_______ bonds are found mainly in teeth and bones. Atoms share electrons to form _covalent______ bonds. Unequal sharing of electrons between atoms are _polar ___ _covalent__ bonds. __Polar____ covalent bonds between hydrogen and other atoms are _hydrogen_________ bonds. 4. Regarding energy and chemical reactions name the 2 principal forms of energy and define briefly. a. __potential nergy__________=__stored energy__________ b. __kinetic energy___________=__energy of motion_______ 5. What is the law of conservation of energy? -energy can neither be created nor destroyed -just converted from one form to another 6. Regarding energy transfer in chemical reactions define briefly: a. exergonic reactions - release more energy b. endergonic reactions - absorb more energy than they release 7. What are inorganic compounds and give examples? -usually lack carbon and are structurally simple -examples are: water, salts, acids, bases 8. What organic compounds and give examples? -contain carbon and usually hydrogen -examples are: carbohydrates, fats, proteins 9. Free radicals? a. What are they? -unstable and highly reactive -atom with an unaired electron in its outermost shell b. How are they produced in the body? -by absorption of energy in ultraviolet light in sunlight, x-rays, by breakdown of harmful substances c. What are they linked to? (give examples) -many diseases - cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer, atherosclerosis and arthritis d. How can the damaged caused by them be slowed down. -with antioxidants such as Vit. C and E, selenium & beta-carotene (precursor to Vit A)