Map of the Human Body
advertisement

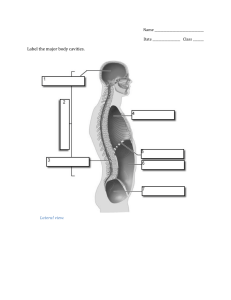
Map of the Human Body Chapter 2 A and P Health Sciences mmoyer@mbit.org Positions • • • • • • Supine Prone Trendelenburg Fowler’s Video Lab Body Positions • Anatomical – Standardized for all anatomy – A Upright position – B Feet apart – C Palms Up – D Face forward Pathology Connections • Relative to certain clinical scenarios • Trendelenburg – Postural drainage – AVOID with ICP – why?? – AVOID pc for 2-4 hours – why?? Pathological Connections • Sim’s – Rectal procedures • Prone/Supine – Examinations • Fowler’s – Orthopnea – Drainage – Orthostatic Hypotension Body Planes • Frontal or Coronal Plane – Divides body into Front and Back • Median Plane – Left and Right sides – Mid Sagittal = halves – Sagittal – left and right sections • Transverse– Divides body into Upper and lower sections Directional Terms • • • • • • • • Superior ( Cranial or Cephalic) Inferior ( Caudal) Medial Lateral Anterior ( Ventral ) Posterior ( Dorsal) Distal Proximal Directional Terms • • • • • • External Internal Superficial Deep – under the surface body Central – locations around center of body Peripheral – surrounding outer regions body Body Cavities • House or protect organs • Ventral – Thoracic • Mediastinal/ pericardial cavity Abdominal pelvic • Dorsal Cavity – Cranial – Spinal Body Cavities • Regions of the Spinal Column – – – – – Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccyx C1-C7 T1-T12 L1-L5 S(fused S1-S5 Tail Bone • Cavities located in the skull – Nasal – Oral /Buccal – Orbital Body Cavities Body Regions • Abdominal Abdominal Quadrants • http://quizlet.com/1847323/organs-found-inthe-four-abdominal-quadrants-flash-cards/ • http://www.freeed.net/sweethaven/MedTech/NurseCare/Gast roNurse01.asp?iNum=17 • http://quizlet.com/2692067/body-cavitiesflash-cards/ Terms used to Describe the Body • • • • • • • • • • • • Antecubital Antebrachial Axillary – Brachial – BuccalDigital Carpal Cervical Lateral – Bi Lateral Ipsilateral – Contralateral elbow- BP forearm arm pit bicep area mouth fingers wrist – Carpel tunnel neck away from both sides same side opposite side Areas of the Body • • • • • • • • • • • Femoral Gluteal Lumbar Nasal Oral Orbital Patellar Plantar Pubic Sternal Thoracic Radiology • Science of Viewing the body • Diagnostic Pathway • High energy radiation that penetrates the body • Provides 2 dimensional views X-ray • Air- Black on film • Tissue/fat thicker area lighter the images • Watermid range density more dense than air less than bone • Bone/metal highest density-absorbs most radiation – film image white Problems/ concerns X-ray • One dimensional • Terms – PA- upright position – chest in front of film radiation moves from back to front (PA)Shoulders commonly rotated distance 6ft – AP- back against cassette- distance 48inches – portable xray – Lateral – from side – perception of 3D – Radiology • MRI- Magnetic Resonance Imaging – Greater detail – No radiation – Precautions • CT – Computerized Tomography – Thin slices – 3D view – Reveals true depth of tumor