Attitudes
advertisement

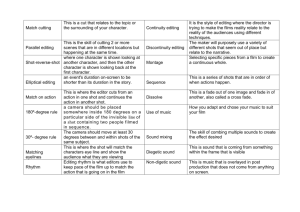
© George Spencer School 2010 AS Media Studies G322 Key Media Concepts: TV Drama Editing lesson 1 Learning Objectives of lesson ALL/grade D To be able to identify different types of transitions Attitudes Skills Knowledge Resources: (incl syll/NC refs and levels) MOST/grade C To be able to understand why some transitions are used and analyse the effects created SOME/grade A To be able to analyse the function of editing within a text with fluency Projector and Youtube Copies of the handouts for wider reading Cards for matching exercise Extract from McDougall on soaps (pp. 87-88) ** ** Environment for learning/Key words CUTTING: shot/reverse shot, eyeline match, graphic match, action match, jump cut, crosscutting, parallel editing, cutaway, insert OTHER TRANSITIONS: dissolve, fade-in, fade-out, wipe, superimpose, long take, short take, slow motion, ellipsis and expansion of time, post-production, visual effects ICT, Literacy, Numeracy, Inclusion (Gender/IN/G&T) , SMSC Connect Starter: Big Picture: Meanings Matching exercise. Rules You must only speak to one person at a time, find a space and confer on your slips. No shouting out across the group. Split groups into two groups, this could be done on hair colour, gender or some other means. Give half the class a pile of definitions; give the other half a pile of terms. They take two each and try to find their matching pair. When they have found a pair that matches they can take another from their relevant pile. Editing is one of the harder areas to analyse, but needs to be covered for the exam. Outcomes: By the end of the two lessons you will be able to identify different types of transitions Activate (Introduction, VAK) Additional comments 30 70 Watch an extract of Eastenders twice and analyse the editing, looking especially at cross-cutting, shot reverse shot and the ideas of continuity editing. In pairs students write about how the editing works and the effect of the editing on the audience. Watch the opening of Hollyoaks and consider how it uses editing differently Discussion: How do soaps use editing differently to other genres? Consolidate (Plenary, Homework) 10 Discuss why editing is used. What is its purpose? Students give ideas of how it works and why. Explain the concept of Continuity editing. Watch the opening of Psycho (Hitchcock 1960) http://uk.youtube.com/watch?v=rOCzvyhrCU and ask students to make notes on how the editing works. Feedback then read through the analysis in Roberts and Wallis pp 49-51 Watch again and comment Demonstrate (Development, MIs) time Consolidate on soaps – read through the extract on soaps from McDougall book. Students return to the cards used for the matching exercise at the beginning of the lesson and look at all of the definitions. They need to find ways of learning the different terms eg Spider diagram/ powerpoint/ making their own video Homework: 1. Learn the terminology for editing 2. Background Reading: Roberts, G and Wallis, H Introducing Film (Arnold 2001) pp. 35-43 Holland, P The Television Handbook (Routledge 1997) pp. 98-101 This resource is good for editing: http://classes.yale.edu/filmanalysis/htmfiles/editing.htm There are video examples of many of the techniques Comments from Forum: I don't think you need to find texts specifically to focus on editing - better to find texts that D:\106764189.doc 10 © George Spencer School 2010 AS Media Studies G322 Key Media Concepts: TV Drama focus on the representation of specific social groups. Any TV drama will construct its characters out of recognisable social traits and then attempt to position its audience in relation to these constructions - this is the basis of representation. A great deal of this process occurs through the editing of a sequence. Your students should be able to see this at work through the amount of screen time that a character is given, the degree to which their actions or dialogue motivate the editing, the use of point of view and reaction shots to create or deny audience proximity, the supply or restriction of narrative information which positions the audience in relation to characters' knowledge and so on. James Baker e-learning independence D:\106764189.doc interdependence information literacy problem solving enrichment