Lecture 3 Flowcharts Charts
advertisement
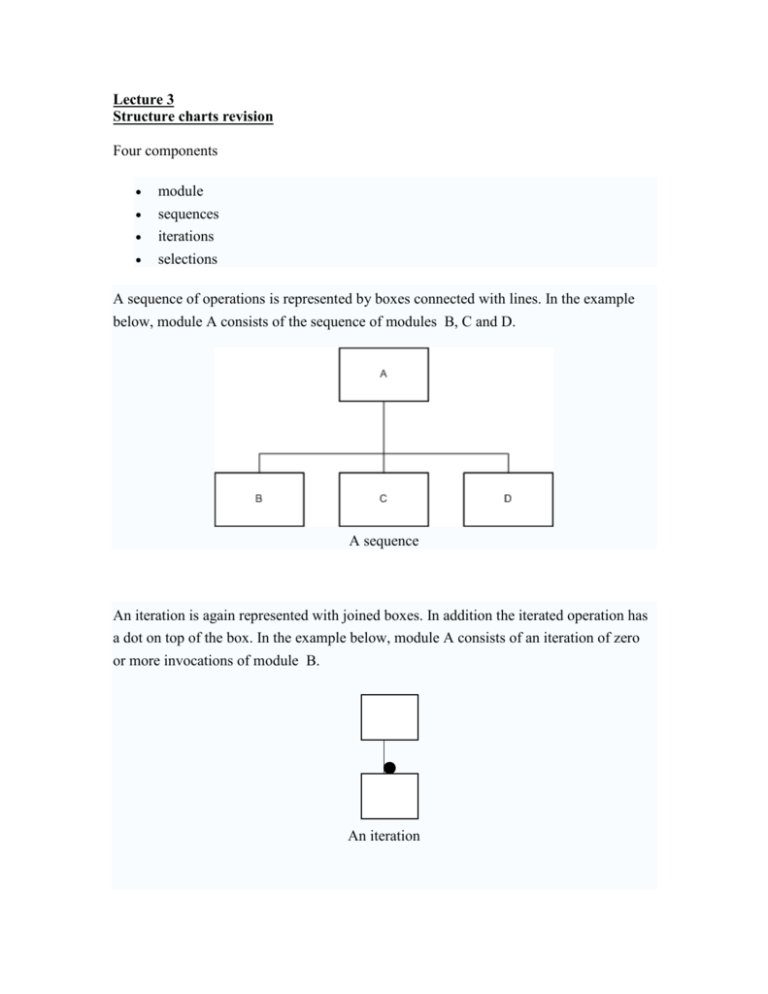
Lecture 3 Structure charts revision Four components module sequences iterations selections A sequence of operations is represented by boxes connected with lines. In the example below, module A consists of the sequence of modules B, C and D. A sequence An iteration is again represented with joined boxes. In addition the iterated operation has a dot on top of the box. In the example below, module A consists of an iteration of zero or more invocations of module B. An iteration Selection is similar to a sequence, but with a diamond. In the example, module A consists of one and only one of operations B, C or D. A B C D The IPO Chart (p46) This extends and organises the information in the problem analysis chart. It shows in more detail what data items are input, what processing takes place on the data and what information will be the end result, the output. In the IPO chart the output is the first to be completed and then the input and then the processing. Input All input data (from section 1 of the Problem Analysis chart) Processing All processing in steps (from Sections 3 and 4 of the problem analysis chart) Module Reference Module reference from the structure chart Output All output requirements (from sections 1 and 2 of the problem analysis chart) Read first number Read second number Read third number Calculate the average of the three numbers Print the average Average TASK :- 1) Construct an IPO Chart for the Average Problem 2) And for the Gross Pay problem Enter 3 numbers 1. Enter three numbers 2. calculate the average of the three numbers 3. print the average 4. end Writing Algorithms After using the structure chart and the IPO chart the next step in organising the solution is to for the programmer to develop a set of instructions for the computer – called algorithms or Psuedocode. An algorithm is set of instructions needed to solve the problem - need to write a separate set of instructions for each module in the structure chart. - the control module uses end because its the end of processing - the other modules use exit because the processing continues Some Programming concepts Relational Operators :- > < = != >= <= greater than x > y less than x<y equals x==y not equals x != y is greater than or equal to x >= y is less than or equal to x <= y Conditional logic – if then else Task 1) – write a pseudocode / algorithm to work out what grade a student got based on the following information :- if student (above or equal) to 90 – A , 80 – B, 70 – C, 60 – D, less then or equal 60 – F If students grade is greater than or equal to 90 Display ‘A’ Else If students grade is greater than or equal to 80 Display ‘B’ Else If students grade is greater than or equal to 70 Display ‘C’ Else If students grade is greater than or equal to 60 Display ‘D’ else Display ‘f’ TASK 2) 1) Write Java code to ask user to enter their name and display it 2) Write Java code to ask user to enter two numbers and workout the average Algorithms to Flowcharts • • • • • • From algorithms the programmer develops flowcharts Graphical representations of algorithms A flowchart shows the flow of processing form beginning to end Each block in flowchart represents one instruction from an algorithm Flowlines indicate direction of data flow Why use flowcharts? – – Flowcharts show errors in logic A set if data can be tested easily using flowcharts Flowchart Symbols (p78) Start / End/ Exit Enter data (e.g form from keyboard ) or Write to printer or screen Variable = expression Assign value of the following expression to a variable location Execute the instructions in named module and then return to execute the next instruction Tasks • Conditional logic – if then else and loops • Task – Write a Flowchart and Algorithm for Average Problem • • Write a Flowchart and Algorithm for Gross- pay problem For each module in the Gross-pay problem – write a flowchart and algorithm control Algorithm Read Calculate Average Print End 1. Process Read 2. Process Calculate the average of the three numbers 3. Process Print the average control Algorithm Read Control Module • • • • • • • Calculate Print false Until noMoreEmployees true End Repeat Process Read Process Calc Process Print Until NoMoreEmployees End Read Read Hours, PayRate exit Read Module 1. Read Hours, Payrate 2. Exit Calc GrossPay = Hours * Payrate Print Print PayRate exit Calc Module 1.GrossPay = HoursWorked * PayRate 2.Exit exit Print Module • • Print Pay Exit Systems Flow Charts Used to document current flows showing where operations take place. The analyst uses flowcharts to describe the processes in the system in pictorial form, making the system easier to understand. Used to document current flows showing where operations take place. The analyst uses flowcharts to describe the processes in the system in pictorial form, making the system easier to understand. The flowchart generally describes processes, files, input and output devises. Split the chart into columns representing different departments/locations and staff associated with the system Flow is normally from top left to bottom right Use arrows to indicate direction of flow No one correct solution Scenario There are three musical concerts taking place in the U.S.A raising money for charity. In order to keep track of ticket applications, customers wishing to purchase a ticket are requested to fill a form. Once a application for a ticket is received by the office, the booking details are checked as is the availability of spaces. If a place is available, details are recorded and customer informed. Draw a flow chart demonstrating the above Customer Booking Office Fill applicati on form Customer Check application form and booking dates Concert Schedule Check availability of concert seats Y Concert Full? Inform cust N Send cust Ticket s Record Concert booking place Update booking file MAKE NOTES Pages 130, 131, 133, 135, 136, 139, 140, 142 A Patient rings a doctor’s surgery to book an appointment. The receptionist takes patient details and checks to see if the patient exists on their system. If the patient does not exist on the system then the receptionist adds the patient to the system. If patient exists on the system then receptionist checks next available appointment and informs patient of appointment dates 1) Draw a Systems Flowchart 2) Write a Programming flowchart to work out the number of patients in the doctor surgery. Consider which variable you need to use and which loop condition you will use