Pseudocode - WordPress.com
advertisement

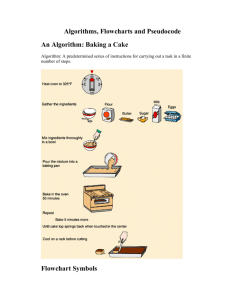
PSEUDOCODE AND FLOWCHART Pseudocode (pronounced SOO-doh-kohd) is a detailed yet readable description of what a computer program or algorithm must do, expressed in a formally-styled natural language rather than in a programming language. Pseudocode is sometimes used as a detailed step in the process of developing a program. It allows designers or lead programmers to express the design in great detail and provides programmers a detailed template for the next step of writing code in a specific programming language. Sample 1 Election Control Structures If age > 17 Display a message indicating you can vote. Else Display a message indicating you can't vote. End Sample 2 Iteration (Repetition) Control Structures count assigned zero While count < 5 Display "I love computers!" Increment count End while Sample 3 Pseudo-code the task of computing the final price of an item after figuring in sales tax. Note the three types of instructions: input (get), process/calculate (=) and output (display) Note that the operations are numbered and each operation is unambiguous and effectively computable. We also extract and list all variables used in our pseudo-code. This will be useful when translating pseudo-code into a programming language Computing Sales Tax 1. 2. 3. 4 5. 6. get price of item get sales tax rate sales tax = price of time times sales tax rate final prince = price of item plus sales tax display final price end Variables: price of item, sales tax rate, sales tax, final price Sample 4 Computing Weekly Wages Gross pay depends on the pay rate and the number of hours worked per week. However, if you work more than 40 hours, you get paid time-and-a-half for all hours worked over 40. Pseudo-code the task of computing gross pay given pay rate and hours worked. Code 1. 2. 3. get hours worked get pay rate if hours worked ≤ 40 then 3.1 gross pay = pay rate times hours worked 4. else 4.1 gross pay = pay rate times 40 plus 1.5 times pay rate times (hours worked minus 40) 5. display gross pay 6. halt variables: hours worked, ray rate, gross pay This example introduces the conditional control structure. On the basis of the true/false question asked in line 3, we execute line 3.1 if the answer is True; otherwise if the answer is False we execute the lines subordinate to line 4 (i.e. line 4.1). In both cases we resume the pseudo-code at line 5. Flowchart A flowchart is a diagrammatic representation that illustrates the sequence of operations to be performed to get the solution of a problem. Flowcharts are generally drawn in the early stages of formulating computer solutions. Flowcharts facilitate communication between programmers and business people. These flowcharts play a vital role in the programming of a problem and are quite helpful in understanding the logic of complicated and lengthy problems. Once the flowchart is drawn, it becomes easy to write the program in any high level language. Often we see how flowcharts are helpful in explaining the program to others. Hence, it is correct to say that a flowchart is a must for the better documentation of a complex program. Basic Symbols Rounded box - use it to represent an event which occurs automatically. Such an event will trigger a subsequent action, for example `receive telephone call’, or describe a new state of affairs. Rectangle or box - use it to represent an event which is controlled within the process. Typically this will be a step or action which is taken. In most flowcharts this will be the most frequently used symbol. Diamond - use it to represent a decision point in the process. Typically, the statement in the symbol will require a `yes' or `no' response and branch to different parts of the flowchart accordingly. Circle - use it to represent a point at which the flowchart connects with another process. The name or reference for the other process should appear within the symbol. GUIDELINES FOR DRAWING A FLOWCHART Flowcharts are usually drawn using some standard symbols; however, some special symbols can also be developed when required. Start or end of the program Computational steps or processing function of a program Input or output operation Decision making and branching Connector or joining of two parts of program Magnetic Tape Off-page connector Flow line Annotation Display Draw a flowchart to find the largest of three numbers A,B, and C. Draw a flowchart to find the sum of first 50 natural numbers.