Determination of Percent ASA
advertisement

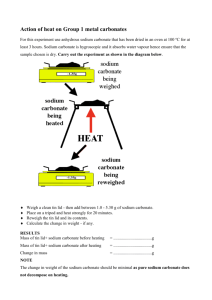
Determination of Percent A.S.A Cost Effectiveness and Related Tests (A.S.A. is acetyl salicylic acid) Procedures Part 1 Percent ASA Carefully weight single tablets of various brands of aspirin to two decimal places. Record the mass of each tablet on the data sheet. Determine the amount of ASA per tablet, as stated on the label. Determine the cost per tablet from the price sticker on the outside of the bottle. Make sure you include the tax. Calculate the percentage of ASA/tablet. Record this data. Part 2 Test for Reducing Sugars A substance other than ASA is needed to give the bulk and to keep it from crumbling. Lactose, a sugar, is often added to some brands. Others contain starch. This part of the lab is a test for a reducing sugar such as lactose. Aspirin will not dissolve in water, but it can be crushed and dispersed to form a fine suspension. Using a small mortar and pestle, crush one tablet of each brand and place them in clean labelled test tubes. Add 15 mL of distilled water and shake them. These are your stock solutions. Transfer 5 mL of each stock solution to separate test tubes. save the remainder of your stock solution for other tests. Test each of the 5 mL solutions with blue litmus paper. To each solution which is acidic, add saturated sodium carbonate solution a drop at a time. Test with your blue litmus paper after adding each drop, until the blue litmus no longer turns pink. To each of the neutralized solutions, add 5 mL of Benedict's solution and heat the tubes to boiling in a water bath. A reducing sugar, like lactose, is one which will chemically reduce the blue cupric ions of Benedict's solution to cuprous ions. The colour of the cuprous precipitate which forms will range from yellow to orange to brick red depending upon how much reducing sugar is present. Record the colours in the data table. Part 3 Test for Salicylic acid To a clean set of test tubes add 5 mL of your stock solutions. To each test tube add 10 drops of 0.1 M iron(III) nitrate solution. A violet colour indicates that the salicylic acid of ASA has reacted with the ferric ions. This is a positive test for the presence of salicylic acid. Record the colour acquired. Part 4 Test for Starch To the remaining stock solution, add 3-5 drops of iodine solution. A bluish-black colour indicates the presence of starch. Record these colours in the data table. Analysis 1. Analyze the results of your experiment by including the following in your lab report. a) difference in ASA % amongst brands b) other substances in the tablets c) results of the iron nitrate test d) cost per tablet e) consumer considerations (best buy) Questions 1. Why is aspirin referred to as: a) an analgesic b) an antipyretic? 2. In the experiment, a saturated sodium carbonate solution was used. Assuming that the solubility curve of sodium carbonate is linear, show how you can determine the amount of sodium carbonate needed to be added to 500 mL of water at 20oC to achieve saturation. DATA: Solubility in grams at 0oC = _____7.1 g_ Solubility in grams at 100oC = ___45.5 g_ 3. Calculate the number of grams of ferric nitrate nonahydrate in 10.0 L of a 0.1 M solution. 4. What is the structure and formula for lactose? 5. Benedict's solution is made in the following way 173 grams of sodium citrate 100 grams of sodium carbonate in 800 mL of water 17.3 g of cupric sulphate pentahydrate in 100 mL of water Dilute to 1000 mL. Calculate the concentration of the following in this solution. a) sodium citrate b) sodium carbonate c) cupric sulphate