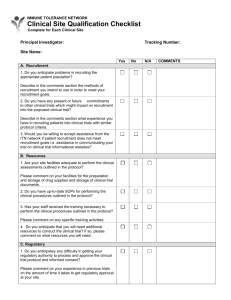
selection process
advertisement

INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Any organization, be it commercial, industrial, educational, comes into existence when a group of people join hands for the attainment of certain objectives. No organization can run successfully unless there is someone to manage its activities. If the people comprising the organization are left to themselves. The result will be utter chaos. As a result of such activities, everybody will be managing its own affairs & nobody will be responsible for anyone. Thus, it is the management which matters people realize the objectives of the organization and directs their efforts towards their achievement. Marketing plans organizes co-ordinates & controls the affairs of the organizations. It brings the human & material resources together material resources for the achievement of the objectives of the organization. Human resource management is the process by which the employees of an organization are helped in a continuous planned way to Acquire and to sharpen capabilities required to perform various function associated with their present or expected future jobs. Develop their general capabilities as individuals and discover and exploit their own inter potentials for their own and or for organizational development purposes and Develop an organization culture in which superior subordinate relationship, teamwork and collaboration among sub-unit are strong and contribute to the professional well-being and promote motivation and pride of the employees. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 1 Management may be defined as ‘’ that field of human behaviour in which managers plan organize, staff, direct and control of human, physical and financial resources in of human, physical and financial resources in an organized effort, in order to achieve desired individual and group objectives with optimum efficiency and effectiveness”. It is clear from above the definition that management is concerned with the accomplishment of objectives by utilizing physical and financial resources through the efforts of human resourcesScope of Human resource Management The scope gradually enlarged to providing welfare facilities, motivation, employee training, performance appraisal, maintenance of human relations and the like. The scope has been continuously enlarging. Presently the scope of HRM includes Nature of HRM Complex human beings Dynamic human resources Employment of human resources Job design and analysis, Human resource planning Recruitment, selection, induction and placement Human resource management Training and management development Career planning and development Organization charge and development Quality of work lift, quality circles Job evaluation www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 2 Compensation management Job evaluation Wage and salary administration Welfare benefits Human relation Motivation Morale Leadership Communication Industrial Relations Trade unions Grievance and discipline Collective bargaining Workers participation in management Prospect of HRM Non union organizations Dejobbing \ Delagening Down sizing Employee empowerment Functions of HRM The functions of the HRM can be gladly classified into 2 categories 1. Managerial functions 2. Operative functions 1) Managerial functions The managerial functions are classified as follows; www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 3 1. Planning: - It is a pre-determined course of action planning is determination of personnel programmes and charges in advance that will contribute to the organizational goals. 2. Organizing: - An organization is a ‘structure and a process by which co-operative group of human beings allocated its task among its members, identifies relationships and integrates its activities towards common objective”. 3. Directing: The next logical function after completing planning and organizing is the execution of the plan. The willing and effective co-operation of employees for the attainment of organizational goods is possible through proper direction. 4. Controlling: After planning, organizing and directing the various activities of personnel management, the performance is to be verified in order to know that the personal functions are performed in conformity with the plans and directions. 2. Operative functions. 1. Procurement of personnel: The first operative function of personnel management is concerned with obtaining the proper kind of personnel necessary to accomplish organizational goals. This step includes determination of Manpower requirements, recruitment, selection, placement, and induction etc of staff. 1. Development of personnel: Measures are taken to increase the efficiency skills and job performance of employees through training and development. The personnel department as to prepare training and development as to prepare training and development programmes for employees at all levels of the organization conduct seminars and group discussions. 3. Compensation to personnel: www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 4 Compensation means determination of adequate and equalable remuneration of personnel for their contribution to organizational objectives. This includes job evaluation, development of a suitable wage structure. 4. Maintaining good industrial relations This is one of the most important functions of personnel management maintaining a harmonious relationship between labour and management is essential since it affects productivity. 5. Record functions: Maintenance of record is essential for the following resources;a) To conduct research in the field of industrials relations. b) To enable the personnel managers to the pare training and development programmes. c) To review and revise pay scales. 6. Employee benefit schemes This includes formulation, implementation, evaluation of various welfare activities such as education, housing, transportation etc. 7. Personnel planning and evaluation: Employee appraisal is systematic evaluation of a workers performance and scope for development. It is a process estimating the values, excellence qualities or status of a person. 8. Personnel research and audit This involves containing studies and various aspects of personnel relations and personnel procedures and practices with the view to bring about necessary improvements in the field of personnel management. Definition of HRM According to Institute of personnel management HRM is defined as “personnel management is a responsibility of all those who manage www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 5 people as well as being a description of the work of those who are employed as specialists. It is that part of management which is concerned with people at work and with their relationships within an enterprise. It applies not only to industry and commerce but also to all field of employment. According to Flipplo”. Human resource management is planning, organizing directing and controlling of the procurement, maintenance development of people for compensations, the purpose integration of contributing and to organizational, individual and social goals”. Manpower planning process 1. HR demand forecast: - Demand forecasting is the process of estimating the future, quantity and quality of people required. The basis of the forecast will be the annual budget and long term corporate plan. The corporate plan is translated into activity levels for each function and development. 2. HR Supply forecast: - The next step is to determine the source from which the personnel can be procured. This information is provided by supply forecasting. Supply forecasting measures the number of people likely to be available from within and outside of an organization. 3. HR programming: - Once the demand forecast and supply forecast is over the next step is to match. These two. This will ensure filling up of vacancies by the right employees at the right time 4. HRP Implementation: - Implementation requires converting the HRP into action. A service of action programmes are taken up such as recruitment, selection and placement, training and development, re-training etc. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 6 5. Control and evaluation: - This is the final phase in HRP process or manpower planning process the human resource plan should include budgets target and standards. Objective of Manpower planning To ensure optimum use of human resources currently employed. To determine future recruitment level To provide control measure to ensure that necessary Resources are available as and when required. To anticipate redundancies and avoid unnecessary dismissals. To forecast future skill requirement to serve as a basic for training and development programmes. To assess future housing needs of employees To decide whether any of the enterprises activities e.g. Maintenance of offloaded or sub-contracted. To identify the areas of surplus personnel or where it is deficient so that it could be balanced. To train the existing employees to meet the challenges of new and charging technology. Objectives of HRM If must satisfy the employees by providing them income, power, prestige, creative satisfaction or a combination of these. It must satisfy the owners by maximizing productivity. It must satisfy the community and society at large by supplying goods and services as efficiently as possible and by preserving and advancing goodwill, morale, loyalty and its reputation. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 7 To ensure the availability of completed and willing work force to an organization. Recruitment Recruitment forms the first stage of acquisition of Manpower or human resources. This process of location and identifying potential and candidate for selection. Recruitment is defined in various ways as indicated follow. “Recruitment is the process to discover the sources of manpower to meet the requirement of the staffing schedule and employ effective measures for attracting that manpower in adequate number’s to facilitate effective selection of an efficient working force”. - Yoder. “Recruitment is the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating and encouraging them to apply for job in an organization, it is often termed positive in that it stimulates people to apply for jobs to increase the hiring ratio that is the number of applicants to a job”. - Edward.Flippo. “Recruitment is the discovery of potential candidates for actual or anticipated organizational vacancies….. It is the linking activity bringing together those with the jobs to fill and those seeking jobs”. - David. According to this definition recruitment is a prospecting job where organization make search for prospective employees. In practice however prospective employees to seek out organization seek out prospective employees. Therefore, the job of recruitment is based www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 8 on the mating theory where success pf both the parties is critically dependent on timing. Unless the two searches synchronize conditions are not ripe for recruitment to succeed. The synchronization in its turn depends on 3 factors: 1. There should be a common communication medium. If an organization advertises its vacancies in newspapers, which is never read by the job seekers, its efforts would go waste. 2. The job seekers must perceive a match between his personal characteristics and prescribed job recruitment. 3. The job seeker must be motivated t0 apply for the job. Recruitment is the process of exhausting all the sources for finding prospective employees. It is the process of finding suitable employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organizations. Its objective is to increase the selection ratio, that is, the number if applications per job opening. Theories of Recruitment There are 3 ways in which an individual make decision to join an organization there are objective factor, subjective factor and critical contact. Accordingly following three theories of recruitment have evolved. 1. Objective factor theory 2. Subjective factor theory. 3. Critical contact theory. 1. Objective factor theory: - www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 9 As per this theory the choice of organization by potential employees depends on objective assessment of certain tangible functions, such as the following. Pay and perks. Location. Opportunities for career growth. Nature of work. Educational opportunities etc. 2. Subjective factor theory:According to this theory compatibility on individual personality with the image of organization by an individual candidate seeking employment. 3. Critical contact Theory There are instances when a candidate is unable to choose an organization, out of alternatives based on objective or subjective factor, which are given above. This is due to many reasons. Such as limited contact and insufficient data, in regards to the organizations or his own inability to analyze and come to any firm and conclusion. In such cases, certain critical factor observed by him during his interview and context with the personnel of the organization will have profound influence personnel of the organization will have profound influence in the decision process. Example of critical factor is the impression made by recruiting personnel on him. The business like manner in which the recruitment process is carried out nature of facilities presented etc. Objectives of Recruitment - To attract with multi- dimensional skills and experience that suit the present and future organization strategies. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 10 - To induct outsides with new perspectives to lead the company. - To infuse fresh flood at all levels of the organization. - To develop an organization culture that attracts competent people to the company. - To search or head hunt\head paunch people whose skills fit the company’s values. - To device methodologies for assessing psychological traits. - To seek out non-conventional development grounds of talent. - To search for talent globally and not just with the company. - To design entry pay that competes on quality but not on quantum. Factors affecting Recruitment Although all organizations at one time or other engage in recruiting activities some do so too much longer extent than others. The various factors, which influence the recruitment efforts in different organization, are:1. Size of the organization. Large organization finds they recruiting more after than smaller organization also the firms that pay lower wages in to recruit more frequently. 2. Employment Conditions. The employment conditions in the community where the organization is located will influence how much recruiting takes place. 3. Past recruitment efforts. The efforts of past recruitment or recruiting efforts will show itself in the organization historical ability to locate and deep people who perform well. 4. Working condition and compensation. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 11 The working conditions and compensation and benefits package offered by the organization would influence labour turnover and therefore the need for future recruiting. 5. Growth of Organization. The rate of growth of organization would affect recruitment organization that are not growing or those that are actually deciding would find little need to recruit. On the hard rapidly growing organization would find recruitment as a major activity. 6. Other Factors Other factors such as level of seasonality of operation, future expansion, and cultural, economic and legal factors also influence recruitment. Sources/Forms of Recruitment Recruitment can either be through 1. Internal sources 2 External sources 1. Internal Recruitment/ Sources: - Internal recruitment means seeking applicants for positions from there that are already employed in the organization. Internal sources are:1. Present employees. 2. Employee referrals. 3. Former employees. 1. Present employees. Promotions and transfers from among the present employees can be good source of recruitment. Transfers without promotion can also be made. 2. Employee Referrals. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 12 The present employees suggest prospective candidates [either family member of friends] to the employer. This is an effective method because many qualified people can be contained at a very low cost to the company. The current employees are conditions while recommending candidates since there will be aware of employer’s expectations. 3. Former employees. In some cases retired employees may be willing to comeback and work on a part time basis. Some candidates, who left the origination for other jobs, might be willing to comeback. The advantage of this source is that the employees already know the performance of such candidates. Merits of Internal Recruitment 1. It is less expensive when compared to external recruitment. 2. Promotions from within will enhance employee morale, commitment to the organization and job satisfaction. 3. The employer need not conduct collaborate orientation programmes. 4. Employer is well aware of the candidate’s skills, abilities, strengths and weakness. De-Merits of Internal recruitment 1. It results in breeding the possibility if getting fresh blood is lost. 2. Internal recruitment doesn’t serve the purpose when an organization wants to expend or diversity. 3. Internal recruitment encourages “The same old way of along thins”. Possibility of Internal polities is high such as favoritism corruption etc. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 13 2. External Recruitment Following are the external sources 1. Professional or trade associations. Certain trade associations provide placement services for there members. They may publish or sponsor trade journals or magazines for their member. These publications after curry classify adds from employers. 2. Advertisement. This is a very popular method of recruitment. “Wants adds describe the job and the benefits, identify the employer and also specify how to apply for the post”. A newspaper is most common media. 3. Employment exchange. Employment exchanges ‘compulsory notification of vacancies acts 1959”. Applies to all industrials establishments having 25 workers are more. The acts specify that such industrials establishments should notify the vacancy to the exchange before filling up the same. This the employment exchange acts as a link between the employer and prospective employee. 4. Campus Recruitment Some companies contact educational institutions like IIMs. IIPs to select candidates selection is generally made from students in the final year. Companies like Hindustan lever, Motorola, Citibank etc., adopt this approach. 5. Walk in, Talk in method. In today’s organization interested candidates contact the organization abjectly at a designative place. Several rounds of Interviews are conducted before deciding the candidates. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 14 6. Contractors. Contractors are used to recruit casual workers. The casual applicants come to the factory gate and contact the recruitment officer. 7. Consultants Consultants perform the recruitment function on behalf of the client company in return for a fee. 8. Radios and Television Government departments generally do radio and television as a source to recruit persons. 9. Acquisitions and Merger. Another method of staffing is through acquisition and merger. When two organizations merge than the new organization will have a port of competent or capable employees. The new organizations as to suitable accommodate the candidate in new organization. 10. Competitors Sometimes rival firms can be source of recruitment. It is popularly called as approaching or riding this method involves identifying the night people in rival companies, offering them better terms than turning them away. 11. Displaced persons Sometimes when a new project is started in a new location it may lead too displacements of several inhabitants of that area. Re-habilitating the displaced people is social responsibility of business such people than become a source of recruitment. Merits of External Recruitment 1) The organization will have the benefit of new skills, new talents and new experiences, if people are hired from external sources. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 15 2) Management requirements will of also the be able government to such satisfy as recruitment recruitment of backward classes, disabled persons etc. 3) External recruitment can sometimes over come the problem of jealousy and resentment among the old employees. De-Merits 1) External recruitment is expensive and also time consuming. 2) Possibility of promoting candidates from among the existing employees is lost. 3) Possibility to mal-adjustment among the old employees and new employee. 4) If external recruitment and selection are not conducted properly than the wrong candidate may enter the organization. Recruitment Process First step The personnel / human resources department receives the requisition list of employees from various department of the company. They from various department of the company. The employed from consists of jobs to be filled number or person to be employed, duties to be performed, skills and knowledge abilities, qualifications and experience of the candidates etc. It also contains terms and conditions of employed time period for joining the duties etc. Second step This step relates to identification of source, their location/ areas at right time and development of source. Third step This step includes searching for prospective candidates in the source developed. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 16 Fourth step This step involves motivating the prospective candidates to apply for the job by providing the information about the company, job, pay scale allowances career, opportunities, terms and candidates of employment etc. Firth step This step involves stimulating the prospective and suitable candidates to apply for the job providing additionally information to the candidates and procuring application from the candidates. Sixth step This step involved evaluating the effectiveness of the recruitment process. Steps in Recruitment Process According to Fumularo personnel recruitment process involves five elements: a. Recruitment policy. b. Recruitment organization. c. Forecast of Manpower requirements. d. The development of sources of recruitment and different techniques used for utilized these sources. e. A method of assessing the recruitment programme. 1. Recruitment policy Recruitment polity assesses the objectives of recruitment objectives and provides a framework of implementation of the recruitment programme in the form of procedure, A good recruitment policy must contain these elements. 1) Organization objectives – both short-term and long-term. 2) Identification of recruitment needs. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 17 3) Preferred sources of recruitment, which would be appeal by the organization, 4) Criteria of selection and preferences. 5) Cost and financial implications of recruitment. Pre-acquisitions of a good recruitment policy The recruitment policy of an organization must satisfy the following conditions: 1. It should be in conformity with the general personnel policies. 2. It should be flexible enough to meet the changing needs of an organization, 3. It should march the qualities of employees with recruitment of the work for employees with recruitment of the work for which they are employed. 4. It should highlight the necessity of establishing job analysis. 2. Recruitment organization There is no general procedure for hiring new personnel, which is applicable to able business enterprises. Every organization uses procedures. Which brings with it the desired quantity and quality of manpower at the minimum possible cost the most commonly adopted practice is to centralize? The most commonly adopted practice is to centralize the recruitment and selection functions in a single office. All employment activities should be centralized if the polices of the top management are to be implemented consistently and efficiently. 3. Forecast of manpower recruitment The management must estimate the structure of the organization at a given point in time. For the organization the number and type of employees need have to be determined. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 18 Many environment factors affect this determination business forecasts expansion and quotation on it philosophy government policy, product and human skills and completion forecasting recruitment provide an early warning system and facilitate maximum preparation for implementing change. Planning the further recruitments of manpower of all types requires two set of information 1. An analysis of the existing manpower strength and the work volume being handled. 2. Detailed forecast of future or preferable changes in methods, type of work, facilities etc. In determining the requirements of human resources the expected losses that are likely to occurs through labour turnover, retirement death, resignation dismissal, promotion and other separation should be taken into account. 4. Sources of Recruitment Before on organization begins recruiting applicants it should consider re most likely sources of the type of employee if need. The sources of employment could be classified into two types Internal and external source. Most organizations depend on both sources and the relatives emphasis and use of these sources night differs from one organization to another. 5. Assessment of Recruitment programme. Sources of recruiting should be periodically evaluated. For his purpose the criteria might be cost per applicant, the applicant-hiring ratio or performance appraisals. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 19 The organization should first identify low an applicant was attracted to the firm. The next step is to determine whether any one method consistently attracts batter applicant the last step is to use this information to improve the recruiting process. SELECTION One of the major activities in “Acquisition function” personnel management [HRM] is the specific section of employed to fill up the vacancies selection process consists of series of steps. This price is followed immediately after the recruitment is completed. The objective of selection process is two fold they are;- Select a candidate whose success of probability in the job is highest. Motivate the right candidate to opt for the vacancy by the proper presentation of the organization to the potential candidates. Selection is defined in various ways as given below;\ According to yoder “selection is the process by which candidates for employment are divided into classes those who will be offered employment and those who will not’. Accordingly to koontz ‘o’ Donnel “Selection is a process of choosing from among the candidates from within the organizations or from outside, the most suitable person for the current position or for the future position”. Selection is always essential for an organization to have a selection programme the need to install such a programme arises only when there is a labour surplus and there are individual differences in job performance. This means that when there is shortage or when the www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 20 work is such that no large differences in job performance exist there is no need top have a selection programme BASIC SELECTION MODEL 1. Job description. 2. Identification of predictor and variables 3. Identification of criterion variables. 4. Performance measurement on predicator and criterion. 5. Co-relation between predictor and criterion. 6. Decision to accept or reject predictor. 7. Follow up. 8. Selection with multiple predictors 9. Profile matching. NEED FOR HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT: The components and dimension of human resource development is of strategic importance. People make things happen. HRD is the process enabling people to make things happen. The main objective being to develop competencies in individual, groups and collective, developing competencies a never ending process. The opening of global markets and increased market orientation of economy. Competitiveness has gone up globally, forcing developing countries to produce and make quality product at competitive prizes. HRD deals with the development of technological capabilities, requiring, investment in science, technology, research and development, industrial high-tech products. This also required policies and programmes that deal with higher education, science and www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 21 technology, and industrialization. The competition in global market requires competitive technologies and managerial efficiencies. Competencies include knowledge, skills, attitudes and values. The competencies so developed would ‘enable’ people to act and improve their own lives and those of others. Factors which are responsible for development of this profession in a phased manner from world prospective are as follows: Technological changes are taking place at a rapid pace through out the world. Such changes the relationship between people and work and a major change in the economic system and the structure of a society. The rising competition both at home and abroad virtually reduces the profit to the level of production. The rise of consumerism, government protection and international competition developed the necessity to maintain quality and price. Social changes. The political development also re-structured trade unionism. The structural charges in employment and changes in sector distribution of employment. Effective utilization of human resources under this technological environment is the challenges before today’s personnel. There is total crisis and recession throughout the world. MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF HRD 1. Determining and staffing for employee needs. 2. Measuring performance and developing employee potential. 3. Preserving effective employment management relationship. 4. Uncovering and resolving employee problems. 5. Anticipating and coping with organizational changes. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 22 HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT AS A SEPARATE PERSONAL DISCIPLINE The importance of human resource Development is to make people effective and resolving the employee problems. It is believed that Karl Lewis (1947) studies of Behaviour of small groups and settings up of National Training Laboratories are the first step of HRD profession was the domain of psychiatrist; psychologists, counselors and nurses are the concept of human relation training. Training group leaders, handling complaints, expressing feelings, giving and receiving feed-back, competition and co-operation, problem solving and increasing awareness on oneself and ones impact on others. HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT AND HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT In the ESCAP region a broad definition of HRD seems to have been implied by several writers. Limteck Ghee takes view that HRD should refer not only to aspect of physical well-being of people such as life expectancy, infant mortability, rates of mortability and level of nutrition, but also social cultural aspects, including education and employment, social coheism and stability political expression, cultural diversity and even ecological harmony. Lorraine Corner (1991) suggests that HRD is used in three senses The first approach emphasizes the contribution of human capital to economic growth. The second emphasis ‘quality of life’, which is considered as an output of development the third is an integrated view combing the first two approach www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 23 Bacchus (1992) the ultimate goal of human resource development in any country is, or should be, to improve quality of life of all its people. The main activity being for a smaller and more productive utilization of the total human resources of a country. Common wealth secretariat and other such agencies seems to prefer HRD. It defines HRD as : Policies and programmes that support and sustain equitable opportunities competitiveness which promote individual and are naturally beneficial to individuals, the community and the larger environment of which they are a part (UNDP, BPPE, 1991, P.19) FACTORS OF HRD ARE: a) Search for Competitive Advantage: The competitive Advantages school of thought argued the better utilization of human resource is necessary to achieve competitive advantage by organization and by any nation. b) Models of Excellence: By Peters and Waterman (1982) and Knater (1984), HRM, as models of Excellence companies isolating it from traditional Personal Management Functions. c) Failure of Personnel Management: Skinner (1981) and many others show personal Management failure to promote potential benefits of effective management of people. d) Decline in Trade Union Pressure: Change in economic and political climate around the world resulted in decline in Trade Union Pressure on Management. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 24 e) Change in the workforce and the Nature of work: Structural change in the occupational pattern is now a world-wide phenomenon, of which India is also no exception. Technology, increased requirement of skills, and knowledge re-structuring of production, near quality system etc…. HRD CONCEPTS: HRD is a process which helps employees of an organization to improve their functional capabilities for their present and future roles, to develop their general capabilities to harness their inner potentialities both self and organizational development. To sustain harmonious superior–subordinate relationship, team work, motivation, quality and sense of belongingness. TRAINING: The focus on training programmes should be such, so as to enable the individual to perform more effectively in his present job position. Training is required when a person is hired without the requisite skills, attitude, or knowledge. Even incases where on employee may be performing very well changes in processes, procedure, material etc., many stimulate the need to further training. Total Quality Management, small group activities or Quality, Circle concepts are called for training them to make them financially more effective in their re-structural jobs. EDUCATION: Since return on investment from education is unclear or uncertain, very few organizations are prepared to invest on employee education programme and develop them. Many organizations allow their employee to go on study because for Research work etc., based on organizational needs for future. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 25 Some organization encourage employee to get enrolled in part-time evening institution and reimbursing the employee. However, some organization, provide education the organization and ensures on-the job activities learning of new techniques for the future roles. DEVELOPMENT: Development component of HRD is to conduct learning experience for a future undefined job. However experience shows carefully planned development experience can be helpful in realizing the human potential. OBJECTIVES OF HRD: 1. To develop capabilities of all such individual in relation to their future role. 2. To develop capabilities of all such individual in relation to their present role. 3. To develop letter inter-personal and employer – employee relationship in an organization. 4. To develop team spirit. 5. To develop organization health by renewal of individual capabilities keeping pace with the technological changes. 6. To develop co-ordination among different with in an organization. ROLE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF HRD: For any dynamic and growth oriented organization to survive in a fast changing environment, HRD activities plays a crucial role. Training, Retraining and re-department has now became buzz word in corporate circles as market globalization, de-licensing and free flow of technology, intensified competition, rendering tradition skills and knowledge redundant. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 26 Many organizations in India are threatened with manpower obsolescence to withstand which HRD activities have received prior importance. HRD SYSTEM: 1. Increasing the ‘enabling capabilities’ by developing human resource organizational health, team spirit and increasing employment, motivation and productivity. 2. Focus on balanced organizational culture – by conducting periodic surveys, workshops, discussion, stimulating openers, mutual trust, workshops, creativity, initiative, collaboration, delegation, management of conflict etc., 3. Focus on having context factors: - from different profession like NIPM, ISTD etc. 4. Focus on periodic reviewing of HRD System – which may call for re-designing, performance appraisal, Reward System, Promotion, Selection, Induction, Training and Development, etc. 5. Focus on integrating HRD with other corporate functions like Production, Finance, Material Corporate Planning etc. such integration will strengthen the development of enabling organization. 6. Focus on diffusion of HRD function – involving line manager in various HRD aspects live training of sub-ordinates, performance appraisal, promotion, placement, selection etc., 7. Focus on working with union by taking them into confidence and collaborating with them. The Union also plays a positive role like Syndicate Bank Employee Union. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 27 STRUCTURE OF HRD SYSTEM ORGANISATIONAL CHART President HRD Vice President / Training Manager Education & Development Manager Executive Education Manager Sales & Marketing www.ikhanmania.weebly.com Vice President / Education & Development Manager OP Manager Management Development Manager Engg. Training Manager Manufacturing Training Manager Staff Support Training 28 ORGANISATIONAL CHART NO.2 – (INTEGRATED HRD) GENERAL MANAGER Manager Finance Manager Customer Service Manager Manager Manager Manager Human Manufacturing Sales & Accounts Resources Supp./Customer Supp / Supp/ Technical Service Training Mgt. & Training training ORGANISATIONAL CHART NO.3 Department Sup / Scales Clerical Training HRD as a separate VICE – PRESIDENT – HR Director / Personnel Admn. Director / HRD Director IR Director / Labour Welfare Director Employee Services ROLE OF HRD MANAGER The Primary goal of HRD is to increase worker’s productivity and firm’s profitability as investment in HRD improves workers skill and enhance motivation. The other goal of HRD is to prevent obsolescence at all levels. To achieve there goals HRD Manager has to:1. Assist people in obtaining the knowledge and skills through proper training for present and future job. 2. To play the ‘enabling’ role providing the organization to reach objectives. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 29 American Society for Training & Development 1988 identified eleven roles of HRD Manager: 1. EVALUATOR: The role of identifying the impact of an intervention on individual on organizational effectiveness. 2. ADMINISTRATOR: The role of providing Co-ordination and support services for the delivery of HRD. 3. Individual Career Development Advisor: The role of helping individuals to assess personal competencies, values and goals. 4. HRD Manager: The role of supporting and leading a groups work and their obtaining organizational goals. 5. Instructor / Facilitator: The role of presenting information directing structured learning experience and managing group discussion and group process. 6. Marketer: The role of marketing and contracting for HRD view points, programmer and services. 7. Material Developer: The role of productivity written mediated institutional methods. 8. Needs Analysts: The role of identifying ideal and actual performance and performance conditions and determining causes of discrepancies. 9. Organizational Changes: The role of influencing and supporting changes in the organizational behaviour. 10. Programme Designer: The role of preparing objectives defining content and selecting sequence of activities. 11. Researchers: The role of identifying developing or testing new information and translating these two implications for improved individual organizational perform. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 30 SELECTION PROCESS The first task of selection process is to define the organizational needs for different position and so also to assess the available To develop in an organization a wide selection and promotion system that supports the over all manpower policy of the organization. To create internal flow of people to suit the future requirements of the organization. The final strategic is matching key executives to the organizational policy. Internal selection is considered to be the best policy to sustain morale of the presence employees, thereby, organization derives motivation benefit. Some time the organization has to book at external source, to make selection process scientific. Selection process is broadly divided into two: a) Discreet Selection Process b) Comprehensive Selection Process Discreet Selection Process: “Discreet Selection Process” – the result / outcome of each step is “success” or “Failure” Yoder “Succession of Hudles”. 1. Application 2. Screening 3. Application Blank 4. Selection Tests 5. Interviews 6. Work History 7. References 8. Provisional Selection 9. Physical / Medical Examination www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 31 10. Final Selection 11. Employment HRD TOOLS: SELECTION Selection process includes both activities relating to Internal hiring and external hiring. The objective of selection process is to determine whether an applicant meets the qualification for a specific job and to choose the applicant most likely to perform. OBJECTIVE OF SELECTION PROCESS: a) Select a candidate whose success probability in the job is the highest. b) Motivate right candidate to opt for vacancy by proper presentation organisation to the potential candidates. Cost of selection is also an important aspect. The best way to reducing cost is to take “Correct Decision”. Thus selection is “Decision – marking” process. COST OF DECISION: Every decision has a cost. There are four types of selection they are 1. Selecting the right person. (Correct Decision). 2. Rejecting the right person. (Wrong decision, reject error) 3. Selecting the wrong person. (Wrong decision, select error) 4. Rejecting the wrong person. (Correct decision). SELECTION PROCESS – DECISION MAKING MATRIX DECISION / SELECT www.ikhanmania.weebly.com ERROR 32 PERFORMANCE GOOD CORRECT (1) Selecting (2) Rejecting the Right the Right BAD ERROR (3) Select the wrong CORRECT (4) Reject Wrong. the “Selection is the process by which candidates for employment are divided into class those who will be offered employment and those who will not”. Yoder “Selection is the process of choosing from among the candidates from within the organization or from the outside; the most suitable person for the current position or for the future position”. Koontz SELECTION TESTS: Psychological Tests are conducted for selecting candidates. Organization historically, relief considerably to a number of tests. These tests are conducted in order to improve the selection decision. “A systematic procedure for comparing the behaviour of two or more persons”. Blum. CLASSIFICATION OF TESTS a) Based on Design Standard tests Tailor made tests. b) Based on Attribute Being Tested Aptitude test (Proficiency Test) Achievement Test (Performance Test) Personality Test Interest Test. c) Based on purpose for which the tests are conducted. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 33 Selection Test Classification Test Placement Test d) Based on number of persons involved. Individual Test Group Test APTITUDE TEST: This test is to measure talent ability and potential capability of specific talent such as learning reasoning, mental ability and mechanical dexterity most common. Aptitude tests are: Intelligence Test: This test enhance mental abilities such as verbal, reasoning, analytical ability etc. IQ = Mental Age Chronological Age Mechanical Aptitude Test: The parameters to check on are spatial visualization, perceptual speed, and manual dexterity. 1. Application: It is the process of identifying potential candidates. Applicants desire to take up the job in the organization is demonstrated formally and voluntarily. Organization has publicity admitted existence of a vacancy and expressed willingness to consider suitable candidate for appointment. 2. Screening: Screening of Application Screening of Interview www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 34 a) Screening of Application: It is based on “Job description” and “Job specification” attributed of a suitable is considered. b) Screening Interviews: 1. To assess how serious is applicant for getting job. 2. To assist management to clarify certain points. 3. To explain nature and type of job from “Job description” 4. To clarify salary package and perks. 3. Application Blank: This is the specially designed “Application Form” by the organization. 1. Biographical data like name, address, date of birth, sex, nationality. 2. Education Qualification & Training. 3. Work Experience – duties, responsibilities, salary and reason of leaving the previous employment. 4. Personal achievement in sports and arks. 5. Professional achievement and membership of professional bodies. 6. Expectation of salary and perks. 7. Individual goal and interest. 8. Assets, outstanding debts and criminal and if any 9. References. a) Correlation Analysis: Test scores are compared with job performance. Ranking of each employee may be tested. X-axis is test score and Y axis is the performance test. Higher positive value approaching to +1 is the better validity of the test. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 35 b) Scatter Diagram 81-90 Success Rate in % 100 71-80 75 51-60 50 25 21-30 0 Test Score INTERVIEW: Interviews are most used widely for selection process. This is a complex technique and its scope is very wide. Factors considered are: Adequate preparation. Type of interview Techniques used Adherence to principles Avoidance of pit falls. OBJECTIVE OF INTERVIEW: a) It is the only way to see an applicant in action how he looks, his manner and his hearing. b) It is the only way to witness how he interacts, how he responds, his way of thinking etc. c) To get first hand information about the candidate. d) To promote goodwill toward the company. e) To give essential facts about the job and the company. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 36 4. Psycho – Motto Test : Dexterity, control and co-ordination of muscles are checked. MC Quarril Test Purdue Mechanical Adaptability Test. ACHIEVEMENT TEST Test of measure knowledge. Test to measure skill level. PERSONALITY TEST Objective Test Projective Test Situation Test ASSESSMENT CENTRE TESTS Interview An “in basket” exercise where applicants are asked to solve day to day problem faced by manager – planning, organizing, directing, co-ordinating and controlling. A care – study exercise. A group discussion. A business game. A set of general ability test. VALIDITY OF TESTS: Explained by Scatter Diagram Expectancy diagram On the basis of the project study made and response received the following suggestions are made to improve HR activities 1) The performance evaluation should be made objective basis. Periodical achievement of tasks should be adopted and allotment of tasks in the succeeding periods should be assessed by the superiors based on the performance of the assesses in the www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 37 assessing period / quarter. If there is 100% achievement, such executives should be considered for higher job responsibilities thereby, utilizing their talents to the full extent. This way the organization will prosper. 2) Every executives, and for the matter, every employee should be looked upon with self-respect. Though “respect for individuals” is one of the organizational values in the company, it seems this value is not being practiced. To overcome this, it may be made one of the aspects in the annual confidential report as which an assessee may comment and the organization could take corrective step accordingly. 3) In case, of recession, the employee should be informed a month before the pink-slip is issued and the reason for which it is issued to be explained. Giving opportunities for the individual to improve or helping him to get absorbed in another organization if the HRD is aware of vacancies. Giving references for absorption in another firm. 4) The performance standards should be discussed with the subordinates / employee so as to involve them in standard setting. This satisfies the individuals ago and desire for self- esteem brings about physical and mental involvement of the people in an activity, particularly in that of decision-making especially matters affecting them. 5) Steps should be taken to analyze hour for the organization / individuals have been objective in various actions, such as promotion of individuals, extending benefits, in assessing subordinates in their annual confidential reports, assigning jobs, development of subordinate etc., with this in view, it would be appropriate if the subordinates also assess their superiors in www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 38 their annual confidential reports, which system is existing in some of the companies. Organizational policies are thus, applied uniformly. 6) Participative management and Consultative supervision have been greatly encouraged. Identification implies that “the individual sees the group mission and goals coinciding with his personal objectives”. It is believed that employees’ helps in setting their individual and group goals are strongly agreed to achieve the target. Identification makes the individual more receptive to organization norms and to suggestion from his associates. It offers an opportunity for increasing the employees’ sense of personal with and high group loyalty tends to the associated with high performance. This company, being a very young is the market, the employee should also grow with the company’s growth and accordingly, their needs will also increase. The company has to keep a watch and make continuous progress in near future. www.ikhanmania.weebly.com 39