第二章 植物病原真菌
Plant disease fungi
are fungi?
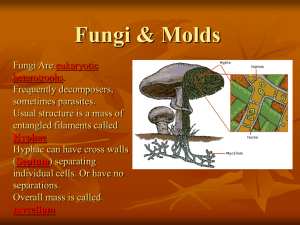
Fungi: Fungi are eukaryotic
organism, hetertrophic in nutrition.
Their structures are simple. They
can produce asexual and sexual
spore.
真菌的概念:What
Nutrition—heterotrophic and
absorptive; investion of food rare.
Thallus—unicellular, filamentous
(mycelial) or occasionally
plasmodial (naked mass of
protoplasm).
Cell wall—made up of chitin
(cellulose only in class Oomycetes).
Nucleus—eukaryotic,
characteristically small, near the
limit of resolution of light
microscope.
Life cycle—simple to complex.
Sexuality—asexual and sexual.
Usually produce spores.
第一节 真菌的一般性状和分类
一、真菌的营养体.Nutrition
body:
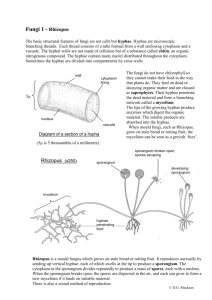
1、菌丝体Thallus;
The thallus may be unicellular on
filamentous (mycelium). Fungi are
characterized by their hyphae (sing.
Hypha)—the long tubular, much
branched structures, which collectively
are called mycelium.
无隔菌丝和有隔菌丝 Coenocytic hypha
( unseptate hypha) and septate hypha
The
hyphae may be unseptate or septate.
The unseptate hyphae have nuclei
scattered in the cytoplasm, this
condition is known as coenocytic
condition
Septa are of tow types: primary and
adventitious
2、原生质体Plasmodium
e.g.
Plasmodiophora brassicae
There are no cell wall in nutrition type of
Plasmodiophora brassicae
菌丝体的变态和菌组织
Special structure and tissue
(1)
吸器Haustorium
(2) 附着胞Appressorium
(3) 假根Rhizoid (Pseudoroot)
(4) 拟薄壁细胞Pseudoparenchyma
(5)
疏丝组织Prosenchyma
(6)菌核 Sclerotium
(7)子座 Stroma
(8) 菌索Rhizomoph
真菌菌丝体图
二、真菌的无性繁殖
Non-sexual reproduction
( vegetative and asexual
reproduction )
1、无性繁殖方式:
(1) 断裂和裂殖 Fragmentation : A small bit of the
broken hypha establishes a new colony. and Fission :
This occurs in fission-yeasts only. It is characteristic
of bacteria. The cell divdes in transverse plane into
two cells
(2) 芽 殖Budding.:A small soft portion of the cell
wall bulges out like a weak zone of the cycle tube,
and a daughter nucleus migrates into it.
(3) 原生质割裂
(4) 其它:
2、无性孢子 (类型图)
(1)游动孢子 zoospores : Spores
formed internally, inside a sac-like structure
called sporangia ,The flagellate spores are
called zoospores 。
(2)孢囊孢子aplanospores. Spores
formed internally, inside a sac-like structure
called sporangia ,he non-flagellate spores
are called aplanospores.
(3)分生孢子Conidia: are borne on
conidiophores, which too may be
characteristically branched and useful in
taxonomy.
(4)厚垣孢子Chlamydospores. These are
thick-walled, resistant spores which are formed
to tide over the adverse environment. These are
formed by formation of thick walls around cells.
Chlamydospores are not detached from the
hyphae. When rest of the hyphae die, these
remain viable.
分生孢子的类型图
三、真菌的有性繁殖
Sexual Reproduction:
1、有性生殖过程和方式:
过程:
质配N+N—核配2N—减数分裂N
方式:
游动孢子配合:
异型配子囊接触交配:
同型配子囊配合:
受精丝作用
体细胞结合
2、真菌有性生殖产生的孢子(类型)
(1)休 眠 孢 子 囊 Resting sporangium: Fusion
between gametes or Planoganetic copulation.
Gametes are naked sex cells, which copulate
to form a zygote.
(2)卵孢子Oospore:The zygote formed by
the fusion between morphologically distinct
gametangia is called a oospore
(3)接合孢子:Zygospore:
Gametangial copulation,fusion between
two similar gametangia results in a
zygote which is called zygospore.
(4)子囊孢子Ascospore:
(5)担孢子Basidiospore
This occours in Asco-- and Basidiomycotina.
Spermatia which are minute, male gametes, are
formed like conidia on spermatiophores. The
spermatium, when comes in contact with the female
gametangium through wind, insects, water sugary
exudates etc., releases the male nucleus into the
female gametangium through a pore.
In some higher Ascomycotina and Basidiomycotina,
sex organs are not formed. The somatic cells, as
such, act as gametangia. Thus somatogamy may
occur between cells of different thalli.
四、真菌的准性生殖
Parasexual reproduction
形成异核,体形成杂合二倍体,
有丝分裂交换与单倍体化
对没有有性生殖的真菌意义很大
Parasexual
reproduction: Some of the
species which exist only as conidial stages
and do not from sex organs. Hyphae of
different strains by anastomosis give rise
to hyphae containing nuclei of different
kinds. Such hyphea are called
heterokaryotic and the process
heterokaryosis. These hyphae derive the
benefit of both nuclei occurs in the
heterokaryotic hyphae.
The diploid nucleus is usually incorporated
in conidia, which on germination, give rise
to diploid thalli.Occasionally during mitotic
divisions ,a peculiar phenomenon- the
‘mitotic crossing over’ occurs which
brings about new genetic recombinations,.
This is the most important phase of
parasexual cycle.
五、真菌分类
1、分类系统
五界系统:(图)
原核生物界、原生生物界、植物界、
菌物界、动物界
八界系统:
真菌界、动物界、胆藻界、绿色植物界、
眼虫动物界、 生动物界、藻物界、
原核生物界
2、Ainsworth的真菌分类系统
菌物界:分为 粘菌门、真菌门
其中真菌门又分为:
鞭毛菌亚门、接合菌亚门、
子囊菌亚门、担子菌亚门、
半知菌亚门
3、几个概念
亚种和变种 var
专化型 f.sp.
生理小种
营养体亲和型