Chapter 2 Reading Guide NOTE: If a True and False question is
advertisement

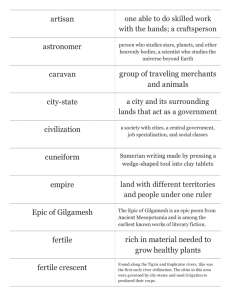
Chapter 2 Reading Guide NOTE: If a True and False question is False, rewrite it on the line below to make it true. Begin on Page 27 THE ART OF THE ANCIENT NEAR EAST 1. Read the clues in the Stele of Naram-Sin that symbolize his religious and political authority. Tell 2 of each: Religious:______________________ Political: _____________________ 2. Which was NOT a major shift in the Ancient Near East that occurred between 4000 and 3000 bce? A. The goddess was the major deity B. Specialized skills beyond agriculture emerged C. Social hierarchies developed D. Cities joined into city-states E. Increased trade with other cultures developed. SUMER 3. Among Sumerian “firsts” were writing, wheels and the plow. Find 2 other Sumerian “firsts” _____________________________________ _________________________________________ 4. In the Epic of Gilgamesh the legendary Sumerian king of Uruk goes on a quest for eternal life but ultimately recognizes that A. The city of Uruk is his lasting accomplishment B. There was a great flood C. He is mortal and must accept it D. The Bible is true E. A and C only 5. In pictographic cuneiform, how would you show a bull eating? Use the square below. 6. Your text describes the Alabaster Vase from Warka that came from the temple of Inanna. What ritual may be depicted here? _________________________________________________________________ Who is dominant in the ritual? _________________________________________________________________ 7. Some conventions of Sumerian sculpture include all EXCEPT A. Arched eyebrows inlaid with dark shell or stone B. Emphasis on the cylindrical shape C. Solemn, respectful poses D. Wide-open eyes for an attentive gaze. E. All of these are conventions 8. The clue to widespread trade on the Sumerian Lyre with Bull’s Head is A. The lapis lazuli in the beard B. The gold leaf on the bull’s head C. The bull motif D. A and B only E. None of these Go to Pg. 34: 9. We can understand that lyres like the one with a Bull’s Head were associated with funerary rites because A. Animals shown are traditional guardians of the gateway of death B. The food may represent a funeral banquet C. We know lyres were used in funerary rites D. Priests and singers sang songs of mourning D. All of these Go to Pg. 32: 10. In what way was or wasn’t the French archaeologist who brought the Stele of Naram-Sin and Law Code of Hammurabi to the Louvre different from the Elamite King of Susa? Write your answer in the class website’s Discussion Forum. AKKAD Go to Pgs. 33 and 36: 11. What is the definition of Semitic? ___________________________________________________ 12. Read the symbolism of these features in the Head of an Akkadian Ruler: A. Enormous curling beard and braided hair _____________________________________________ B. Damage to the left side of the face __________________________________________________ C. Removed ears and eyes __________________________________________________________ 13. Which is an innovation found in the Stele of Naram-Sin? A. First celebration of an achievement by an individual ruler B. Horned helmet to signify he made himself divine C. Hieratic scale D. All of these E. A and B only NEO-SUMERIAN (Ur and Lagash) 14. The Guti who conquered the Akkadians were themselves conquered by King _______________ who reintroduced the Sumerian language and built a ziggurat to the god ___________ or ________. CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE -215. What power centers of the human body are emphasized in the Votive Statue of Gudea of Lagash from the Neo-Sumerian period? A. Head, eyes and hands B. Eyes, head and muscled chest and arms C. Head, hand and heart D. Head, arms and body E.None of these is correct 16. Briefly tell how Gudea’s face is similar to those on the Tel Asmar Votive Figures. ________________________________________________________________________________ BABYLONIAN Go to Pg. 3 17. T F The Stele of Hammurabi is not only an artwork, it is also a historical document recording a conversation about justice between god and man. ________________________________________________________________________________ 18. List 3 things that show Shamash the sun god’s divinity: ________________________ ________________________ ____________________________ 19. T F The Law Code of Hammurabi stele shows Hammurabi’s ground-breaking attempt to create a society based on wealth, class and gender. ________________________________________________________________________________ ASSYRIAN 20. Which would NOT have been a favored subject on Assyrian wall panels? A. Battles B. Tribute to the king C. Religious imagery D. Hunting E. Mythological creation scenes 21. Do research: The Assyrian capital of Assurnasirpal II has been called by different names: Nimrud, Kalhu, and __________________. 22. T F Most of the buildings in Assyrian Nimrud were made from limestone and alabaster because they were more durable. ________________________________________________________________________________ 23. The immediacy of the Lion Hunt scene is created by A. The traditional scene of a hunt B. The register on which the figures are situated C. The emotions of the animals D. The drama of the scene E. C and D only 24. Tell how was Sargon II’s citadel at Khorsabad (Dur Sharrukin) demonstrated art used as political propaganda.___________________________________________________________________ 25. Give 2 clues why the scene of Assurbanipal and his queen in the garden is not a tranquil domestic scene. A. ___________________________ B. ______________________________ NEO-BABYLONIAN 26. Using figure 2-14, Reconstruction drawing of Babylon, locate these: ☐ A. Processional Way ☐ B.Ishtar Gate ☐ C. Hanging Gardens ☐ D. Ziggurat of Marduk 27. Do research: What is the Mushhushshu of Marduk? Find it in Figure 2-15 PERSIAN 28. Persian art is termed “eclectic” because it combined many different cultural traditions. Where did these ideas come from? Put A for Assyrians, E. for Egyptians, G. for Greeks, M. for Mesopotamia _____Persepolis was placed on a raised platform _____Reliefs of animal combat, gift bearers _____Elegant drawing, sleek figures _____Laid out on a rectangular grid 29. Which of the following people put an end to the Achaemenid dynasty and prevented the Persians from entering Europe? A. Neo-Sumerians B. Medes C. Egyptians D. Greeks E. Minoans 30. Go to Pg. 43: Of the various methods for creating textiles discussed in your text, which was not made by spinning, weaving or knitting? ____________________