Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle
advertisement

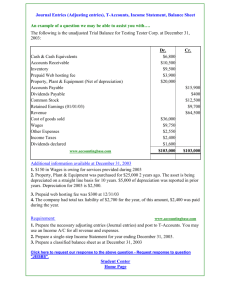
Chapter 4 Completing the Accounting Cycle 高立翰 Study Objectives 1. Prepare a worksheet. 2. Explain the process of closing the books. 3. Describe the content and purpose of a postclosing trial balance. 4. State the required steps in the accounting cycle. 5. Explain the approaches to preparing correcting entries. 6. Identify the sections of a classified statement of financial position. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 2 Completing the Accounting Cycle Using a Worksheet Steps in preparation Preparing financial statements Preparing adjusting entries Closing the Books Preparing closing entries Posting closing entries Preparing a postclosing trial balance Summary of Accounting Cycle Reversing entries—An optional step Correcting entries—An avoidable step 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq Classified Statement of Financial Position Intangible assets Property, plant, and equipment Long-term investments Current assets Equity Non-current liabilities Current liabilities 3 Using A Worksheet (1/2) Worksheet (工作底稿) A multiple-column form used in preparing financial statements. Not a permanent accounting record. Five step process. Use of worksheet is optional. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 4 Using A Worksheet (2/2) Illustration: pp. 149-151 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq Illustration 4-1 5 Steps in Preparing a Worksheet (1/5) 1. Prepare a Trial Balance on the Worksheet Cash Advertising Supplies Prepaid Insurance Office Equipment Notes Payable Accounts Payable Unearned Revenue Share Capital Dividends Service Revenue Trial Balance Dr. Cr. 15,200 2,500 600 5,000 5,000 2,500 1,200 10,000 500 10,000 Salaries Expense Rent Totals 4,000 900 28,700 Account Titles Adjustments Dr. Cr. Adjusted Trial Balance Dr. Cr. Income Statement Dr. Cr. Statement of Financial Position Dr. Cr. 28,700 Trial balance amounts come directly from ledger accounts. Include all accounts with balances. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 6 Steps in Preparing a Worksheet (2/5) 2. Enter the Adjustments in the Adjustments Columns Trial Balance Adjustments Account Titles Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Cash 15,200 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies 2,500 (b) Prepaid Insurance 600 50 Office Equipment 5,000 Notes Payable 5,000 Accounts Payable 2,500 Unearned Revenue 1,200 (d) 400 Share Capital 10,000 Dividends 500 (d) 400 Service Revenue 10,000 (e) 200 (g) Salaries Expense 4,000 1,200 Rent 900 Totals 28,700 28,700 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies Expense (b) Insurance Expense 50 (c) Accumulated Depreciation 40 (c) Depreciation Expense 40 (e) Accounts Receivable 200 (f) Interest Expense 50 (f) Interest Payable 50 (g) Salaries Payable 1,200 Totals 3,440 3,440 Adjusted Trial Balance Dr. Cr. Income Statement Dr. Cr. Statement of Financial Position Dr. Cr. Adjustments Key: (a) Supplies Used. (b) Insurance Expired. (c) Depreciation Expensed. (d) Service Revenue Earned. (e) Service Revenue Accrued. (f) Interest Accrued. (g) Salaries Accrued. Enter adjustment amounts, total adjustments columns, and check for equality. Add additional accounts as needed. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 7 Steps in Preparing a Worksheet (3/5) 3. Complete the Adjusted Trial Balance Columns Trial Balance Adjustments Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Cash 15,200 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies 2,500 (b) Prepaid Insurance 600 50 Office Equipment 5,000 Notes Payable 5,000 Accounts Payable 2,500 Unearned Revenue 1,200 (d) 400 Share Capital 10,000 Dividends 500 (d) 400 Service Revenue 10,000 (e) 200 (g) Salaries Expense 4,000 1,200 Rent 900 Totals 28,700 28,700 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies Expense (b) Insurance Expense 50 (c) Accumulated Depreciation 40 (c) Depreciation Expense 40 (e) 200 Accounts Receivable (f) Interest Expense 50 (f) Interest Payable 50 (g) Salaries Payable 1,200 Totals 3,440 3,440 Account Titles Adjusted Trial Balance Dr. Cr. 15,200 1,000 550 5,000 5,000 2,500 800 10,000 500 10,600 Income Statement Dr. Cr. Statement of Financial Position Dr. Cr. 5,200 900 1,500 50 40 40 200 50 30,190 50 1,200 30,190 Total the adjusted trial balance columns and check for equality. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 8 Steps in Preparing a Worksheet (4/5) 4. Extend Amounts to Financial Statement Columns Trial Balance Adjustments Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Cash 15,200 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies 2,500 (b) Prepaid Insurance 600 50 Office Equipment 5,000 Notes Payable 5,000 Accounts Payable 2,500 Unearned Revenue 1,200 (d) 400 Share Capital 10,000 Dividends 500 (d) 400 Service Revenue 10,000 (e) 200 (g) Salaries Expense 4,000 1,200 Rent 900 Totals 28,700 28,700 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies Expense (b) Insurance Expense 50 (c) Accumulated Depreciation 40 (c) Depreciation Expense 40 (e) 200 Accounts Receivable (f) Interest Expense 50 (f) Interest Payable 50 (g) Salaries Payable 1,200 Totals 3,440 3,440 Account Titles Adjusted Trial Balance Dr. Cr. 15,200 1,000 550 5,000 5,000 2,500 800 10,000 500 10,600 Income Statement Dr. Cr. Statement of Financial Position Dr. Cr. 10,600 5,200 900 5,200 900 1,500 50 1,500 50 40 40 200 50 30,190 40 50 50 1,200 30,190 Extend all revenue and expense account balances to the income statement columns. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 7,740 10,600 9 Steps in Preparing a Worksheet (5/5) 5. Total Columns, Compute Net Income (Loss) Trial Balance Adjustments Account Titles Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Cash 15,200 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies 2,500 (b) Prepaid Insurance 600 50 Office Equipment 5,000 Notes Payable 5,000 Accounts Payable 2,500 Unearned Revenue 1,200 (d) 400 Share Capital 10,000 Dividends 500 (d) 400 Service Revenue 10,000 200 (e) (g) 1,200 Salaries Expense 4,000 Rent 900 Totals 28,700 28,700 (a) 1,500 Advertising Supplies Expense (b) Insurance Expense 50 (c) Accumulated Depreciation 40 (c) Depreciation Expense 40 (e) 200 Accounts Receivable (f) Interest Expense 50 (f) Interest Payable 50 (g) 1,200 Salaries Payable Totals 3,440 3,440 Net income Totals Adjusted Trial Balance Dr. Cr. 15,200 1,000 550 5,000 5,000 2,500 800 10,000 500 10,600 Income Statement Dr. Cr. Statement of Financial Position Dr. Cr. 15,200 1,000 550 5,000 5,000 2,500 800 10,000 500 10,600 5,200 900 5,200 900 1,500 50 1,500 50 40 40 200 50 30,190 Compute Net Income or Net Loss. 40 40 200 50 50 1,200 30,190 7,740 2,860 10,600 10,600 22,450 10,600 22,450 50 1,200 19,590 2,860 22,450 10 Preparing Financial Statements from a Worksheet Worksheet Income statement is prepared from the income statement columns. Statement of financial position and retained earnings statement are prepared from the statement of financial position columns. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 11 Income Statement from a Worksheet Illustration 4-4 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 12 Retained Earnings Statement from a Worksheet Illustration 4-4 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 13 Statement of Financial Position from a Worksheet Illustration 4-4 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 14 Preparing Adjusting Entries from a Worksheet The adjusting entries are prepared from the adjustments columns of the worksheet Journalizing and posting of adjusting entries follows the preparation of financial statements when a worksheet is used Illustration 3-22 General journal showing adjusting entries Adjusting Journal Entries (Chapter 3) 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 15 Closing the Books (1/4) At the end of the accounting period, the company makes the accounts ready for the next period. Temporary (暫時性) and Permanent (永久性) accounts 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 16 Closing the Books (2/4) Closing Entries (結帳分錄) formally recognize, in the general ledger, the transfer of Net Income (or Net Loss), and Dividends to Retained Earnings. Closing entries are only at the end of the annual accounting period Note: Dividends are closed directly to Retained Earnings and not to Income Summary because Dividends are not an expense. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 17 Closing the Books (3/4) Closing entries need to be posted Illustration 4-7 Closing entries journalized 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 18 Closing the Books (4/4) Posting closing entries Illustration 4-8 Posting of closing entries 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 19 Preparing a Post-Closing Trial Balance Purpose is to prove the equality of the permanent account balances after journalizing and posting of closing entries. Illustration 4-9 Temporary accounts will have zero balances. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 20 Summary of the Accounting Cycle Illustration 4-12 1. Analyze business transactions 9. Prepare a post-closing trial balance 2. Journalize the transactions 8. Journalize and post closing entries 3. Post to ledger accounts 7. Prepare financial statements 4. Prepare a trial balance 6. Prepare an adjusted trial balance 5. Journalize and post adjusting entries 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 21 Correcting Entries – An Avoidable Step Correcting Entries (更正分錄) are unnecessary if the records are error-free are made whenever an error is discovered must be posted before closing entries Instead of preparing a correcting entry, it is possible to reverse the incorrect entry and then prepare the correct entry 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 22 Closing Entries – Illustration (1/2) Case 1 On May 10, Mercato Co. journalized and posted a $50 cash collection on account from a customer as a debit to Cash $50 and a credit to Service Revenue $50. The company discovered the error on May 20, when the customer paid the remaining balance in full. Incorrect entry Cash Correct entry Cash Correcting entry 50 Service revenue 50 50 Accounts receivable Service revenue 50 50 Accounts receivable 50 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 23 Closing Entries – Illustration (2/2) Case 2 On May 18, Mercato purchased on account office equipment costing $450. The transaction was journalized and posted as a debit to Delivery Equipment $45 and a credit to Accounts Payable $45. The error was discovered on June 3. Incorrect entry Correct entry Correcting entry Delivery equipment 45 Accounts payable Office equipment 45 450 Accounts payable Office equipment Delivery equipment Accounts payable 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 450 450 45 405 24 The Classified Statement of Financial Position Presents a snapshot at a point in time To improve understanding, companies group similar assets and similar liabilities together Standard Classifications Assets Illustration 4-17 Equity and Liabilities Intangible assets Equity Property, plant, and equipment Non-current liabilities Long-term investments Current liabilities Current assets 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 25 Classified Statement of Financial Position (1/ Intangible Assets (無形資產) Assets that do not have physical substance. – Goodwill (商譽) – Franchises (特許權) – Trademark (商標) 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 26 Classified Statement of Financial Position (2/ Property, Plant, and Equipment (固定資產,PP&E) Long useful lives Currently used in operations Depreciation – allocating the cost of assets to a number of years Accumulated depreciation – total amount of depreciation expensed thus far in the asset’s life 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 27 Classified Statement of Financial Position (3/ Long-term investments (長期投資) Investments in stocks and bonds of other companies Investments in long-term assets such as land or buildings that a company is not currently using in its operating activities 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 28 Classified Statement of Financial Position (4/ Current Assets (流動資產) Assets that a company expects to convert to cash or use up within one year or the operating cycle, whichever is longer Operating cycle is the average time it takes from the purchase of inventory to the collection of cash from customers 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 29 Classified Statement of Financial Position (5/ Equity (權益) Proprietorship - one capital account (Owner’s Equity) Partnership - capital account for each partner Corporation – Share Capital and Retained Earnings 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 30 Classified Statement of Financial Position (6/) Non-current Liabilities (非流動負債) Obligations a company expects to pay after one year. 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 31 Classified Statement of Financial Position (7/) Current Liabilities (流動負債) Obligations the company is to pay within the coming year Usually list notes payable first, followed by accounts payable. Other items follow in order of magnitude Liquidity (流動性) – ability to pay obligations expected to be due within the next year 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 32 Appendix: Reversing Entries Reversing Entries (迴轉分錄) It is often helpful to reverse some of the adjusting entries before recording the regular transactions of the next period Companies make a reversing entry at the beginning of the next accounting period Each reversing entry is the exact opposite of the adjusting entry made in the previous period The use of reversing entries does not change the amounts reported in the financial statements Illustrations: pp.176 會計學(一) http://ppt.cc/mJFq 33