Genetics Practice: Colorblindness & Dimples - High School Biology
advertisement

Biology:
Chapter l4.l
Name
Practic.e Sheet
Period \
Date
l-70-TI
Follow the direaiors on the front of this paper. on the back you have a homework problem.
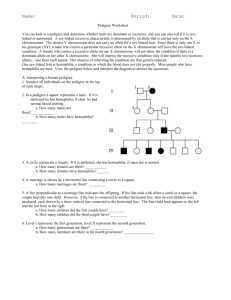
Part I : Colorblindness is a sexlinked trait. Let C represent an allele for normal ^color vision. Let c represent an
The genotype for a female
allele for colorblindness. The genotype for a male with normal color vision is
heterozygous for normal color vision is,ttlf.
Complete the Punnett square to show the genotypes and phenotypes of their possible offspring.
llf
MaleGamete:
Male Gamete:
\E
Genotlpe:
Genotype:
Female Gamete:
xo
Phenoqpe:
\loffnO_t.
lhenotype:
NtrmiQ-\
Genoqpe:
Female Gamete:
Phenotvpe:
\fUO\.fnA_\
C.Crrnt\
'CCiCr
Phenot pe:
-
E\rnd'-
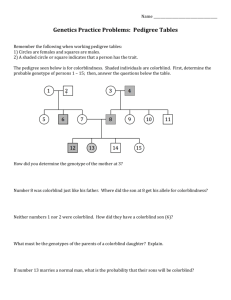
Dimples in the cheeks are inherited as a dominant trait on an autosome. Using the proper form and symbols,
draw a pedigree chart, beginning with a heterozygous, dimpled father (Dd), and a nondimpled mother (dd).
part
2:
,qu"."
f5a&'
n.9. r,"r"r ro*
phenotvpes and genotvpes.
ffifl"fit
I
o-
&
*nnp'6
{Uodlrnpq
drmptA
tD"/o
N
Date
t
- 2b't2
Sex-Linked Dlsorders
The X and Y chromosomes are the sex chromosomes. Females have
two X chromosomes. Males have one X and one Y chromosome.
Because males have only one allele for X-linked genes, the allele is
expressed, even if it is recessive.
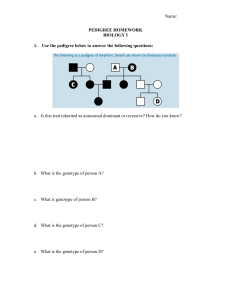
The pedigree below shows the ffipring at' a t'mtale
and a male usho does not suffer from the disorder.
caniu
ot'
€
hemophilia
Use the pedigree to ansu)er the questions.
1, Color each square or circle that indicates an
i
individual who is a
carrier of the hemophilia trait in red.
2. Color each square or circle that indicates an individual who has
hemophilia inblue.
S.
these parents have a daughter with hemophilia?
fou]{
txDlaln.
N)0. -D-od cll,c\n-+ v^\a\/p hov
\\l&
it Ofl
4.
Why are sexlinked diseases more common in males than
\tctvc
@
Peorson fducolion, Inc., publishing os Peorson Preniice
14E
lloll.