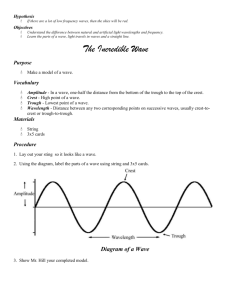
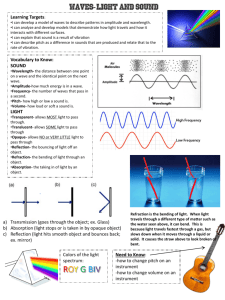
Wave Anatomy
advertisement

Wave Anatomy DO NOW 9.15 • In your own words, define a wave. • Give examples when/how we see waves. • Make connections from the Bill Nye video you watched for homework What is a Wave? A wave is a disturbance that travels through space or matter. What do you notice about the movement of this water? In a wave what is actually "waving"? 1 Wave Anatomy What causes a wave to form? A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels through a medium from one location to another location. Anatomy of a WAVE 2 Wave Anatomy The Anatomy of a Wave Crest (C) is the point of maximum displacement C C C The Anatomy of a Wave The Trough (T) is the point of minimum displacement T T 3 Wave Anatomy The Anatomy of a Wave ­­­­­­­­­ marks the equilibrium/rest position The Anatomy of a Wave Amplitude (y) is the distance away from rest position 4 Wave Anatomy Wavelength Wavelength is defined as the distance it takes a wave to complete one up and down motion or vibration. It can be measured in various places along the wave. Medium What a wave travels through. What are some examples of a medium? • • • • • • Matter Space Water Air Slinky Rope, etc. 5 Wave Anatomy REVIEW Wavelength Label the following wavelengths by dragging the arrow line. From Crest to Crest From Trough to Trough From Starting Point to Ending Point along the Equilibrium Position. 6 Wave Anatomy World Record ­ stadium Wave http://www.cleanvideosearch.com/media/action/yt/watch?videoId=H0K2dvB­7WY Stadium wave Simulation http://interactives.ck12.org/simulations/physics/stadium­wave/app/index.html? referrer=ck12Launcher&backUrl=http://interactives.ck12.org/simulations/ 7