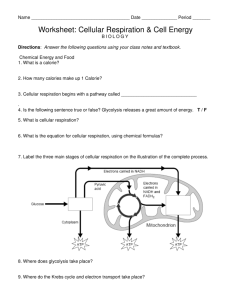
Cellular Respiration - Defiance City Schools
advertisement

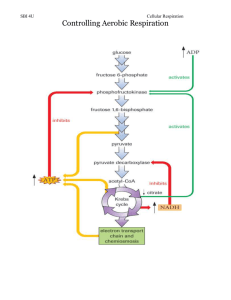
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration • The process of breaking down food molecules to release energy • Plants, algae, animals, and some bacteria use cellular respiration to break down food molecules • The energy released through cellular respiration is used to create ATP • Cellular respiration occurs in three phases: – Glycolysis – Krebs cycle – Electron transport • The process starts with a molecule of glucose • The reactions of cellular respiration occur with the use of enzymes • Respiration is the primary means by which cells obtain useable energy Glycolysis • First phase in cellular respiration • This step occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell, and it can occur whether or not oxygen in present Glycolysis • In this phase, the glucose molecule (a 6-carbon sugar) is broken in half through a series of reactions Glycolysis • The energy released by breaking down the glucose converts into ATP. Glycolysis • Additionally, some high energy electrons are removed from the sugar during glycolysis • These electrons pass on to an electron carrier called NAD+, converting it to NADH. • These electrons will later be used to create more energy • If oxygen is present, the 3-carbon sugars produced from glycolysis enter the mitochondria, along with the oxygen • As the sugars enter the mitochondria, they convert to citric acid in phase two of cellular respiration • The citric acid cycle, or Krebs cycle, is the cyclical process that breaks down the citric acid by a series of reaction Citric acid cycle/Krebs cycle • The citric acid cycle produces more ATP, as well as some GTP (a high-energy molecule similar to ATP). • More high-energy electrons are released, forming NADH from NAD+ • The last phase of cellular respiration is the electron transport chain, which occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane Electron transport chain • In this phase, the NADH releases the highenergy electrons it picked up during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle • The energy from these electrons is used to convert large quantities of ADP into ATP Electron transport chain • The electrons transfer through a series of carrier proteins and they eventually pass on to oxygen, converting it to water • Each electron transfer releases energy Chemosynthesis • The process by which inorganic chemicals are broken down to release energy Chemosynthesis • The only known organisms that are able to carry out chemosynthesis are bacteria Chemosynthesis • These organisms form the base of the food chain around thermal vents found on the ocean floor • These organisms are also found around other aquatic volcanic vents like found around Yellowstone National Park Chemosynthesis • Chemosynthetic bacteria can oxidize sulfates or ammonia to produce two free electrons • The two free electrons are used to fix carbon dioxide into carbohydrates Chemosynthesis • This process is similar to the way that green plants utilize light energy and carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrates • These bacteria are an important part of the nitrogen cycle • Some of these bacteria are well specialized to conditions that would have existed on the early Earth, leading some scientists to hypothesize that these are living representatives of the earliest life on Earth Photosynthesis • • • • • Function: Energy storage Location: Chloroplasts Reactants: CO2 & H2O Products: C6H12O6 & O2 Chemical Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2 Cellular Respiration • • • • • Function: Energy release Location: Mitochondria Reactants: C6H12O6 & O2 Products: CO2 & H2O Chemical Equation: 6O2 + C6H12O6 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O Chemosynthesis • Function: Energy storage • Location: Prokaryotic cells • Reactants: CO2 + H2O + O2 + sulfate or ammonia • Products: carbohydrates & varied acids • Chemical Equation: varies Anaerobic Respiration • Anaerobic respiration, or fermentation is the process by which sugars break down in the absence of oxygen • The process of cellular respiration described earlier is called aerobic respiration, which is the break down of sugar in the presence of oxygen • Our muscle cells, fungi, and some bacteria are capable of carrying out anaerobic respiration • These cells convert the products of glycolysis into either alcohol or lactic acid • Glycolysis releases energy, while the production of alcohol or lactic acid provides NAD+, the electron carrier needed for glycolysis Alcoholic fermentation • Yeast and some bacteria can carry out alcoholic fermentation Alcoholic fermentation • Yeast produce ethanol (C2H6O) through a process called alcoholic fermentation • Carbon dioxide gas is released during alcoholic fermentation Alcoholic fermentation • This carbon dioxide gas is responsible for the holes in bread • Yeast is commonly put in bread to make it rise Alcoholic fermentation • During alcoholic fermentation the yeast produces carbon dioxide, which becomes trapped in the dough, forming small bubbles and causing the bread to rise Alcoholic fermentation • Carbon dioxide produced by yeast in beer gives the beer its bubbles • Other uses of alcoholic fermentation are the making of bread, beer, wine, and liquor Lactic acid fermentation • Animal cells cannot perform alcoholic fermentation • Instead, they produce lactic acid from the products of glycolysis, through the process of lactic acid fermentation Lactic acid fermentation • Human muscle cells produce lactic acid during strenuous exercise • During strenuous exercise, a person cannot take in enough oxygen through breathing to supply all the muscles with the necessary oxygen Lactic acid fermentation • As a result, lactic acid fermentation occurs to supply the muscles with the needed energy Lactic acid fermentation • During and after intense physical activity, muscles are sore due to the presence of lactic acid Lactic acid fermentation • Some bacteria use lactic acid fermentation to obtain food energy Lactic acid fermentation • Bacteria that can convert lactose into lactic acid are used to make yogurt and cheeses • The presence of the lactic acid gives yogurt and some cheese a sour taste