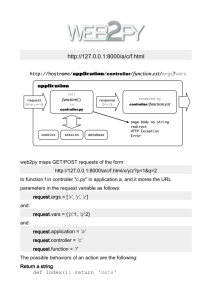
Definition chapter 8
advertisement

Definition chapter 8 1. Economic profit DEF: the amount of money that a firm gets from selling its product minus the money it spent on everything. EX: If a firm’s total revenue is $300 million dollars and it spent about $100 million dollars, in this case, the economic profit is $200 million dollars. Connection: it has connection with the price per unit of output and the quantity it sold. In other words, it has connection with quantity demand and quantity supplied. Test question: when a firm uses its total revenue to subtract its total economic cost, what can the firm get? 2. Economic cost EDF: The things that a firm has to use to produce it goods of inputs. This can be described better to think it as the cost of all the inputs used in the production process. EX: a firm has to use $200 million to produce the total goods. This is the economic cost. Connection: it has connection with economic profit Test question: a firm used $200 million dollars to produce the total goods and it used 50,000 dollars to fix its factory. In this case, what is the economic cost? 3. Explicit cost DEF: the cost that is the actual monetary payments for inputs EX: for instance, monetary payments for labor, capital, materials. Connection: it has connection with implicit cost Test question: the opportunity cost of entrepreneur’s time is one of good examples of explicit cost. Right or wrong? 4. Implicit cost DEF: the cost that is not actually involved a monetary payment. EX: opportunity cost of funds Connection: it has connection with explicit cost Test question: the opportunity cost of entrepreneur’s time is one of good examples of implicit cost. Right or wrong? 5. Accounting cost DEF: the monetary payment of production EX: for instance, monetary payments for labor, capital, materials. Connection: it has connection with explicit cost Test question: according to the accounting cost, does the opportunity cost of entrepreneur’s cost include it? 6. Accounting profit DEF: the total money a firm earns minus the explicit cost EX: if a firm’s total revenue is $200 million dollars and the explicit cost is $100 million dollars, the accounting profit is $100 million dollars Connection: it has connection with explicit cost Test question: a firm’s accounting cost is always lower than its economic cost. Right or wrong. Quantiy of product 7. Marginal product of labor DEF: how much change in what is made from one additional labor. EX: Labor Quantity of output Marginal Product of Labor produced 1 1 1 2 5 4 3 8 3 4 10 2 Connection: it has connection with economic capital, labor capital. Test question: the more labor, the more benefit. Right or wrong? 8. Diminishing returns DEF: when one input increases, the output increases at a decreasing rate. EX: such as the chart in the question 7, the third worker, the production process is subject to diminishing returns. Connection: it has connection with Labor Test question: the reason why the third or fourth labor can cause diminishing return is because they specialize operation. Right or wrong. 9. Total-­‐product curve DEF: a curve that demonstrates the relationship between the number of workers and the quantity of product. EX: Number of Workers Connection: it has connection with marginal product of labor Test question: the total-­‐ product curve shows the relationship between number of workers and the quantity supplied. Right or wrong? 10. Fixed cost DEF: the cost that does not change with the quantity produced EX: workshop such as the mold and the building. Connection: it has connection with explicit cost Test question: does the fixed cost change with the quantity produced? 11. Variable cost DEF: the cost that is changed with the quantity produced EX: to produce more boots, one must hire more workers Connection: it has connection with the labor force Test question: does the variable cost change with the quantity produce? 12. Short-­‐run total cost DEF: the sum of the Fixed cost and Variable cost EX: if the cost of per worker is $40, and the daily variable cost is $50, the short-­‐run cost is $90. Connection: it has connection with fixed cost and variable cost. Test question: if the fixed cost is $10 and the variable cost is $20, what is the short-­‐run total cost? 13 Average fixed cost DEF: Fixed cost divided by how many amount of goods produced. !" EX: AFC= ! Connection: it has connection with fixed cost. Test question: if the Fixed cost is $50, and the quantity of the production is 100. What is the average fixed cost? 14 Average variable cost DEF: Variable cost divided by how many amount of good produced !" EX: AVC= ! Connection: it has connection with variable cost. Test question: if the variable cost is $50 and the quantity produced is 100. What is the average variable cost? 15 Short-­‐run average total cost DEF: the total cost divided by the sum of fixed cost and the variable cost. EX: ATC=AFC+AVC Connection: it has connection with total cost, fixed cost and variable cost. Test question: the short-­‐run total cost is the sum of fixed cost and variable cost. 16. Short-­‐run marginal cost DEF: one unit increase in output will change in shirt-­‐run total cost. EX: suppose a firm produced one unit of production with one worker with $100, if it hires one more workers with $100 the total production is 6. Therefore the short-­‐run marginal cost is 100/5=20 Connection: it has connection with marginal cost and the total cost. ∆!" Test question: the short-­‐run marginal cost can be seen as MC= ∆! ? right or wrong 17. long-­‐run total cost DEF: the long-­‐run total cost is the total cost of the amount of good it produced as the firm can perfectly choose its inputs. EX: Connection: it has connection the total cost Test question: if one’s form doubles its output from 20 paddles to 30 paddles, the long-­‐run average cost doubles too. 18. long-­‐run average cost DEF: the long-­‐run cost divided by how many amounts of goods produced. EX:LAC= !" ! . Connection: it has connection with long-­‐run total cost Test question: the long-­‐run average cost, the line’s slope is relative horizontal. Right or wrong? 19. Constant returns to scale DEF: when the fraction of long-­‐run total cost increases over output has a certain relationship, therefore average cost is constant. EX: Labor Output Long-­‐run average cost 4 10 30 8 20 30 12 30 30 Connection: it has connection with long-­‐run total cost and labor and output Test question: in the constant returns to scale, the fraction of long-­‐run total cost over output will be al ways the same no matter the change in each of them. Right or wrong. 20. long-­‐run marginal cost DEF: on unit increase in output will change in long-­‐run cost. EX: the firm increases the cost and the firm can change its production facility as well as its workforce, labor. Connection: it has connection with capitals. Test question: when a firm changes its workforce and the facilities, will it increase the cost? 21. Indivisible input DEF: an input which can not be counted as a way to produce output. EX: such as mold. Connection: it has connection with capitals. Test question: according to the definition of the indivisible input, does it include into the necessary way to give output? 22. Economies of scale DEF: when the long-­‐run average cost of production decreases as output increase. EX: the curve below shows a good example of it, the point between a and b. Connection: it has connection with long-­‐run average cost. Test question: according to the graph below, which part shows the economies of scale? 23. Minimum efficient scale DEF: the situation when the quantity of output stay the same EX: the picture below shows a good example of minimum efficient scale, between the point b and c Connection: it has connection with economiew of scale and the output. Test question: according to the graph below which part best shows the minimum efficient scale? 24. diseconomies of scale DEF: the increase in output will increase the average cost. They have a positive relationship. EX: for instance, when a firm increases the boots output, it will demand more of each of its materials and labor force and may be forced to pay higher prices for some of these inputs. Connection: it has connection with demand and supply. Test question: according to diseconomies of scale, the relationship between output and the average cost is positive. Right or wrong?