Extension Inheritance Notes Simple Dominance = Dominant alleles
advertisement

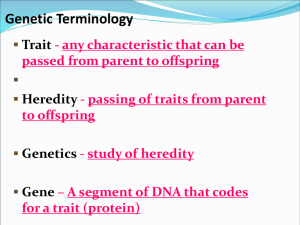
Extension Inheritance Notes Simple Dominance = Dominant alleles mask recessive alleles Codominance = Neither allele is dominant or recessive. Both traits are expressed in the offspring. Example: Chickens with both black and white feathers. Incomplete Dominance = The dominant allele does not completely mask the recessive allele. The recessive allele is also partly expressed. Example: A red snapdragon plant (dominant) crossed with a white plant (recessive) will give offspring with pink flowers. Sex-Linked Traits = A sex-linked trait is a trait located on a sex chromosome, like a X or a Y. Example: The gene for color-blindness is only on the Xchromosome (Xc). Because of this, boys can be only color-blind (XcY) or normal (XY). Girls can be color-blind (XcXc), carriers (XcX), or normal (XX). If the mother is color-blind, all her boys will be color-blind. Carrier = A person who has one gene for the trait, and one gene that’s “normal.” The carrier is unaffected by the trait, and may not know that they’re a carrier of the trait. Example: Sickle cell anemia.