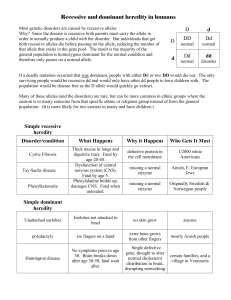
AP Biology Name___________________ Genetics Problems 4 In
advertisement

AP Biology Name___________________ Genetics Problems 4 1. In tigers, a recessive allele causes an absence of fur pigmentation (a white tiger), and a cross-eyed condition. If two phenotypically normal tigers that are heterozygous at this locus are mated, what percentage of their offspring will be cross-eyed? What percentage will be white? 2. In maize (corn) plants, a dominant allele I inhibits kernel color, while the recessive allele i permits color when homozygous. At a different locus, the dominant allele P causes purple kernel color, while the homozygous recessive genotype pp causes red kernels. If plants heterozygous at both loci are crossed, what will be the phenotypic ratio of the offspring? 3. A man has 6 fingers on each and 6 toes on each foot. His wife and their daughter have the normal number of digits. Extra digits is a dominant trait. What fraction of this couple’s children would be expected to have extra digits? 4. In mice, black color (B) is dominant to white (b). At a different locus, a dominant allele (A) produces a band of yellow just below the tip of each hair in mice with black fur. This gives a frosted appearance known as agouti. Expression of the recessive allele (a) results in a solid coat color. If mice that are heterozygous at both loci are crossed, what is the expected phenotypic ratio of their offspring? 5. A man with hemophilia ( a recessive, sex-linked condition) has a daughter of normal phenotype. She marries a man who is normal for the trait. What is the probability that a daughter of this mating will be a hemophiliac? That a son will be a hemophiliac? If the couple has four sons, what is the probability that all four will be born with hemophilia? 6. Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy is an inherited disorder that causes gradual deterioration of the muscles. It is seen almost exclusively in boys born to apparently normal parents and usually results in death in the early teens. Is this disorder caused by a dominant or recessive allele? Is its inheritance sex-linked or autosomal? How do you know? Explain why this disorder is almost never seen in girls. 7. Red-green color blindness is caused by a sex-linked recessive allele. A color-blind man marries a woman with normal vision whose father was color-blind. What is the probability that they will have a color-blind daughter? What is the probability that their first son will be color-blind? (note the different wording in the two questions) 8. A wild-type fruit fly (heterozygous for gray body color and normal wings) is mated with a black fly with vestigial wings. The offspring have the following phenotypic distribution: wild type, 778; black-vestigial 785; black-normal 158; gray-vestigial 162. What is the recombination frequency between these genes for body color and wing size?