Cell Reproduction Answer Key: Mitosis, Meiosis, DNA
advertisement
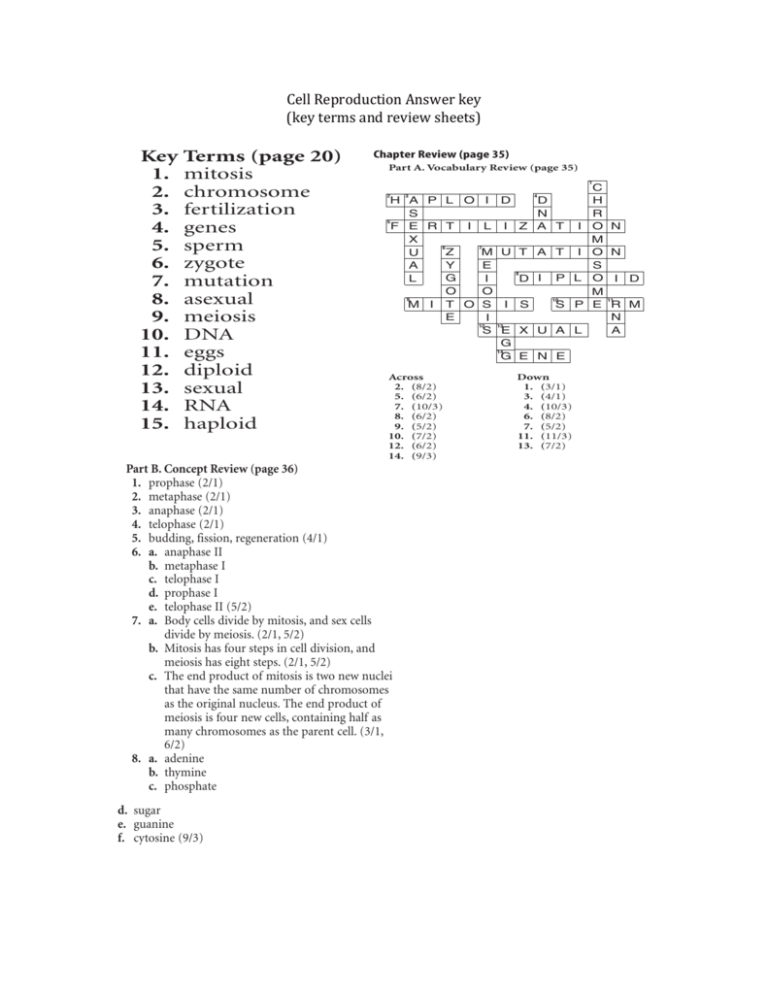
Teacher Support & Pl 1 2 3 4 5 7 6 1 8 2 3 4 5 9 10 11 6 12 7 13 8 9 10 11 14 12 13 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 14 10. (7/2) 11. (11/3) 12. (6/2) 13. (7/2) Section 2 (page 29) 12. (6/2) 13. (7/2) during meiosis is Each sperm egg that is produced during meiosis is 14.or (9/3) 14. (9/3) on has been unique because the genetic information has been Part B. Concept Review (page 36) Part B. Concept Review 36) traded between chromosomes early(page in meiosis. n meiosis. 1. prophase (2/1) Section 3 (page 30) 1.Sinopsis prophase (2/1) (pág. 21) 2. metaphase (2/1) 1. Radiation2.has very high-energy metaphase (2/1) waves and can 3. anaphase (2/1) break up DNA. 1. telofase aves and can 4. telophase (2/1) 3. anaphase (2/1)breaks up the skin cells’ 2. The ultra-violet radiation 5. budding, fission, regeneration (4/1) DNA. The DNA molecules don’t repair properly, 2. profase 4. telophase (2/1) 6. a. anaphase II up the skin cells’ and the cell can reproduce with a mutation. b. metaphase I 5. budding, fission, genetic regeneration (4/1) 3. metafase 3. The first way radon destroys information epair properly, is by breaking c. telophase I the DNA 6. a. up anaphase II with high energy d. prophase I mutation. waves. TheFases second way is by the emission of large detear mitosis b. metaphase Ilaup e. telophase II (5/2) alpha cells that physically the cell. ic information 7. a. Body cells divide by mitosis, and sex cells c. telophase I 4. X rays can 4. damage a growing baby. Exposure to telofase divide by meiosis. (2/1, 5/2) igh energy high-energy d. waves of growing cells in the baby’s prophase I b. Mitosis has four steps in cell division, and mission of large body may 5. causeprofase damage and health problems. meiosis has eight steps. (2/1, 5/2) e. telophase II (5/2) he cell. c. The end product of mitosis is two new nuclei metafase Note-Taking Worksheet (page 31) 7.6. a. Body cells divide by mitosis, and sex cells that have the same number of chromosomes y. Exposure to Refer to Teacher Outline, student answers are underby meiosis. (2/1, 5/2) as the original nucleus. The end product of 7. divide anafase s in the baby’s lined. meiosis is four new cells, containing half as b. Mitosis has four steps in cell division, and many chromosomes as the parent cell. (3/1, h problems. 8. meiosis interfase has eight steps. (2/1, 5/2) 6/2) c. The end product of mitosis is two new nuclei 8. a. adenine b. thymine that have the same number of chromosomes c. phosphate wers are underasCell the original nucleus. The end product of Reproduction Cell Reproduction T11 meiosis is four new cells, containing half as many chromosomes as the parent cell. (3/1, 6/2) 8. a. adenine thymine Teacherb.c.Guide & Answers (continued) phosphate Lectura dirigida para Dominio del contenido (pág. 21) T10 Teacher Support & Planning d. sugar e. guanine f. cytosine (9/3) Cell Reproduction Chapter Test (page 37) I. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Testing Concepts (page 37) l (8/2) m (8/2) e (8/2) k (11/3) b (1/1) i (2/1) h (5/2) T11 III. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Applying Concepts (page 40) b (1/1) a (5/2) a (6/2) a, b (3/1, 5/2) a (5/2) b (2/1) sugar phosphate adenine guanine cytosine thymine Teacher Support & Planning Assessment number of the parent. chromosome Section (page 19) Chapter Review (page335) Note: The left-side molecule should be circled. Part A. Vocabulary Review (page 35) G: cytosine; A: 1. The three bases on the tRNA were matched with C the mRNA to which they would the three bases on fic proteins. e L O I D H D Cell Reproduction H A P attach. Answer key & Answers (continued) nd it is single-Teacher Guide N (key R S No, the base 2. pairs would notsheets) be complementary. A terms and review 9. They contain only half the chromosomes. I O N R Z A I I T E T F L Assessment will only attach to U, and C will to m the nucleus 10. Two sex cells join only attach G. to form a zygote. M X27) Section 3 (page Chapter Review (page 35) Key (page 20) T:A;Terms C:G s the code from1. T:A; G:C; A:T; Part A. Vocabulary Review (page 35) A T I A:O N Z T: adenine; M U T 2. A: uracil; C:U guanine; G: cytosine; 1. mitosis re ribosomal uracil. A the making Eof specific proteins. S C 3. A gene directs o acids. Transfer 2. Ychromosome 4. deoxyribose (sugar) and phosphate H D H A P L O I D I P L ids in the cyto-5. It has uracilLinsteadGof thymine, O I D D I and it is single3. fertilization N R S bosomes. stranded. O proteins O from the nucleusM F E R T I L I Z A T I O N code for genes s can result in 6. It carries the 4. to the ribosomes. M X I O S I S M P E R M S T ll receiving an 7. Messenger RNA, 5. orsperm mRNA, carries the code from Z M U T A T I O N U the nucleus to the cytoplasm. N E I There ribosomal zygote A S Y E RNA (rRNA)6. attaches to the amino acids. Transfer S X U A L E I P L RNA, or tRNA, picks up amino acids in the cyto- A O G I D D L I 7. mutation plasm and brings them to these ribosomes. O O M G 8. X rays, sunlight, toxic chemicals can result in 8. or asexual M I T O S I S S P E R M errors in copying a gene or in a cell receiving an G E N E N E I extra chromosome. n the single9. meiosis S E X U A L A 10. Enrichment (page 28) DNA Across Down G Section 1 (page 28) eggs 2.11. (8/2) (3/1) G E N E 1. No. The Eukaryotic cell is found in1.the single5.12. (6/2) diploid 3. (4/1) celled foram. Across Down 2. amoebas 7. (10/3) 4. (10/3) 2. (8/2) 1. (3/1) 3. It has a shell 13. sexual 5. (6/2) 3. (4/1) (6/2) 6. (8/2) of a dime exually, it will 4. about the8.size 7. (10/3) 4. (10/3) 5. by mitosis 9.14. (5/2) RNA 7. (5/2) 8. (6/2) 6. (8/2) 6. No. Since the foram reproduces asexually, it will 10.15. (7/2) haploid11. (11/3) 9. (5/2) 7. (5/2) be identical to the parent. te. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Reinfo Sec 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Sec 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.







