Mitosis & Meiosis Study Guide: Cell Division Explained
advertisement

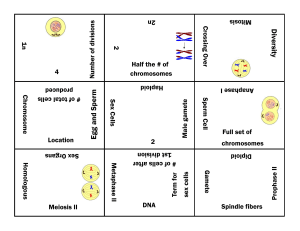
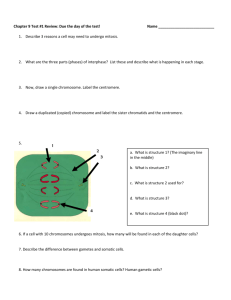
Chapter 8: Mitosis & Meiosis Study Guide Chapter 8: Mitosis & Meiosis Study Guide How does DNA become more compact? Why? What is a centromere? How many chromosomes and chromosomal pairs are in a human cell? o How many are autosomes, how many are sex chromosomes? What is the purpose of autosomes? What is the purpose of sex chromosomes? Describe what diploid and haploid mean. o If the diploid number is 46, what is the haploid number? o If the haploid number is 8, how many chromosomes does the body cell have? o If a body cell contains 12 chromosomes, how many does the gamete have? Describe the following stages: o G1, S, G2 Describe and draw a picture of Interphase. Describe and draw pictures of each of the following Meiotic phases: o Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I Describe and draw pictures of each of the following Meiotic phases: o Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II Describe and draw pictures of each of the following Mitotic phases: o Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase What is the correct sequence of the cell cycle? What does synthesis mean? With respect to mitosis, the daughter cells compare how to the parent cell and to each other? With respect to meiosis, the daughter cells compare how to the parent cell and to each other? What is the difference between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis? What is crossing-over, and when does it occur? What is a karyotype? What is a chromatid made from? What is the result of spermatogenesis and oogenesis? What is a tightly packed and coiled DNA structures called? What are histones? What phase is DNA copied? What is the cleavage furrow and during what phase is it visible? The diploid phase of the human life cycle begins with… XX represents what gender? XY represents what gender?