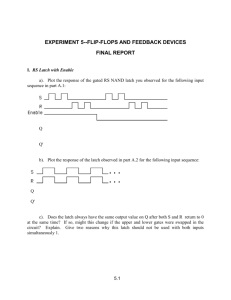
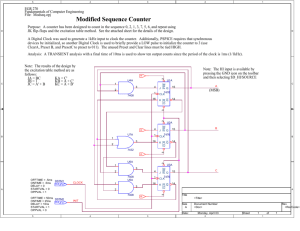
Types of Flip-Flops Flip
advertisement

EE241 Types of Flip-Flops Latch Pair (Master-Slave) L1 Data Pulse-Triggered Latch L2 D Q D Q Clk Clk L Data Clk D Q Clk Clk UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic Flip-Flop Delay l l Sum of setup time and Clk-output delay is the only true measure of the performance with respect to the system speed T = TClk-Q + TLogic + Tsetup+ Tskew D Q Logic D Q N Clk TClk-Q UC Berkeley EE241 Clk TLogic TSetup B. Nikolic 1 EE241 Delay vs. Setup/Hold Times 350 300 Minimum Data-Output Clk-Output [ps] 250 200 150 Setup Hold 100 50 0 -200 -150 -100 -50 0 50 100 150 200 Data-Clk [ps] UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic Master-Slave Latches Positive setup times l Two clock phases: l » distributed globally » generated locally Small penalty in delay for incorporating MUX l Some circuit tricks needed to reduce the overall delay l UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 2 EE241 Master-Slave Latches Case 1: PowerPC 603 (Gerosa, JSSC 12/94) Vdd Clk Vdd Clkb Q D Clkb Clk UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic T-G Master-Slave Latch Feedback added for static operation Unbuffered input input capacitance depends on the phase of the clock over-shoot and under-shoot with long routes wirelength must be restricted at the input Clock load is high Low power Small clk-output delay, but positive setup UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 3 EE241 Master-Slave Latches Vdd Vdd Case 2: C2MOS Ck Ckb Ckb Ck D Vdd Q Vdd Clk Vdd Ck Feedback added for static operation Locally generated clock Poor driving capability Robustness to clock slope Vdd Vdd Vdd Ckb Ck Ck Ckb UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic Pulse-Triggered Latches First stage is a pulse generator generates a pulse (glitch) on a rising edge of the clock Second stage is a latch captures the pulse generated in the first stage Pulse generation results in a negative setup time Frequently exhibit a soft edge property Note: power is always consumed in the pulse generator UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 4 EE241 Pulse-Triggered Latches Case 1: Hybrid Latch Flip-Flop, AMD K-6 Partovi, ISSCC’96 Vdd Q Q D Clk UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic HLFF Operation 1-0 and 0-1 transitions at the input with 0ps setup time UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 5 EE241 Hybrid Latch Flip-Flop Flip-flops features: single phase clock edge triggered, on one clock edge Latch features: Soft clock edge property brief transparency, equal to 3 inverter delays negative setup time allows slack passing absorbs skew Hold time is comparable to HLFF delay minimum delay between flip-flops must be controlled Fully static Possible to incorporate logic UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic Soft Edge Property Also known as cycle borrowing, or slack passing In latch based designs, if longest path datum reaches latch before its setup time, clock skew does not affect cycle time If longest path reaches latch close to setup time, clock skew is directly subtracted from cycle time Flip-flop presents a ‘hard’ edge - no slack passing. HLFF is a compromise - has a controlled transparency period, that can absorb skew Price is paid in the hold time UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 6 EE241 Hybrid Latch Flip-Flop Skew absorption UC Berkeley EE241 Partovi et al, ISSCC’96 B. Nikolic Pulse-Triggered Latches Case 2: AMD K-7 UC Berkeley EE241 Courtesy of IEEE Press, New York. 2000 B. Nikolic 7 EE241 Pulse-Triggered Latches Case 3: Semi-Dynamic Flip-Flop (SDFF), Sun UltraSparc III, Klass, VLSI Circuits’98 Vdd Vdd Q Q D Clk Pulse generator is dynamic, cross-coupled latch is added for robustness. Loses soft edge on rising transition Latch has one transistor less in stack - faster than HLFF, but 1-1 glitch exists Small penalty for adding logic UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic Pulse-Triggered Latches Case 3: 7474, Texas Instruments’64 S Q Clk Q R D UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 8 EE241 7474 Karnaugh maps for signals S and R SR SR R 00 01 11 10 00 x 1 1 1 01 x 1 1 1 Clk, D Clk D 11 x 1 1 0 10 x 1 0 0 R 00 01 11 10 00 x 1 1 1 01 x 1 1 1 11 x 0 0 1 10 x 0 1 1 Clk, D Clk D Clk Clk R S DR S DS S D S = Clk ⋅ R ⋅ D ⋅ S R = Clk ⋅ S ⋅ D ⋅ R S Q Clk Q R UC Berkeley EE241 D B. Nikolic Pulse-Triggered Latches Case 4: Sense-amplifier-based flip-flop, Matsui 1992. DEC Alpha 21264, StrongARM 110 First stage is a sense amplifier, precharged to high, when Clk = 0 After rising edge of the clock sense amplifier generates the pulse on S or R The pulse is captured in S-R latch Cross-coupled NAND has different propagation delays of rising and falling edges UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 9 EE241 Sense Amplifier-Based Flip-Flop Courtesy of IEEE Press, New York. 2000 UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic Flip-Flop Performance Comparison Test bench Data D Q 200fF Total power consumed Clk Q internal power Clock 200fF data power 50fF clock power Measured for four cases no activity (0000… and 1111…) Delay is (minimum D-Q) maximum activity (0101010..) average activity (random sequence) Clk-Q + setup time Stojanovic, Oklobdzija JSSC 4/99 UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 10 EE241 Flip-Flop Performance Comparison Delay vs. power comparison of different flip-flops Flip-flops are optimized for speed with output transistor sizes limited to 7.5µm/4.3 µm Total transistor gate width is indicated Total power [uW] 70 60 TG M-S 52µm Original SAFF 60µm 50 HLFF 54µm 40 30 2 mSAFF 64µm SDFF 49 µm 20 C MOS 80µm 10 0 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 Delay [ps] UC Berkeley EE241 500 B. Nikolic Energy Consumption Energy Breakup in TG-MS (PowerPC603) • Always consume q Clocked Nodes 8% External Load 54% 42fJ ECLK = E0-0 = E1-1 • When Q : 1-0 or 0-1 6fJ q Eint = E1-0 – E0-0 • Only when Q : 0-1 q Internal Nodes 29fJ Eext = E0-1 – E1-0 • Non-inverting Flops: 38% q Eavg = ECLK + α Eext + (1- α) Eint • • • Inverting Flops: q Eavg = ECLK + (1-α) Eext + α Eint • • (α - probability of D : 0-1) UC Berkeley EE241 [Markovic] B. Nikolic 11 EE241 Energy Dissipation Comparison of Master Slave and Pulse-Triggered Flip-Flops 250 0--0 0--1 1--0 1--1 Energy [fJ] 200 198 183 150 114 114 101 102 100 103 94 85 64 59 42 50 31 30 23 14 57 36 23 14 0 TG FF C2MOS HLFF SDFF SAFF Resized for Energy/Delay UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic Local Clock Gating 2 Q CKI 0.85 D 1.2 0.85 DI 0.5 0.85 0.5 0.5 CKIB CKIB 0.5 0.5 Data-Transition Look-Ahead Pulse Generator 0.85 0.5 0.85 0.5 XNOR CKIB 0.85 ‘Clock on demand’ Flip-flop CKI CP 0.5 UC Berkeley EE241 B. Nikolic 12