Web Development Module Study Guide
advertisement
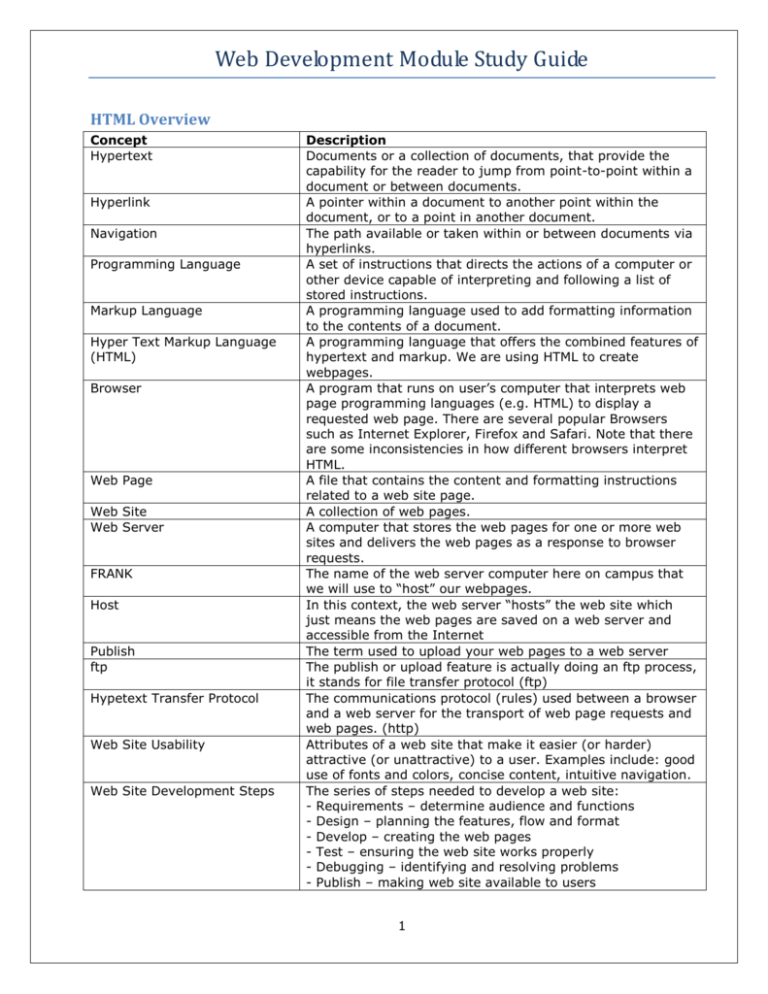
Web Development Module Study Guide HTML Overview Concept Hypertext Hyperlink Navigation Programming Language Markup Language Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) Browser Web Page Web Site Web Server FRANK Host Publish ftp Hypetext Transfer Protocol Web Site Usability Web Site Development Steps Description Documents or a collection of documents, that provide the capability for the reader to jump from point-to-point within a document or between documents. A pointer within a document to another point within the document, or to a point in another document. The path available or taken within or between documents via hyperlinks. A set of instructions that directs the actions of a computer or other device capable of interpreting and following a list of stored instructions. A programming language used to add formatting information to the contents of a document. A programming language that offers the combined features of hypertext and markup. We are using HTML to create webpages. A program that runs on user’s computer that interprets web page programming languages (e.g. HTML) to display a requested web page. There are several popular Browsers such as Internet Explorer, Firefox and Safari. Note that there are some inconsistencies in how different browsers interpret HTML. A file that contains the content and formatting instructions related to a web site page. A collection of web pages. A computer that stores the web pages for one or more web sites and delivers the web pages as a response to browser requests. The name of the web server computer here on campus that we will use to ―host‖ our webpages. In this context, the web server ―hosts‖ the web site which just means the web pages are saved on a web server and accessible from the Internet The term used to upload your web pages to a web server The publish or upload feature is actually doing an ftp process, it stands for file transfer protocol (ftp) The communications protocol (rules) used between a browser and a web server for the transport of web page requests and web pages. (http) Attributes of a web site that make it easier (or harder) attractive (or unattractive) to a user. Examples include: good use of fonts and colors, concise content, intuitive navigation. The series of steps needed to develop a web site: - Requirements – determine audience and functions - Design – planning the features, flow and format - Develop – creating the web pages - Test – ensuring the web site works properly - Debugging – identifying and resolving problems - Publish – making web site available to users 1 Web Development Module Study Guide Cascading Style Sheet Javascript Another programming language for enhancing web pages/sites. It allows for the formatting of the pages to be separated from the content of the pages. A programming language that provides the ability to add more dynamic/interactive contents to web pages. Examples are pop-up windows, or forms that prompt users. Hypertext Markup Language - HTML Concept HTML File Basic Page Tags Tags Attributes Error Checking Basic HTML Commands – Know what the results of these tags will look like in the browser program Know the structure of html to do the following Lists Description HTML statements are stored in a file of file type .html. Every page should have the following tags to define the page: <html> <head> <title> </title> </head> <body> page contents go here </body> </html> HTML commands delimited by < and > used to inform the browser how to render the following content. E.g. <p> indicates following text is the beginning of a new paragraph. Some Tag actions are terminated with and End Tag delimiter </tag_type>. E.g. </p> indicates the end of a paragraph. Attributes are used with certain tags to add additional formatting information. The general format is <tag_type attr1=‖ ―>. Single (‘) or double (“) quotes are acceptable. E.g. <font color=‖blue‖> Few errors in HTML web page coding result in an error message. In general, a browser will ignore errors skipping the tag, or a portion of a tag that contains an error. As such it is up to the developer to verify that everything they expect to occur is occurring. <p> <br> <b> <u> <i> <h1> <h6> <marquee> <center> <hr> <!—comments--> Insert a picture Put a hyperlink to another webpage Change background color as a part of html <body> tag Change text color as part of html <font> tag Insert a list Insert a table Know the difference between <ul> unordered lists versus <ol> ordered lists 2 Web Development Module Study Guide Cascading Style Sheets - CSS Concept Style Sheet Properties Span Element Class Selector Div Element (actually a XHTML specification) Description A style sheet is a set of page formatting instructions, like HTML. Style sheet commands can be located in the <head> section of a web page, or as a separate file (.css) called and External Style Sheet. CSS provides greater control of page content formatting. Using External Style Sheets developer(s) can more easily control cross page format consistency. CSS Properties serve the same function as Attributes in HTML. The Span feature of CSS allows limiting the scope of formatting within a web page. Is another method of providing more specific formatting within a web page. The <div> element allows for the designations of sections on a web page and the control of formatting within the section. Typical sections are navigation tab, header, body and footer. The Div element allows specification of different formats for each web page section. CSS Syntax A CSS rule has two main parts: a selector, and one or more declarations: The selector is normally the HTML element you want to style. Each declaration consists of a property and a value. The property is the style attribute you want to change. Each property has a value. 3











