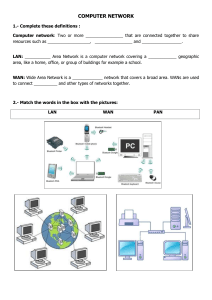
A local area network, wide area network, and worldwide
advertisement

A local area network, wide area network, and worldwide network are all computer networks, which are comprised of a group of computers connected to each other for the purposes of communication and the sharing of data. A local area network, LAN, is a computer networking system covering a small geographic location, such as a home, office, or school. The computers on this network are connected through Ethernet or wireless systems. A wide area network, WAN, is a computer network that covers a broad geographic area, such as a region or nation. A wide area network uses routers and public communication lines, such as phone carriers, to communicate and transfer data. The largest form of a wide area network is the Internet. Compared to a wide area network, a local area network has a faster rate of data transfer, because of the smaller proximity, and has no need for telecommunication lines. Lastly, a worldwide network is a global network, expanding across the globe. Communication occurs across various transmission facilities and phone carriers. The largest worldwide network is the worldwide web. Works Cited: Introduction to network types. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://compnetworking.about.com/od/basicnetworkingconcepts/a/network_types. htm