Chapter 15: Kinetics
advertisement

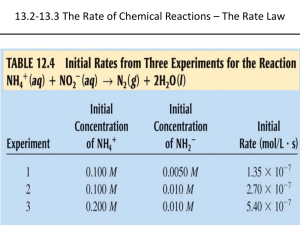
Chapter 15: Kinetics 15,1 Photochemical Smog 15.2 Reaction Rates. Express as rate of consumption of reactant, or rate of production of product. The time rate of change of concentration. CONCENTRATION vs TIME CURVES 1 Relative Rates of Reaction. How reactant disappearance rates and product appearance rates relate to each other. N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) From Relative Rates to Actual Rates. 2 Average Rates of Reaction. Rate over a defined interval 3 Instantaneous Rate of reaction. Rate at a single specific time point during the reaction Book example pages 709-710 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) Different instantaneous rates. The initial instantaneous rate is important. 4 15.3 Effect of Concentration on Reaction Rates. Reactions occur via collisions. Rate Law expresses the concentration dependence of the reaction rate 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) Eq 15.2 General rate law from inspection of the reaction. Reaction Order and Rate Constant How to experimentally determine reaction orders and rate laws. Determining the specific form of the rate law means we must--Determine the Reaction Order(s) of each reactant or product (usually reactants). The ratio method or graphical (integrated rate law) methods are ways of doing this. The Ratio Method uses concentrations of reactants and reaction initial rates. Example: Data 1. Reaction: A → B 5 Data 2. Data 3. 6 Additional Examples: Data 4. This reaction at 400 °C. Example Data 5. CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → HCl(g) + CCl4(g) 7 INTEGRATED RATE LAWS (0th, 1st, 2nd ORDER) First-Order Reactions O3(g) → O2(g) + O(g) General Rate Law: Integrated Firstt-Order rate equation. Graph of data plotted according to the integrated 1st order rate equation. 8 Reaction Half-Lives The half-life of a reaction (t1/2) is the time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to decrease to one-half its original concentration. The concept of half-life derives directly from the integrated form of the rate law. For First-Order reaction: 9 Second-Order Reactions Concentration vs time curve General Rate Law: Integrated Second-Order rate equation. 10 Pseudo-First-Order Reactions. The integrated Second-Order rate equation in the form: works only in one circumstance, when both reactants are identical: The integrated form of a 2nd-order reaction like, NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g), is more complex and beyond the scope of this class. Kineticists simplify these second order reactions into pseudo-1st-order reactions. General Rate Law for NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g): Simplification to pseudo-1st-order: Treat as first-order. Pseudo-1st-order rate constant: 2nd-order rate constant: Example problem 15.9 done in a rational, normal way. Modified Table 15.12, a & b, pages 725 and 726. Time, μsec 0 100 200 300 400 500 1000 [NO], M 1.661 x 10-12 1.389 x 10-12 1,159 x 10-12 9.684 x 10-13 8.0897 x 10-13 6.7614 x 10-13 2.7413 x 10-13 Ln[NO] -27.124 -27.302 -27.483 -27.663 -27.843 -28.022 -28.925 11 Zero-Order Reactions (oth-order) A → B Rate Law: Integrated rate law: 15.4 Reaction Rates, Temperature and the Arrhenius Equation Energy flows during a chemical reaction. It takes energy to break bonds, wherease bond-making releases energy. Charting the energy flow during a reaction takes the form the Fig. 15.6a (Energy Profile). A prominent feature is the Activation Energy, Ea. NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) Hypothetical Energy Profile illustrating general features Kinetic-Molecular Energy: molecular kinetic energy distribution is temperature dependent. # collisions increase with temperature => Rate of Reaction increases with temp. 12 Which lead to the Arrhenius Equation: -Ea/RT (rate constant): k = Ae Energy Profile specific to the reaction NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g). 13 Energy Profile specific to the reaction NO2(g) + O2(g) → NO(g) + O3(g). Manifestations and uses of the Arrhenius Equation. Temperature dependence of the rate constant. 14 15.5 Reaction Mechanisms Every chemical reaction can be written as a molecular-level mechanism that consists of simple, one-event atomic rearrangements. A reaction mechanism is a series of these elementary reaction steps that show the details of bond breaking and bond making during the course of a reaction. A complete mechanism starts with reactants and ends with products. The sum of the elementary steps must equal the overall reaction. The elementary steps may include chemical intermediates, which are typically shortlived. Chemical intermediates are produced in one elementary step and consumed in a subsequent elementary step. Illustration for the Complete Reaction: Which is composed of two Elementary Steps: 15 Combined with the reaction’s Energy Profile: Omit section: “Rate Laws and Reaction Mechanisms”. 16 15.6 Catalysis Catalysts are used to speed-up reactions by lowering the activation energy (Ea). This is illustrated by the chlorine-catalyzed decomposition of ozone (O3) In this case Cl atoms are HOMOGENEOUS catalysts. This reaction is a primary cause of atmospheric ozone depletion. Atomic chlorine is produced by the decomposition of chloro-fluorocarbons in the upper atmosphere. 17 In automobiles catalytic converters catalyze the following reaction: 2NO(g) → N2(g) + O2(g) Catalytic Converters are an example of a HETEROGENOUS catalyst. End Ch. 15. 18







![1 [A]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009563931_1-7a369d18638f75aaafb200fb61a0b929-300x300.png)

