Power Generation Green Project Mainly Using Woody Biomass
advertisement

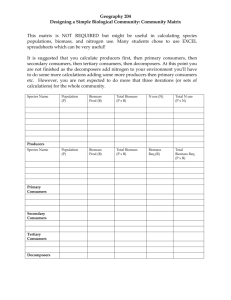
Power Generation Green Project Mainly Using Woody Biomass Hirohisa Shima, Technical Advisor ICETT 1. Background ★ ★ ★ Curtailment of CO2 emission by energy produced from woody biomass Kyoto Protocol (enforced in Feb.2005): ▲6% compared with the emission level in 1990 (Japan) Small incinerators have difficulties in incinerating wood chips. Enforced the Law Concerning Special Measures against Dioxins Effective use of woody biomass, an energy source not fully utilized yet ★ Mie Prefecture is rich in forestry resources, mainly artificial forests, and woody biomass resources. ★ Strong support of the Japanese Government for promoting effective use of woody biomass: Biomass Nippon Comprehensive Strategy (Decided at the Cabinet Meeting in Dec. 2002) 2. Biomass-Related Events Dec. 1997: July 1999: Jan. 2001: Dec. 2001: Jun. 2002: Apr. 2003: Oct. 2004: Dec. 2004: May 2005: Dec. 2005: 20??: Adopted ‘Kyoto Protocol’ Established and enforced ‘Law Concerning Special Measures against Dioxins’ Revised ‘Outline for Promotion Effects to Prevent Global Warming’ ‘Biomass Nippon Comprehensive Project’ decided at the Cabinet Meeting Kyoto Protocol signed by Japan Enforced RPS(Renewables Portfolio Standard) Law Enforced ‘Law for Enhancing Motivation on Environmental Conservation and Promoting of Environmental Education’ ‘Kyoto Protocol’ ratified by Russia Enforced ‘Kyoto Protocol’ The First Meeting to the Kyoto Protocol (COP/MOP1) Adopted ‘Montreal Action Plan (MAP)’ CO2 reduction target setting and introduction of environmental tax? バイオマスニッポン総合戦略 基本戦略 実施体制 Key Points of ‘Biomass Nippon Comprehensive Strategy’ Biomass Greatly Expected as an Alternative Energy Source 1) 2) 3) 4) Prevention of Global Warming: Use of carbon-neutral biomass in lieu of CO2 emitting energy and products of fossil resource origin Creation of a environment-friendly society: Effective utilization of limited resources through utilization o of biomass for contributing to making a shift to a sustainable society Revitalization of agriculture, forestry and fishery and agricultural, forestry and fishery villages: To be achieved by utilizing biomass, abundant resources that is nourished in nature Nourishment of competitive strategic industries in Japan: To reconstruct competitive Japanese industries through developing biomass-related industries as strategic industries originated in Japan Unclear visions Status Quo and Challenges - Biomass not fully and comprehensively utilized as a competitive energy source - Common understandings not developed in all tiers of Japanese people on utilizing biomass Abundant biomass not fully and effectively utilized Reference (1) Toward Realization of Biomass Nippon Development of Basic National Strategies and Presentation of it in an Easy to Understand Manner - Target setting - How to establish a system best suit for the current conditions of each local area and how to conduct demonstration experiments at model regions - How to nourish understanding of Japanese people - How to enhance cost effectiveness of producing, collecting, transforming and using biomass Others (Source: The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry) 3. Outline of the Green Project (1) Objectives ① To establish a sustainable forest management (to establish a system supporting ‘sustainable green ecosystem’) ② To contribute to revitalization of timber and lumber industries ③ To take an initiative for forming a recycle-oriented society ④ To take an initiative against global warming To contribute to form a environmentally advanced ⑤ prefecture (2) Selection of Candidate Areas Matsuzaka Lumber and Timber Complex ・ One of the major site in Japan for manufacturing and distributing Japan-made wood ・ Favorable geographic locations 4. Basic Concept for Utilizing Woody Biomass ① Woody Biomass as an Energy Resource Volume of left-over wood in forests, discarded wood after sawing, construction woody wastes and their demands are precisely assessed in order to construct a system that demands and supplies of energy produced from woody biomass are well balanced. ② Promotion of Actions Involving the Entire Region Actions under cooperation among forestry industries, lumber and timber businesses, forestry cooperative, theprefecture and municipalities and volunteers, etc. ③ Establishing a System of Stimulating use of Woody Biomass Mie Prefecture: To promote the project and to form a support system Citizens in Mie: To understand and cooperate the project by using woody biomass Promotion of Using Woody Biomass Project Scheme Upstream: Supply of woody biomass (Supply of energy) ● Lumber companies in Matsuzaka City and in Wood Pia Discarded wood after sawing and sawdust, bark and wood chips ● Material producers centered on Kushida River Wood Materials Producing Association Wood Pia Woody Biomass Utilization Cooperative Association (tentative name) Wood chip production (factories in Wood Pia) 【Wood Chip Manufacturing Facilities】 Manufacturing of woody biomass fuel 〈Fuel supply: 120t〉 Woody biomass power station (Ureshino Plant) 【Thermal and Electricity Supply Facility】 Supplies electricity and heat ● ● Wrecking companies in Mie ● Major residential builders and local builders Construction woody wastes generated in Mie ● ● To be constructed within a land owned by the association members Boiler and direct fuel power generation facility Land: Site owned by the association members is leased. Power generation volume: 1,600kwh Supply of steam:12,000kg/h Controls under the RPS regime 〉 〈 Power Supply Left-over wood in forests such as thinned wood and those in raw wood markets Factory owned by association members ● To be located in Wood Pia Matsuzaka ● Stock yards and buildings ● Land: To purchase land in Wood Pia Matsuzaka ● Raw wood market in Wood Pia Ichiuri Association ● Raw wood market of Matsuzaka Iinan Forestry Association 〈 Supply of electricity and 〉 steam ● Lumber companies in former Iinan Town Supply of electricity and steam Woody biomass supply facility Electric company RPS procurement cost Characteristics of Biomass Power Generation Conceptual Diagram of Circulating Woody Biomass Energy CO2 is absorbed by forests Lumber and timber resources Thinned and trimmed wood Sawing and processing wood Lumber and timber Sawing waste Biomass power generation Residential construction Electricity supply Construction waste Reduced use of fossil fuels Heat supply Electric company DRAFT 400kW Interconnected power system 2,000kW Electricity for industrial use Steam turbine Output at generation end =1,600kW+ Electricity consumed by the plant Generator Boiler 12t/h 0.8MPa 185℃ Steam for industrial use Biomass fuel transported by a truck Condenser Cooling tower 90% 90℃ Effluent gas treatment Chip acceptance yard Chimney Water supply equipment Ash is removed using a truck Water supply Condensation tank Effluent water treatment Ash yard Discharged to rivers System Diagram of a Woody Biomass Power Generation and Heat Distribution Facility Expected Effects of a Biomass Heat and Electricity Supplying Facility ① Direct Effects ・ Releasing of air pollutants can be reduced. ・ It is an initiative against global warming (by significant reduction of emission of CO2 to air) ・ Transformation of biomass into energy resources ・ Significant reduction of generating industrial waste water ・ Reduction of odors by thermal decomposition ・ It is an initiative toward realizing zero emission ・ It is an initiative participation in utilizing biomass by the Japanese Government ② ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ Indirect Effects Illegal disposal of wastes can be prevented. Open air burning of wastes can be prevented. Unutilized biomass resources can be utilized effectively. Social responsibility to the local community can be fulfilled. Contribution to forming a recycle-oriented society Contribution to form an environmental advanced prefecture 5 Actions for Using Woody Biomass as an Energy (1) ★ ① ② ③ ④ ⑤ ⑥ ⑦ Establishing a Stable Woody Biomass Supply System Setting up a supply system of thinned wood (leftover wood in forests) Supply of discarded wood after sawing Promotion of improving infrastructures Establishing an economic system taking into consideration of an environmental value Improving a wood processing and distribution system Establishing a system to collect left-over wood in forests Establishing a system to collect construction woody wastes 5. Actions for Using Woody Biomass as an Energy (2) ★ Formation of Social Agreement on Utilization of Biomass Promoting an agreement among the local society that woody biomass can realize self-supply of energy by the local industries and revitalize the area through creation of jobs by encouraging utilization of the resource in a unified manner. In order to raise more understanding of the local residents on utilization of biomass, various efforts are needed in cooperation with environmental preservation activities initiated by various entities. 5. Actions for Using Woody Biomass as an Energy (3) ★ Formation and Dissemination of an Economic System incorporating Eco Management It is necessary that what ripples effects woody biomass can make to the local economy and the environmental sustainability and the scope of support for introducing the resource be clarified by the administration including: ① creation of a system that returns money generated by forests to the forests, ② collecting and providing information and ③ developing new products 6. Supply of Fuels for Promoting Use of Woody Biomass ★ Woody Biomass as a Fuel 》Stable Supply of Woody Biomass《 ・Wastes from sawmills: sawdust, discarded wood, bark and other waste wood ・Thinned and trimmed trees: leaves, discarded wood, roots and branches, etc. ・Wastes from constructors, wrecking companies and builders: construction woody wastes 7. Fuel Supply for Promoting Use of Woody Biomass ★ Stable Fuel Supply Plan ① Waste wood such as discarded wood generated from sawmills, etc. (60T/D) ② Thinned trees left unused in forests(12T/D) ③ Construction woody wastes(48T/D) ★Challenges in Procuring Fuels ① How to promote a cascade use system of biomass ② How to promote local-production for localconsumption ③ How to establish a forest management plan for producing energy ④ How to set up a construction woody waste collection system 8. Volume of Construction Woody Waste Available for Biomass Use (Waste Survey by Mie Prefecture in FY2000) Region Generation of Volume of construction Reuse (t) waste (t) biomass (t) 23,700 18,400 10,500 6,200 4,300 Iga 3,600 2,400 1,200 Owase and Kumano 6,800 5,400 1,400 North Ise South Ise Total 42,100 Volume of 37,700 25、300 9. Volume of Biomass Resources Available from Left-Over Wood after Sawing (Lumber and timber industry database project in FY2001) Region Incinerated Used as (t/Y) Fuel (t/Y) Unknown (t/Y) Total (t/Y) 6,711 North Ise 2,821 1,587 2,303 South Ise 3,986 3,655 7,555 15,196 295 360 3,046 3,701 Owase and Kumano 1,037 214 3,018 4,269 Total 8,139 5,816 15、922 29,877 Iga 10. Volume of Thinned Trees (Left-Over Wood in Forest) (Forestry statistics) Region Forest area (㎥) Unused wood generated by thinning (㎥) Branches and leaves (㎥) Total resources of left-over wood in forests (㎥) North Ise 56,170 49,430 12,357 61,787 South Ise 128,420 113,010 28,252 141,262 16,562 14,575 3,643 18,218 68,104 59,932 14,983 74,915 269,256 236,947 59,235 296,182 Iga Owase and Kumano Total 11. Volume of Woody Biomass by Region Left-over wood and trimmed trees in forests (t) Total (t) 6,711 27,186 52,297 4,300 15,196 62,155 81,651 Iga 1,200 3,701 8,016 12、917 Owase and Kumano 1,400 4,269 32,963 38,632 25,300 13.6% 29,877 16.1% Region Construction wastes (t) North Ise 18,400 South Ise Total Waste wood after sawing (t) 130,3270. 3% 185,497 12. Woody Biomass Utilization Cooperative Association (Tentative Name) Establishment and Operation Plan ★ Operation and management of woody chip manufacturing facilities ★ Sales of electricity and steam ★ Operation and management of boiler power generation facilities Heat and electricity supply facilities 13. Ripple Effects Expected by the Woody Biomass Utilization Promotion Project ★ Return of profits to forests and forestry ・Return of profits to forests and forestry ・Stable management of sawmills ★ Initiatives for Anti-Global Warming Measures ・ Reduction of CO2 Due to the use of the alternative energy to fossil fuels ★ Initiatives for Zero Emission ・ Nourishing new recycle-oriented industries ・ Prevention of open air burning of wastes ・ Prevention of illegal disposal ★ Control against Emission of Pollutants (Reference) Projects Expected for Promoting Use of Thinned Wood (by Mie and other prefectures) Project for securing absorption of CO2 through reforestation Forest environment creation project Project for improving protection forests Private initiatives Bioethanol and Biodiesel Bioethanol ・ Waste materials ・ Cone ・ Sugarcane ・ Others Biodiesel Waste cooking oil