Genetics – Final Exam Summer 2012 VERSION A Name Multiple
advertisement

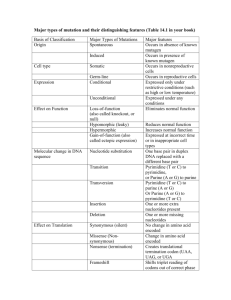
Genetics – Final Exam Summer 2012 VERSION A Name Multiple Choice (50 pts. possible) Problems (50 points possible) Total (100 points possible) KEY IF you completed the in-class workshop put a CHECK MARK HERE ---> There are two sections in the exam: MULTIPLE CHOICE 25 questions worth 2 points each. - Answer on the Scantron Form PROBLEMS 11 problems worth 5 points each. If you completed the workshop we will drop the 2 lowest scores. OR If you did not complete the workshop we will drop the 1 lowest score. U C A G UUU UUC UUA UUG CUU CUC CUA CUG AUU AUC AUA AUG GUU GUC GUA GUG U Phe Phe Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Ile Ile Ile Met Val Val Val Val UCU UCC UCA UCG CCU CCC CCA CCG ACU ACC ACA ACG GCU GCC GCA GCG C Ser Ser Ser Ser Pro Pro Pro Pro Thr Thr Thr Thr Ala Ala Ala Ala 5' Base in Anticodon G C A U I UAU UAC UAA UAG CAU CAC CAA CAG AAU AAC AAA AAG GAU GAC GAA GAG A Tyr Tyr Stop Stop His His Gln Gln Asn Asn Lys Lys Asp Asp Glu Glu UGU UGC UGA UGG CGU CGC CGA CGG AGU AGC AGA AGG GGU GGC GGA GGG G Cys Cys Stop Trp Arg Arg Arg Arg Ser Ser Arg Arg Gly Gly Gly Gly 3' Base in Codon U or C G U A or G U, C or A 1 1. In the table below you are given the genotypes of 4 E. coli strains. All 4 strains are "diploid" for the Lac Operon region. For each of the strains, indicate (using + or -) whether or not the Lac gene products will be expressed at high levels in the presence or absence of inducer. Assume that the inducer IPTG is used rather than lactose. Beta Galactosidase no inducer with inducer GENOTYPE S + + - + I P O Z Y + + c + I P O Z Y + + c + I P O Z Y C + + + + I P O Z Y S + c + I P O Z Y + + + - + I P O Z Y + + + + I P O Z Y C + + - + I P O Z Y - HINTS: I = I C c O =O Lactose Permease no inducer with inducer + + - - + + - + + + - - - - - + - For wild-type E. coli the correct responses would be: GENOTYPE + + + + + I P O Z Y Beta Galactosidase no inducer with inducer + Lactose Permease no inducer with inducer + 2. The diagram below depicts a charged tRNA interacting with a codon in a mRNA. The six squares represent the nucleotides of the codon paired with the anticodon, and the rectangle represents the amino acid attached to the acceptor stem of the tRNA. Some of the 7 identities represented by the squares and the rectangle are given. Work out the identities for the remaining empty shapes and add them to the diagram. i.e. fill any remaining empty squares and/or rectangle with the correct nucleotide or amino acid. If there are any boxes where the identity cannot be unambiguously determined, GIVE ALL THE POSSIBILITIES. Ser tRNA A G U C I U C A mRNA NOTE: DO NOT ASSUME that the mRNA is shown in the usual orientation. You must determine the orientation from the information provided. 2 3. Describe the molecular basis for the fact that GC base pairs in which the C is methylated (5-methylcytosine) are hotspots for a certain type of mutation. Deamination of 5-me C creates a G T mismatch. G T mismatches cannot be repaired by the uracil DNA glycosylase which repairs the normal cytosine deamination lesion (i.e. G U mismatch). 4. For a CGA (Arg) codon, how many of the possible single base pair substitution changes are synonymous, missense, and nonsense? 4 synonomous 4 Missense 1 Nonsense 3 5. This is a matching problem that involves the mutational processes we considered in detail. These mechanisms are listed in the left-hand column. In column 2, write the letter designation only for the pre-mutagenic lesion that is created by each mechanism. In column 3 write the letter or letters designation for the repair mechanism/s that can correct the lesion. In column 4 write the letter designations to indicate the overall mutational change that results from each process. Each choice may be used one or more times. Each box may have one or more appropriate responses. MUTAGENIC PROCESS Tautomeric Shifting of Bases (e.g. keto/enol) Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation Deamination of 5-methyl Cytosine Deamination of Cytosine 2. 2. 3. 4. PREMUTAGENIC LESION/S REPAIR MECHANISM/S OVERALL MUTATION/S A (+ B OK) H, K, L M (+N OK) D F N B I N C J, G, L N 3. PREMUTAGENIC LESION/S LETTER All possible Normal Base Pair Mismatches with incorrect base in newer DNA strand G - T Mismatch A Photolyase F AT ↔ GC Bidirectional Transitions M B AP Excision G N G - U Mismatch C H TT Intrastrand Dimer T - T Mismatch D Methyl-Directed Mismatch Repair No specific repair mechanism Uracil DNA Glycosylase Proofreading by DNA Polymerase Single Strand Gap Repair GC → AT Unidirectional Transition Transversions E REPAIR MECHANISM/S 4. Letter OVERALL MUTATION/S LETTER O I J K L 4 6. Imagine that a mutation eliminates expression of the gene for the regulatory protein CAP. (i.e. As a result of this mutation there is no longer any CAP protein in the cell.) How would this mutation alter expression of the Lac operon genes? (i.e. How would Lac gene expression be different in the mutant compared to the wild-type strain where CAP was present?) Adenyl cyclase is required to synthesize cAMP under conditions of glucose limitation. Therefore CAP activation of Lac (and other catabolic operons) would not occur. Production of lac mRNA would still be regulated by lactose, but even in the absence of glucose would not be produced at levels as high as in a wild-type strain. High levels of Lac mRNA transcription would not be observed even in presence of lactose and absence of glucose because the CAP regulator would not bind to its operator. 7. Give the anticodon sequences (with polarities) of ALL possible Tyrosine-specific tRNA's. Circle the anticodon sequences in your complete set that would represent a minimum set needed to translate all Tyrosine codons. If they are all required, circle them all. (There may be more than one minimum set. If so, you need give only one of them.) Tyrosine = “Tyr” 3' AUA 5' 3' AUG 5' 5 8. The diagram represents a segment in a larger DNA molecule, where a base mismatch (A with C) has resulted from tautomeric shifting of a base in the template strand during DNA replication. The diagram also shows a nearby GATC sequence. ! 1. Which of the bases in the mismatch is erroneous? C 2. Use an arrow to indicate the approximate location of strand cutting by the endonuclease mutH. Unmethylated GATC sequence. 3. If the mismatch is not repaired, the overall mutation that would result is: (Circle One) AT ---> GC 4. What is the identity of the base that experienced the tautmeric shift? (Circle one) A 9. Angelman syndrome (AS) is a rare human genetic disorder in which individuals exhibit unusual seizures and repetitive symmetrical muscle movements and which is due to lack of expression of the gene UBE3A. Expression of UBE3a is subject to paternal imprinting. Two normal parents have a female child born with AS who carries a defective copy of UBE3a. a. Which one of her parents must be heterozygous for the defective UBE3a allele? (Defective UBE3a alleles are very rare in the human population, so it is unlikely that both parents carry it.) Female parent is heterozygous for UBE3. b. If the couple has a son, what is the probability that he will have AS? 1/2 6 10. Give 3 important and significant differences between bacterial genomes and eukaryotes. Circular vs Linear DNA no nucleus vs nucleus mostly coding DNA vs mostly non-coding DNA single vs multiple origins of replication other responses may be acceptable as well 11. In a paragraph, describe the differences between "maternal effect" and "maternal inheritance". The differences you address should include the inheritance pattern of traits as seen in genetic crosses, and the cellular/molecular bases of the two phenomena. If you wrote your answer ahead of time, just staple it to the back of your exam. Maternal effect genes are transcribed in cells of a female during oogenesis and the mRNA or protein products of the gene are transported into oocytes where the effect early development of the embryo. Therefore the phenotype of the offspring reflects the genotype of the mother. Maternal inheritance is due to the transmission of mitochondria and chloroplasts, and their associated genomes, via the egg but not the sperm. Therefore the genotype of the offspring will be identical to that of the mother. 7