Critical Thinking Table—Lifespan Development—Chapter 11
advertisement
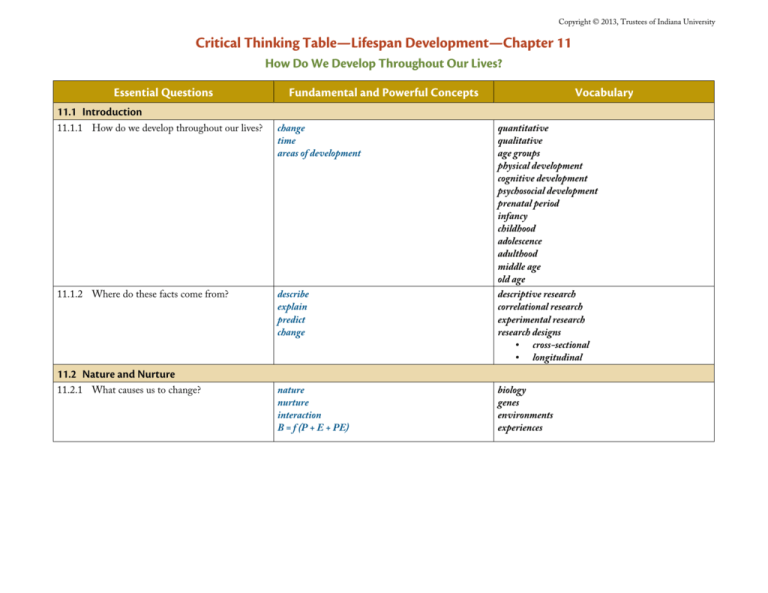
Copyright © 2013, Trustees of Indiana University Critical Thinking Table—Lifespan Development—Chapter 11 How Do We Develop Throughout Our Lives? Essential Questions Fundamental and Powerful Concepts Vocabulary 11.1 Introduction 11.1.1 How do we develop throughout our lives? change time areas of development 11.1.2 Where do these facts come from? describe explain predict change 11.2 Nature and Nurture 11.2.1 What causes us to change? nature nurture interaction B = f (P + E + PE) quantitative qualitative age groups physical development cognitive development psychosocial development prenatal period infancy childhood adolescence adulthood middle age old age descriptive research correlational research experimental research research designs • cross-sectional • longitudinal biology genes environments experiences Copyright © 2013, Trustees of Indiana University 11.3 Areas of Development 11.3.1 How does my body develop over time? normative physical change individual differences physical development prenatal period • conception • zygote oo ectoderm oo mesoderm oo endoderm • embryo • placenta • fetus • myelin • teratogens infancy • motor skills • milestones childhood • motor skills adolescence • puberty • menarche • synaptic pruning adulthood • young adulthood • midlife • menopause • senior years Copyright © 2013, Trustees of Indiana University 11.3.2 How does my thinking change over time? How do we explain these changes? stage theories social interactions information-processing theories cognitive development Piaget’s Stage Theory • sensorimotor stage oo object permanence • preoperational stage oo egocentrism oo conservation • concrete operational oo basic logic • formal operational oo abstract reasoning • post-formal thinking Vygotsky’s Socio-cultural Theory • scaffolding Information Processing Theories • input-storage-output Copyright © 2013, Trustees of Indiana University 11.3.3How and why are relationships important to my development attachment parenting describe explain B = f(P + E + PE) psychosocial development Bowlby • Internal Working Model Ainsworth • strange situation • basic types of attachment oo secure oo avoidant oo ambivalent oo disorganized Baumrind • warmth • control • parenting styles oo authoritative oo authoritarian oo permissive oo indifferent/uninvolved Bronfenbrenner • Ecological Systems Theory oo microsystem oo mesosystem oo exosystem oo macrosystem oo chronosystem lifespan Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory • dilemmas • trust vs. mistrust • identity vs. role confusion • intimacy vs. isolation • generativity vs. stagnation • integrity vs. despair Life-span Perspective (Baltes) • multiple directions • plasticity • historical context • multiple causes 11.4 B = f(P + E+ PE) Plus Time! 11.4.1 What’s the bigger picture? 11.5 Conclusion











