Carbohydrate Metabolism
advertisement
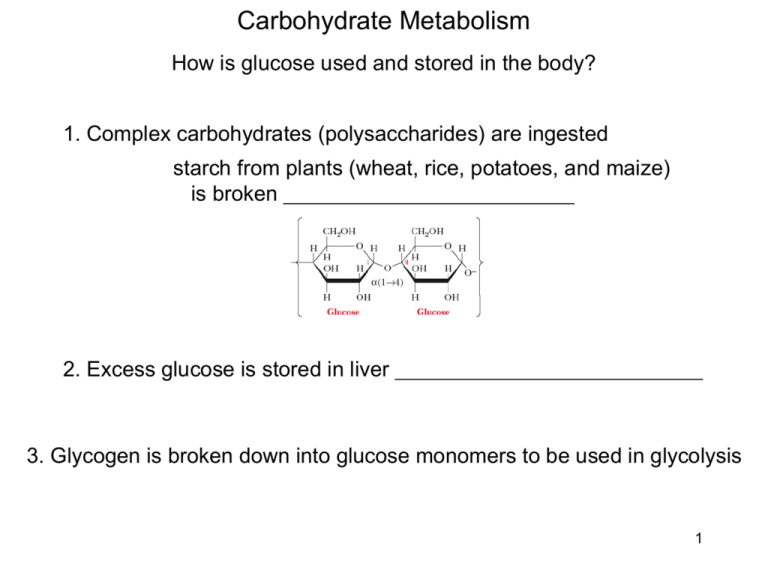
Carbohydrate Metabolism How is glucose used and stored in the body? 1. Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) are ingested starch from plants (wheat, rice, potatoes, and maize) is broken 2. Excess glucose is stored in liver 3. Glycogen is broken down into glucose monomers to be used in glycolysis 1 Carbohydrate Metabolism Polysaccharides Monosaccharide - Oligosaccharides – linkage of ____________________________________ disaccharide of glucose Polysaccharides - linkage of 2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Polysaccharides Glycosidic bond - a bond between the #1 _________________________________ - can be between __________________________________ - bond can be in the __________ depending the OH orientation around C#1 αβ- 3 Carbohydrate Metabolism Polysaccharides Polysaccharides can be linear or branched Two forms of starch: 1. amylose 2. amylopectin - 4 Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycogen Glucose from ingested complex carbohydrates ______________________ Excess glucose is used to form ________________________. During low glucose, glycogen can be broken down into glucose for glycolysis Glycogen - a branched polymer _____________ - about _____________ units per glycogen molecule - linear portions have ________________________ - branch points are __________________________ - 13: average chain length of glycogen branches 5 Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycogen Break down of glycogen - glucose is released from glycogen at - highly branched structure allows for release of many ______________ _____________________________ - allows for quick _____________________ at times of need 6 Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycogen breakdown Glycogen phosphorylase - enzyme that releases - uses Pi to phosphorylate glucose to G1P, breaks Phosphoglucomutase - enzyme that isomerizes - this G6P can then be put directly into _________________ α-1,6 branch bond broke by ______________________ 7 Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycogen breakdown Glycogen phosphorylase - enzyme that releases _________________ - note that the phosphate for G6P formation from glycogen - thus, glycolysis from glycogen - net from glycolysis 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism First step: Glycogen formation Energy for glycogen production from glucose uses _________________ ____________________ to form uridine diphosphate glucose (UDPG) UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase - enzyme that carries out this reaction 9 Carbohydrate Metabolism Second step: Glycogen formation - UDPG is linked to another ________________________________ - carried out by __________________________________ 10 Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycogen formation Branching step: - branching enzyme transfers 7 glucoses from ______________________ _____________________________________________ - forms _________________ - each transferred segment comes from at least - each branch point at least 4 glucoses 11 Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycogen formation Why do athletes that perform endurance events (long distance running, cycling) eat pasta before exercise? Glycogen loading (carbo loading) - _________________________ __________________________________________ - extra glycogen allows for ______________________________ by anaerobic glycolysis during extended exercise 12 Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis - Conversion of ___________________ - essentially ____________________, but not exactly - _________________ of glucose - occurs in ________________ - occurs in time of _________, __________, or intense _________ - requires energy (ATP) input 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis - Many of the steps in glycolysis are ________ - 3 steps in glycolysis are irreversible: 1. G6P production from ______________ _____________________ 2. F1,6BP production from ___________ 3. ________________________ from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) These reactions must be __________ in gluconeogenesis 14 Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis Step 1. Conversion of pyruvate to __________ - carried out by enzyme __________________ - uses 1 ATP - reaction takes place 15 Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis Step 2. Conversion of oxaloacetate to Mg2+ + GTP Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase O C O- O C O P CH2 +CO2 + GDP O- O- phosphoenolpyruvate - carried out by enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase - uses 1 instead of ATP - reaction takes place in ________________ - now PEP is produced, - PEP continues through gluconeogenesis 16 Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis Step 9. Conversion of F1,6BP 11 10 9 8 6 7 - carried out by enzyme ________________ ___________________________ 5 4 - removes __________________ from F1,6BP 3 2 - reaction takes place in ________________ 1 17 Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis Step 11. Conversion of G6P to _____________ 11 10 9 8 6 7 - carried out by enzyme ________________ _______________________________ 5 4 - removes phosphate from G6P 3 2 1 - reaction takes place in Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are not exact reversals of each other, 18 Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis 11 Entry points for gluconeogenesis 10 1. Lactate can be 9 2. Amino acids can be converted to 8 6 7 3. Glycerol can be converted to 5 4 3 2 1 19 Carbohydrate Metabolism The Cori Cycle - fast twitch muscle mostly carries out . - during exercise such as sprint fast twitch muscles will _______ ________________________ - lactic acid is transported _____ - lactic acid is converted to glucose via _______________ - glucose is shuttled back to __________________ 20 Carbohydrate Metabolism The Cori Cycle Why warm down or have massage after exercise? - muscle soreness after exercise - warm down or massage keeps blood flowing to ____________ _______________________ 21 Carbohydrate Metabolism The Cori Cycle Carl Ferdinand Cori & Gerty Theresa Cori - naturalized Americans - born in Prague - worked at the State Institute for the Study of Malignant Diseases (now the Roswell Park Cancer Institute) in Buffalo, New York - defined Cori Cycle in 1929 - Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1947 22