Test Canvas: Quiz 6
advertisement

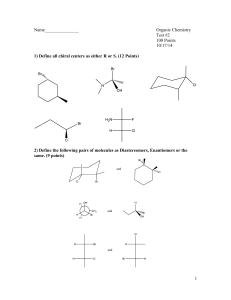
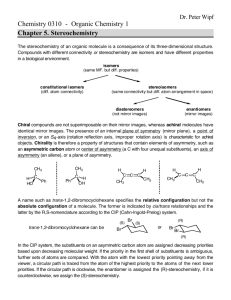
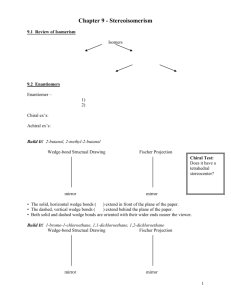
Test Canvas: Quiz 6 1 of 3 https://my.oregonstate.edu/webapps/assessment/do/auth... ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH_334_001_F2011) Tests, Surveys, and Pools Tests Test Canvas : Quiz 6 Edit Mode is: Test Canvas: Quiz 6 The Test Canvas allows instructors to add and edit questions, add Question Sets or Random Blocks, reorder questions, and review the test before deploying it to users. More Help Create Question Description Reuse Question Upload Questions Question Settings Sixth weekly quiz Instructions Total Questions 10 Total Points 10 Select: All None Points Select by Type: Update - Question Type - Hide Question Details 1. Multiple Choice: The sugar ribose is shown in a Fische... Question Answer Points: 1 The sugar ribose is shown in a Fischer projection below. The correct assignment of configuration is: a. 1-R, 2-R, 3-R b. 2-R, 3-R, 4-R c. 2-R, 3-S, 4-R d. 2-R, 3-R, 4-S 2. Multiple Choice: A stereoselective reaction (which I w... Question Answer Points: 1 A stereoselective reaction (which I will not specify) creates a mixture of two enantiomers: 95% of one, and 5% of the other. The enantiomeric excess in this reaction is: a. 95% b. 5% c. 90% d. 100% 3. Multiple Choice: In the monobromination of 3-methylhep... Question Answer Points: 1 In the monobromination of 3-methylheptane, the stereochemical outcome of the reaction is: a. A single enantiomer. b. A pair of enantiomers in a 1:1 mixture (racemic). c. A pair of enantiomers with one being formed in an ee > 0. d. Two diastereomeric pairs of enantiomers, 4 stereoisomers total. OK 11/05/11 10:01 Test Canvas: Quiz 6 2 of 3 https://my.oregonstate.edu/webapps/assessment/do/auth... 4. Multiple Choice: Monochlorination of methylcyclohexane... Question Answer Points: 1 Monochlorination of methylcyclohexane gives which outcome, including sterochemical isomerism? a. A single enantiomer of one isomer. b. Two enantiomers of one regioisomer. c. 5 regioisomers, each in a single enantiomer. d. A total of 12 regio- and stereochemically distinct isomers. 5. Multiple Choice: Imagine the 1-phenylethyl radical (Ph... Question Answer Points: 1 Imagine the 1-phenylethyl radical (Ph(CH3)CH·) reacting with chlorine (Cl2). Select the answer that best relates the stereochemical outcome to a potential energy diagram. a. A given molecule of the radical will have a fixed stereochemical configuration at carbon, so there is only a single pathway available to produce a single enantiomer. b. The planar radical can be approached from either side to give two different transition states leading to the two enantiomers. Because these two have identical energies (they are enantiomeric), a racemic product is formed. c. The planar radical can be approached from either side to give two different transition states leading to the two enantiomers. However, because these two have different energies (they are diastereomeric), one enantiomer of the product is formed in preference to the other. d. The delocalized radical provides a mechanism for placing chlorine at every carbon in the molecule. 6. Multiple Choice: Choose the best method for determning... Question Answer Points: 1 Choose the best method for determning the ee if I try to stereoselectively make R-1-phenyl-1-chloroethane (shown below). a. Measure the melting point, since this will vary linearly with ee. b. Measure the boiling point, since this will vary linearly with ee. c. Measure the rotation of plane-polarized light by the product, even if I don't know the rotations of the pure enantiomer. d. Perform chromatography on a chiral medium, as the interactions between enantiomeric molecules and the chiral medium creates a diastereomeric relationship that allows separation and measurement. 7. Multiple Choice: How do the outcomes for monobrominati... Question Answer Points: 1 How do the outcomes for monobromination of the two isomers (cis, trans) of 1,3-dimethylcyclohaxane compare? a. Stereochemically distinct radical intermediates lead stereospecifically to diastereomeric products, one from each isomer. b. The cis isomer gives one stereoisomer in a stereoselective reaction but the trans isomer is nonstereoselective and gives a mixture. c. Both isomers give the same intermediate, which produces identical mixtures of products from each isomer. The reaction is slightly stereoselective, but nonstereospecific. d. Each isomer gives a different mixture of products, and is thus stereospecific but not highly stereoselective. 11/05/11 10:01 Test Canvas: Quiz 6 3 of 3 https://my.oregonstate.edu/webapps/assessment/do/auth... 8. Multiple Choice: 4-chloromethylcyclohexane can be isol... Question Points: 1 4-chloromethylcyclohexane can be isolated as either of two different stereoisomers. What is their relationship? Answer a. Diastereomers (cis/trans). b. Enantiomers (4-R, 4-S). c. Enantiomers (1-R, 1-S). d. Racemates. 9. Multiple Choice: How do enzymes accomplish enantiosele... Question Points: 1 How do enzymes accomplish enantioselective reactions? Answer a. They can turn racemic products into diastereomeric derivatives, one of which the organism will not use. b. Enzymes are chiral molecules, so production of different enantiomers within the enzyme will have different potential energy curves. c. Enzymes cannot react with achiral molecules. d. Enzymes incorporate self-correction chemistry to turn the "wrong" enantiomer into its mirror image. 10. Multiple Choice: An enzyme called "chloroperoxidase" c... Points: 1 Question An enzyme called "chloroperoxidase" can catalyze the following conversion using free radical chemistry. Select the most likely mechanism by which this enzyme achieves enantioselectivity. Answer a. Creation of a chiral radical intermediate. b. Equilibration of enantiomeric products in a chiral environment. c. Differential metabolism of the enantiomeric products. d. Selective delivery of the chlorinating agent to one face of the radical intermediate. Select: All None Points Select by Type: Update - Question Type - Hide Question Details 11/05/11 10:01