Guilfoyle Course - AP Bio Steps Monday 10/12
advertisement

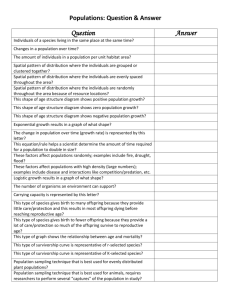
Guilfoyle Course - AP Bio EQ: Relationships are very important in biology, how many relationships can you identify/explain within the characteristics of life? Elaborate on the need for these relationships? Predict how they evolved. Steps Focus Catalyst Goal/Objective Common Core 21st Century Skill STEM Technology Monday 10/12 Catalyst - Human Evo Stabilizing Evo DBQ See Separate Sheet for Unit Goal/Objectives (College Board and NCSCOS) W1 - Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence W4 - Produce clear and coherent writing W7 - Research R1 - Cite textual evidence Team work Deductive reasoning Promethean board Big Idea 1 – Evolution: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Goal/Objective Big Idea 3 – Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes Big Idea 4: Interactions with biological systems lead to complex properties Big Idea 1 – Evolution: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life EU 1A – Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution EU 1A1. Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution EU 1A2. Natural selections acts on phenotypic variations in populations EU 1A3. Evolutionary change is also driven by random processes EU 1A4. Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines, including mathematics EU 1B – Organisms are linked by lines of descent from common ancestry EU 1B1. Organisms share many conserved core processes and features that evolved and are widely distributed among organisms today EU 1B2. Phylogenic trees and cladograms are graphical representations of evolutionary history that can be tested EU 1C – Life continues to evolve within a changing environment EU 1C1. Speciation and extinction have occurred through the Earth’s history EU 1C2. Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other EU 1C3. Populations of organisms continue to evolve LO 1.2 - Evaluate evidence provided by data to qualitatively and quantitatively investigate the role of natural selection in evolution LO 1.3 - Apply mathematical methods to data from a real or simulated population to predict what will happen to the population in the future LO 1.4 - Evaluate data based evidence that describes evolutionary changes in the genetic makeup of a population over time LO 1.5 - Connect evolutionary changes in a papulation over time to a change in the environment Define allele frequency and gene pool. State that evolution involves a change in allele frequency in a population’s gene pool over a number of generations. Outline the evidence for evolution provided by the fossil record State that populations tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. Explain that the consequence of the potential overproduction of offspring is a struggle for survival. State that the members of a species show variation. Explain how sexual reproduction promotes variation in a species. Explain how natural selection leads to evolution. Agenda Independent Work CFU Closure Homework STANDARD ALIGNMENT Explain two examples of evolution in response to environmental change; one must be antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Explain the three modes of selection based on the normal distribution curve. Catalyst - Human Evo Stabilizing Evo DBQ Flipchart - None Activity - Case Study: Natural Selection of the Rock Pocket Mouse Activity - 5 Agents of Evo Change Anchor Chart TOTD - Debriefing Interactive Video, Lab and DBQ Individual consultations during the independent practice portion of the lesson TOTD - Debriefing Study Big Idea 1 – Evolution: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life EU 1A – Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution EU 1A1. Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution EU 1A2. Natural selections acts on phenotypic variations in populations Define allele frequency and gene pool. Student Goals State that evolution involves a change in allele frequency in a population’s gene pool over a number of generations. Student Goals State that populations tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. Explain that the consequence of the potential overproduction of offspring is a struggle for survival. State that the members of a species show variation. Explain how natural selection leads to evolution. See all AP College Board objectives above AGENDA ACTIVITY 1 Human Stabilizing Selection DBQ What is it that students must be able to know, understand and do by the end of the activity? Students will analyze a famous study on human childbirth weight vs mortality How will you assess students have learned? Individual consultations and class discussion How will you respond if they cannot demonstrate learning? Re-loop and Remediate as needed (today or tomorrow) ACTIVITY 2 What is it that students must be able to know, understand and do by the end of the activity? How will you assess students have learned? Case Study - Natural Selection of the Rock Pocket Mouse Students will analyze the natural selection of the rock pocket mouse (HHMI interactive video ~10 minutes) Class Discussion as needed after the interactive quiz How will you respond if they cannot demonstrate learning? Re-loop and Remediate as needed (today or tomorrow) ACTIVITY 3 What is it that students must be able to know, understand and do by the end of the activity? Anchor chart - 5 Agents of Evolutionary Change Students will create an anchor chart for the 5 agents of evolutionary change - very vocab driven How will you assess students have learned? Individual Discussions as needed How will you respond if they cannot demonstrate learning? Re-loop and Remediate as needed (today or tomorrow) ACTIVITY 4 Activity - Chi Square Analysis of M&M's Review as needed What is it that students must be able to know, understand and do by the end of the activity? Students will use a bag of M&M's for a Chi Square Analysis comparing observed results to the expected results (from the Mars Co.); Students will learn how to use and apply Chi Square Analysis; SP 2 (2.1–2.3) The student can use mathematics appropriately How will you assess students have learned? Individual consultations and class discussion How will you respond if they cannot demonstrate learning? Re-loop and Remediate as needed (today or tomorrow) ACTIVITY 5 Peppered Moth DBQ (Time permitting) What is it that students must be able to know, understand and do by the end of the activity? Students will analyze the Kettlewell study on the Peppered Moth How will you assess students have learned? Individual consultations and class discussion How will you respond if they cannot demonstrate learning? Re-loop and Remediate as needed (today or tomorrow) COMMENTS/NOTES