Naming Binary Covalent Compounds Worksheet
advertisement

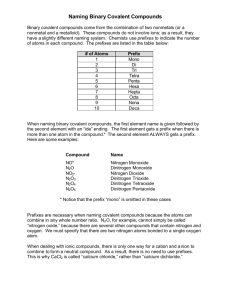
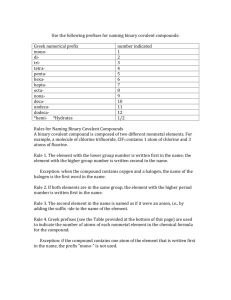
Name Date K Naming Binary Covalent Compounds Binary covalent compounds come from the combination of two nonmetals (or a nonmetal and a metalloid). These compounds do not involve ions; as a result, they have a slightly different naming system. Chemists use prefixes to indicate the number of atoms in each compound. The prefixes are listed in the table below: # of Atoms 1 2 3 4 5 6 Prefix Mono Di Tri Tetra Penta Hexa Hepta Octa Nona Deca 7 8 9 10 When naming binary covalent compounds, the first element name is given followed by the second element with an "ide" ending. The first element gets a prefix when there is more than one atom in the compound * The second element ALWAYS gets a prefix. Here are some examples: Compound Name NO* N2O N02* N203 N204 N205 Nitrogen Monoxide Dinitrogen Monoxide Nitrogen Dioxide Dinitrogen Trioxide Dinitrogen Tetraoxide Dinitrogen Pentaoxide - * Notice that the prefix "mono" is omitted in these cases Prefixes are necessary when naming covalent compounds because the atoms can combine in any whole number ratio. N2O, for example, cannot simply be cal ed ' oxide " because there are several other compounds that contain mtrogen Wemust specify that there are two nitrogen atoms bonded to a single oxygen atom. When dealing with ionic compounds, there is only one way for a cation and anlon to combine toform a neutral compound. As a result, there is no need to use prefixes, is why CaCI2 is called "calcium chloride," rather than "calcium d,chlor,de. Writing the Names of Covalent Compounds 1) List the name of the first element in the formula. 2) List the second element and add the -ide suffix. 3) Use Greek prefixes to indicate the number of each atom in the formula. • Exception; do not use mono- for the first element in the name. • The o or a at the end of the Greek pre-fix is usually dropped when the element name begins with a vowel Example: Write the name for N2S4 1) List the name of the first element in the formula. nitrogen 2} list the second element and add the -ide suffix. nitrogen sulfide 3) Use Greek prefixes to indicate the number of each atom in the formula. • See your textbook or lecture notes for a table of the Greek prefixes. nitrogen sulfide dinitrogen tetrasulfide Exception; do not use mono- for the first element in the name. Not applicable in this example The o or o at the end of the Greek pre-fix is usually dropped when the element name begins with a vowel Not applicable in this example Example: Write the name for S03 1) List the name of the first element in the formula. sulfur ?) List the second element and add the -ide suffix. sulfur oxide 3) Use Greek prefixes to indicate the number of each atom in the formula. sulfur oxide sulfur trioxide • Exception: oo not use mono- for the first element in the name. • NOTE, we did not write monosulfur because of this rule! Example: Write the name for CO 1) List the name of the first element in the formula. carbon ?) List the second element and add the -ide suffix, carbon oxide 3} Use Greek prefixes to Indicate the number of each atom ,n the formula. carbon _ oxide carbon monoxide . . Exception: do not use mono- for the first element in the name . NOTE we did not write monocarbon because of this rule. The o or o at the end of the Greek pre-fix is usually dropped when the e,ement name begins with a vowel . NOTE, we did not write monooxygcn because of this rule.