Recap: Epithelium
advertisement

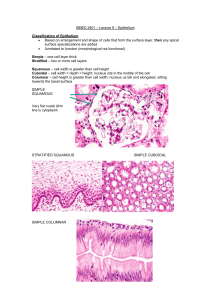
Recap: Epithelium - one of four basic tissues - avascular/cellular - specialized cells according to function - occurrence: sheets of cells (=lining) solid aggregations of cells (=glandular) Epithelial Classification Layers Cell Shape Squamous Columnar Simple Cuboidal Pseudostratified Squamous Stratified Cuboidal Transitional Stratified Epithelia - consists of multiple layers => even if there are just 2 layers = stratified - only basal layer of cells attached to the basement membrane - if cells appear stratified but contain cilia, they are pseudostratified => True stratified epithelia do NOT have cilia 1 Stratified Squamous - bottom layer in contact with basement membrane - other layers adhere to one another - referred to as squamous => many cell layers not flattened - may vary from few to many layers Non-keratinized: cornea, lips, oral cavity, esophagus, vagina rectum Keratinized: skin, lips Keratin -fibrous structural protein -tough, insoluble !Rivaled by chitin only -consituent of structures growing from skin -soft epithelial keratin and hard hair keratin -nutrition of infectious fungi, i.e. athlete’s foot Stratified Cuboidal -multiple layers of cuboidal cells -found e.g. in sweat gland and male urethra -in most places two-layered -only in ovary can they become large and multilayered 2 Transitional - also called urothelium - urinary tract only - multiple cell layers, cuboidal in appearance - cell can expand and contract - expanded = cells squamous in appearance - function: accommodates volume fluctuation protection against caustic urine Apical Domain Modifications Microvilli - fingerlike projections on most epithelial cells - highly varied in appearance - form brush border on apical surface - absorbtion, secretion, adhesion, transduction Stereocilia -unusually long, immotile microvilli -male reproductive system and ear -resemble hairs of a paintbrush Cilia - mobile cytoplasmic structures - female reproductive system, respiratory tract - organized core of microtubules in 9+2 pattern => ectopic pregnancy Lateral Domain Adhesions Occluding Junctions - closely associated areas (vertebrates only) - prevent movement between cells = no passive/active transport => receptor mediated - strands of transmembrane proteins Anchoring Junctions - cell adhesion molecules - desmosomes => attach adhesion proteins to intracellular keratin Communicating Junctions - gap junctions - small molecules pass freely - heart, neurons, eye 3 Basal Domain Adhesions - non-cellular - lamina densa (30-70nm thick) - underlying network of reticular tissue - also contains macromolecule components = basement membranes Function: 1. anchoring epithelium 2. mechanical barrier against malignant cells 3. development of new blood vessels 4. glomerular filtration 4