I. Chromosomes A. composed of chromatin – a complex of DNA and
advertisement

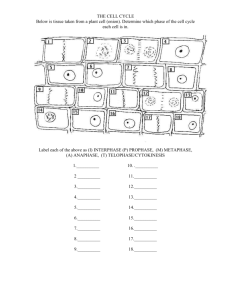
I. Chromosomes A. composed of chromatin – a complex of DNA and proteins B. Homologous chromosomes: pairs that contain the same genes, one from each parent Homologous pair C. Chromosomes must be replicated before cell division. 1. sister chromatids: 2 copies of the same chromosome 2. connected to each other at their kinetochores 3 II. Why do cells divide? A. Replacement - cells wear out & die B. Repair - tissues can be damaged by injury or infection C. Growth of the organism D. Reproduction 5 1 III. Mitosis A. New cells are identical to the old cells B. Chromosome number is the same in parent & daughter cells (diploid – 2N) C. Growth, repair, & asexual reproduction IV.Phases of Mitosis A. Interphase 1. Growth & normal cell activities 2. DNA is duplicated MITOSIS B.Prophase 1. Chromosomes condense (sister chromatids) 2. Centrioles move to poles 3. Nuclear membrane dissolves C.Metaphase 1.Sister chromatids line up along equator of cell 2.Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers 12 2 D.Anaphase 1.Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids to opposite ends of cell **an identical set of chromosomes moves to each pole 13 E.Telophase 1.Chromosomes uncoil 2.Nucleus reforms 3.Cytokinesis: cell membrane pinches in to form 2 separate cells MEIOSIS B.Meiosis 1.Parent cell divides twice to produce 4 cells 2.Produces gametes (sex cells) 3.Daughter cells have half the original number of chromosomes (haploid -1N) 4.When two gametes join to form a zygote, it will have the normal # of chromosomes 3 5.Daughter cells are not genetically identical: a) Homologous chromosomes separate, sending one version of each to the new cells b) crossing over: sometimes chromosomal segments are exchanged between homologous chromosomes 21 V. Phases of Meiosis A. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are held together by proteins 1. Interphase I 2. Prophase I 3. Metaphase I:line up next homologous partner 4. Anaphase I: homologous pairs separate, sister chromatids remain together 5. Telophase I 4 Meiosis I: (Reduction division) 25 Meiosis II: (Mitotic division) B. Meiosis II 1. Prophase II 2. Metaphase II 3. Anaphase II: sister chromatids separate 4. Telophase II 5