Genetics
advertisement

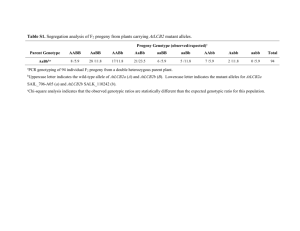
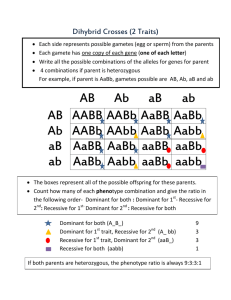
Definition: the expressed version of a trait (what you actually see) A. Determined by the two genes present that were inherited from the parents. EX: Blue eyes, freckles, lactose intolerance, flower color, fur color Definition: The genes that are present for any trait. A. These are the genes that were passed on from your parents in their egg and sperm. B. The genotype may not always be evident (clear) from the traits expressed. C. Some traits are stronger than others and can mask (hide) the expression of the “weaker” trait. Allele Def: an alternate version of expression for a gene Ex: Gene – Hair color Alleles – brown, black, red, blonde Ex: Gene- Freckles Alleles- freckles present or absent A. Alleles can be dominant or recessive B. You can get different ones from each parent Copy of chromosome from dad Allele for dimples Present Absent Copy of chromosome from mom Recessive: The “weaker” version you must have both recessive genes to have that phenotype expressed. Dominant: A. The “stronger” version B. Dominance does not mean the genes are “aggressive”, it just expresses itself more often. C. 3 types of Dominance: Complete Dominance Incomplete Dominance Co-dominance Definition: the actual combination of the genes you inherited (the alleles) A. Alleles in a genotype are represented by letters: capital letter = Dominant lowercase letter = Recessive B. There are 2 possible combinations: heterozygous homozygous 1 copy of 2 copies of the each allele same allele Aa AA or aa (both dom. or both rec.) Complete Dominance: - A. You will have the trait (phenotype) it codes for if you received the dominant gene from one or both parents. - Ex: Freckles Genotype: AA Aa aa Phenotype: freckles freckles no freckles Incomplete Dominance: A. You must be homozygous to have the phenotype (show the trait) B. If you are heterozygous then the phenotype is an “intermediate” (blending of the traits). - Ex: hair texture Genotype: Phenotype: AA curly Aa wavy aa straight Co-dominance: A. when two alleles are equal to each other, but are dominant to another B. Being heterozygous for these two alleles means both phenotypes will be expressed - Ex: Blood Type Genotype: Phenotype: AA or AO A BB or BO B AB AB OO O How can two people with brown eyes have a blue eyed baby? Figuring out possible outcomes… Punnet Squares How Do Monohybrid crosses work? Ff x ff 2 Parents One has Freckles Ff F One does not ff What is the chance that they will have a child without freckles At the end of meiosis, the chromosomes carrying the genes for those traits will separate and go into opposite gametes. f f Ff Ff f ff ff How Do Dihybrid Crosses Work? Just the same as a monohybrid test cross, the traits from the parents will separate from each other and end up in separate gametes. Simply put, the “A” genes will separate from each other, as will the “B’s”. Father: AaBb Possible Gametes: AB Ab aB ab Mother: AaBb Possible Gametes: AB Ab aB ab AaBb x AaBb AB Ab aB ab AB AABB AABb AaBB AaBb Ab AABb AAbb AaBb Aabb aB AaBB AaBb aaBB aaBb ab AaBb Aabb aaBb aabb