Amines and Amides Lab Manual: Solubility, Neutralization, Hydrolysis
advertisement

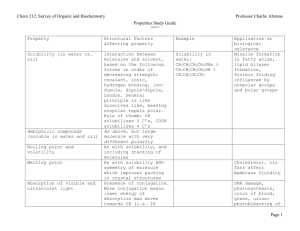
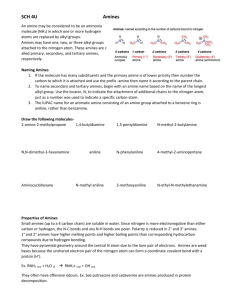
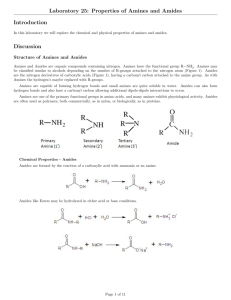
Name:______________ Section:_____________ Pre-lab 7: Amines and Amides Read the background information and answer the following question before lab. 1. Draw out the structure for the following amines. a. Ammonia b. Methylamine c. Dimethylamine d. Trimethylamine e. aniline 2. Classify each of the amines in number 1 as primary (10), secondary (20), or tertiary (30). 3. From the solubility rules you learned in lecture. Are the amines in number 1 soluble in water? ~ 84 ~ 4. Draw the structures for the following amides. a. Acetamide b. benzamide ~ 85 ~ Lab 7: Amines and Amides Objective: The objectives of this experiment are to construct and compare the structures of amines, to check their solubility and pH, and do some reactions to neutralize amines and hydrolyze amides. Background Information: The Structure of Amines: Amines are derivatives of ammonia that has had one or more H atom replaced by a carbon chain (R). A representation of this is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. The Solubility of Amines: In water ammonia and animes with one to four carbon atoms act as a base and form an ammonium ion (an ammonia with an extra H causing it to become positive) or alkyl ammonium ion and a hydroxide ion. The reaction is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. ~ 86 ~ The Neutralization of Amines with acid: Amine are a base, so in order to neutralize them an acid is used. The reaction of an amine with an acid will form an amine salt (an amine with an extra H causing it to be positive). The reaction is shown in Figure 3. Figure 3. The Structure of Amides: Amides are formed in a reaction called amidation when a carboxylic acid reacts with ammonia or an amine and is heated. This reaction and some amide structures are shown in Figure 4. Figure 4. Hydrolysis of an Amide: When an amide is hydrolyzed the bond between the carbon and nitrogen is broken and a carboxylic acid and an amine are formed. This is a reverse to the reaction shown in Figure 4. Hydrolysis occurs in either an acid or a base and heat. When is occurs in an acid such as HCl, a carboxylic acid and an ammonium salt are formed. When hydrolysis occurs in a base such as NaOH, a salt of carboxylic acid (carboxylic acid minus a H causing it to become negative) and ammonia are formed. The two different reactions are shown in Figure 5. ~ 87 ~ Figure 5. Procedure/data: Equipment list: pH paper Red Litmus paper Blue Litmus paper Stirring rod Ring stand Clamp(s) Hot plate 150mL beaker Structures of Amines 1. Look at the models of ammonia, methylamine, dimethylamine, trimethylamine, and aniline. 2. Compare them to the structures that you drew in the pre-lab. 3. Answer the questions on the report sheet. Solubility of Amines 1. Use the vials labeled aniline, N-methylamine, and triethylamine. 2. Cautiously note the odor of each. Remember to waft. 3. Record the odor you detect on the chart below. ~ 88 ~ Compound: Odor: Solubility: yes/no pH Aniline N-methylamine Triethylamine 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Add 2mL of water to each vial. Cap the vial and swirl gently to mix. Record their solubility on the above chart and on the report sheet. Determine the pH by dipping a stirring rod into each amine solution. Touch the end of the stirring rod to pH paper. Record the results on the chart above and on the report sheet. *Save the vials of solution for the next part.* Neutralization of Amines 1. Add 10% HCl drop wise to each amine solution until the solution is acidic. 2. Acidity is tested by dipping a stirring rod into the solution and touching it to blue litmus paper. Note: if blue litmus paper turns red, the solution is acidic. if red litmus paper turns blue, the solution is basic. 3. Record the solubility of each amine again in the chart below and on the report sheet. 4. Record the odor of each amine solution on the chart below (use wafting). Compound: Solubility: yes/no Aniline N-methylamine Triethylamine ~ 89 ~ Odor Solubility of Amides 1. 2. 3. 4. Use the vials labeled acetamide and benzamide Add 2mL of water to each vial Record the solubility of each amide on the chart below and on the report sheet. *Save the vials for the next part.* Compound: Solubility: yes/no Acetamide Benzamide Acid Hydrolysis of Amides 1. 2. 3. 4. Add 2mL of 10% HCl to each vial from the last part. Place the vials in boiling water. Heat gently for 5 minutes. Record the Odor on the chart below. Compound: Odor: HCl Acetamide Benzamide Base Hydrolysis of Amides 5. Use the two other vials labeled acetamide and benzamide. 6. Add 2mL of water to each vial. 7. Add 2mL of 10% NaOH. 8. Place the vials in boiling water. 9. Wet a piece of red litmus paper and hold it over the mouth of each vial. 10. Gently heat for 5 minutes. ~ 90 ~ 11. Record any change in color of the litmus paper on the chart below and on the report sheet. 12. Note the odor of each amide solution and record on the chart below. Compound: Litmus: Odor: NaOH Acetamide Benzamide ~ 91 ~ Name:_______________________ Lab 7: Amines and Amides Report Sheet Partner(s):____________________ _____________________________ Section:______________________ Structures of Amines 3. a. If amines are derivatives of ammonia, explain how this is using the structures and models. 1. Give the IUPAC names for methylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine. Solubility of Amines 5. And 8. Record the amine’s solubility and pH on the chart. Compound: Solubility: yes/no aniline N-methylamine triethylamine ~ 92 ~ pH: Neutralization of Amines 3. Record the new solubility on the chart. Compound: Solubility: yes/no aniline N-methylamine triethylamine Solubility of Amides 3. Record the solubility of each amide on the chart. Compound: Solubility: yes/no Acetamide benzamide Hydrolysis of Amides 11. Record any change in color of the litmus paper on the chart below. Compound: Litmus: Acetamide benzamide ~ 93 ~ Addition Questions 1. Write and balance the reaction for the neutralization of N-triethylamine. 2. Write and balance the reaction for the acid and base hydrolysis of acetamide. 3. Use the bottom equation in Figure 5 as a reference. If the ammonia is a base, explain your results for the litmus color change in the chart for the base hydrolysis of amides. ~ 94 ~ This page was intentionally left blank!! ~ 95 ~