Camosun College
advertisement

Camosun College
Chemistry 230
Assignment # 2
Functional Groups / Acids and Bases
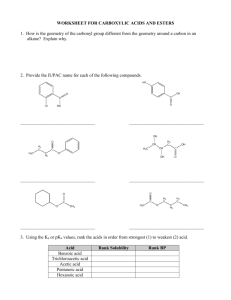
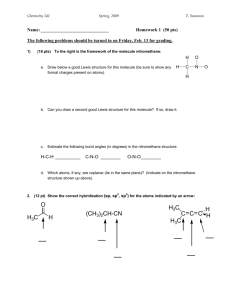
1. Classify each of the following compounds as an alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, aldehyde, amine and
so forth:
OH
O
a.
c.
b.
O
d.
H
O
CH 3
e.
g.
f.
NH2
O
O
CO 2H
h.
i.
H
NH 2
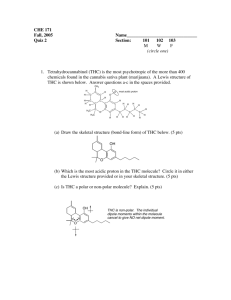
2. Classify the following alcohols as primary, secondary, or tertiary:
OH
a.
(CH 3)3CCH 2OH
b.
c. (CH 3)2CHCH(OH)CH(CH 3)2
d.
OH
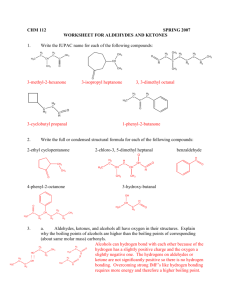
3. Classify the marked carbon atoms as 1o , 2o , or 3o:
a.
*
Cl
*
b.
Br
OH
c.
*
d.
*
H
N
*
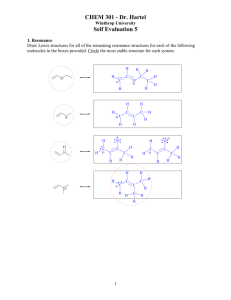
4. Write structural formulas for each of the following:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Four primary alkyl halides with the formula C5H11Br
Three aldehydes with the formula C5H10O
Two amides with the formula C2H5NO
Three ethers with the formula C4H10O
A tertiary alkyl halide with the formula C5H11Cl
5. Write equations showing the acid-base reactions given below:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
CH 3OH + BF3
CH 3OCH 3 + BF3
ClCH 2CO 2H + HCO 3
Al(H 2O) 63+ + OH
CH 3COOH + NH 3
CH 3CH2COOH + CH3O
CH 3CH2OH + HCl
6. List the following acids in order of decreasing acidity:
CH3CH2CH2COOH
ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
CH3CH2CHClCOOH
CH3CHClCH2COOH
7. In each group of structures, arrange the following in order of decreasing acidity:
a. H CCH
3
CH2
b. CH3CH 2OH
c.
CH3CH 3CH3
H3CC
CH 3CH2OH 2
SO3H
CH
CH3OCH3
OH
OH
8. Using data tables in text (or in a first year text), estimate the equilibrium constants for each of the
K a ( reactant acid )
following reactions at 25 oC:
{ K eq
}
K a ( productacid )
a. (CH 3)3N +
HCN
(CH 3)3NH + CN
pKa 9.76
b. CH 3CH2SH
+ OH
CH 3CH 2S +
H2O
pKa 10.5
c.
OH + NH3
O
+
NH 4
9. Supply the curved arrows necessary for the following reactions:
a.
H
O
+
H
H3C
I
H
H
CH 3
H
b.
+
H
O
H
H
d.
H3C
F
H
F
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
O
c.
H3C
I
F
O
H 3C
+
+
CH 3
O
H
H 3C
O
H
O
O
H 3C
CH 3
+
O
H
CH 3
H
O
H
H3C
H3C
H
10. Provide resonance structures for the conjugate base of each of the following:
a.
O
H
O
O
O
O
b.
H
11. The compound of sodium with hydrogen, sodium hydride, is ionic (Na+H-).
a. What is the Lewis dot structure of sodium hydride?
b. When NaH is placed in water, the hydride ion is converted to hydrogen, H2 , and the resulting
solution has a pH >7. Write a balanced chemical equation showing the reaction of sodium
hydride with water.
c. Is the hydride ion an acid or a base? What is the relationship of hydrogen, H2 , to hydride ion?
d. Hydride ion reacts with ethanol in exactly the same way as it does with water, generating
hydrogen as one of the products. Complete the following reaction:
CH3CH2OH
+
NaH
?
Chemistry 230- Answers to Assignment #2
1. a. aldehyde
f. alkene
b. alkyne
g. 1o amine
c. 2o alcohol
h. carboxylic acid
d. ketone
i. amide
2. a. 1o alcohol
b. 3o alcohol
c. 2o alcohol
d. 2o alcohol
e. ester
3.
primary carbon
Cl
*
*
b.
a.
Br
OH
c.
secondary carbon
tertiary carbon
4. a. C5H11Br (full structural formula are drawn)
*
d.
*
primary carbon
H
H
H
H
H
C
C
C
C
C
H
H
H
H
H
Br H
H
H
H
H
C
C
C
C
H
H
H
C
H
H
Br
H
H
H
H
C
H
H
C
C
C
H
C
H
H
H
H
*
secondary carbon
H
H
H
N
Br H
H
H
C
H
H
H
C
C
C
C
H
H
H
H
Br
H
b. C5H10O
(As you can see from the top example, it may be quite a task to draw all the bonds. You may want to
draw partial dash structures for convenience. Only draw the full structural formula if asked to do so!!)
H 3C
O
H 3C CH 2
CH2
H3C
CH 2 C
CH
CH 2 CH 3
C
H
H
O
CH CH 2 C
H 3C
O
H
c. C2H5NO
O
O
C
C
H 3C
NH 2
H
N
H
CH3
d. C4H10O
H 3C
H 3C CH2 O CH 2 CH 3
H 3C
O CH2
CH 2 CH 3
CH
O
CH 3
H 3C
e. C5H11Cl
CH 3
H 3C CH2 C
Cl
CH 3
5. These are all acid-base reactions. Identify the acid and the base first, then, complete the reaction. For
example, in part a, the acid is BF3 (a Lewis acid) and the base is the alcohol (a Lewis base).
a. CH 3OH
+
H3C
BF 3
O
BF 3
H
b. CH 3OCH 3
+
H3C
BF3
O
BF 3
CH3
O
c.
Cl
O
C
CH2
d. [Al(H2O)6]3+
OH
+
OH
+ HCO 3
Cl
C
CH2
[Al(H2O)5OH] 2+
O
+
+ H 2CO3
(carbonic acid dissociates into
H 2O and CO 2)
O
H
H
e. CH3COOH
+
f. CH3CH2COOH
NH3
+
CH3COO
CH3O
+
NH 4
CH3CH2COO
+
CH3OH
H
f. CH3CH 2OH
+
HCl
CH3CH2
+
O
Cl
H
6. The carboxylic acids are listed from strongest to weakest acid. The strongest acid has the chlorine
substituent (which exerts an inductive effect) closest to the carboxyl group in the conjugate base,
whereas the weakest acid does not have a chlorine in its structure. Keep in mind that the strongest acid
has the weakest (most stable) conjugate base.
O
Cl
OH
O
O
>
>
O
>
Cl
OH
OH
OH
Cl
7. a. Make the conjugate base of each acid and compare the stability of the conjugate bases based on
hybridization effect of the carbon atom bearing the negative charge in the base.
H3C
C
C
H3C
>
H
CH
CH
H
>
H3C CH2
CH2 H
b. The protonated alcohol is the strongest acid (think of the acidity of water compared to that of the
hydronium ion). The order here is then based on a periodic trend (a hydrogen attached to an oxygen
versus one that is attached to a carbon).
H
H3C CH 2
H3C CH 2
>
O
O
H
>
H3C
O
CH 2 H
H
c. The conjugate base of benzenesulfonic acid is stabilized by both resonance effects and inductive
effects and is therefore the most stable of the three conjugate bases. The phenolate ion is stable due to
resonance effects. These resonance effects are absent in the case of the conjugate base generated from
cyclohexanol.
O
S
O
H
>
O
H
O
>
H
O
pK a ~ -9
pKa ~ 10
pKa ~ 16
8. Use the formula provided to calculate Keq. The missing Ka values can be obtained from your organic
textbook or from any first year textbook. If you are provided with the pKa values, make sure to convert
these into Ka values. Notice that the nominator is the Ka of the reactant acid and the denominator is
the Ka of the product acid (no concentration terms are involved here!!).
a. (CH 3)3N +
HCN
(CH 3)3NH + CN
pKa 9.76
K a HCN (reactant acid) is 7.9x10 -10 and K a (CH 3)3NH (product acid) is 1.73x10 -10
therefore, K eq f or the reaction is 4.6
b. CH 3CH2SH
pKa 10.5
+ OH
CH 3CH 2S +
H2O
K a CH 3CH2SH (reactant acid) is 3.16x10-11 and Ka H 2O (product acid) is 2.0x10 -16
therefore, K eq f or the reaction is 1.6x105
c.
OH + NH3
O
+
NH 4
K a phenol (reactant acid) is 1.3x10 -10 and K a NH 4 (product acid) is 6.31x10 -10
therefore, K eq f or the reaction is 0.21
9. When drawing curved arrows, make sure to follow the direction of electrons movement.
a.
H
O
+
H
H3C
I
H
H
CH 3
H
b.
+
H
O
H
+
H
H
H
H
H
O
+
CH 3
O
H
H 3C
O
H
CH 3
H3C
H
H
H
CH 3
O
O
H 3C
H3C
H
O
c.
d.
F
F
F
H
H 3C
I
H
O
+
H
O
H
H3C
H3C
H
10. First, generate the conjugate base (the acid minus H+) and then draw resonance structures for the
conjugate base you have generated.
a.
O
+
O
H
H
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
b.
+ H
O
O
O
H
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Can you see anything wrong with this resonance structure:
+
O
O
O
O
-
11. a. NaH is an ionic compound. Na :H
b. The solution is basic (pH> 7) due to the formation of hydroxide ions.
NaH
+ H2O
mechanism:
Na
H:
NaOH
+
O
H
H
+
H2
H:H +
Na
+
O-H
c. Hydride ion is a base. Hydrogen, H2 , is the conjugate acid of the hydride ion
d. The hydride ion reacts with ethanol to give an ethoxide ion and hydrogen gas.
NaH
+ HOCH2CH 3
mechanism:
Na
H:
+
NaOCH 2CH3
O
H
CH2CH 3
+
H2
H:H +
Na
+
O-CH 2CH3