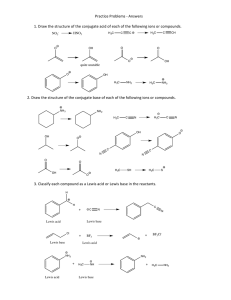
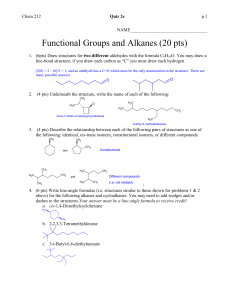
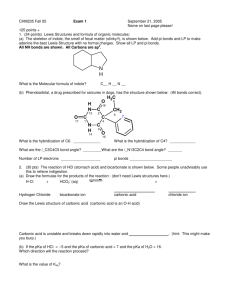
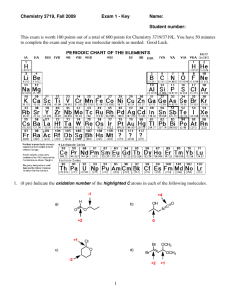
Answer Key
advertisement
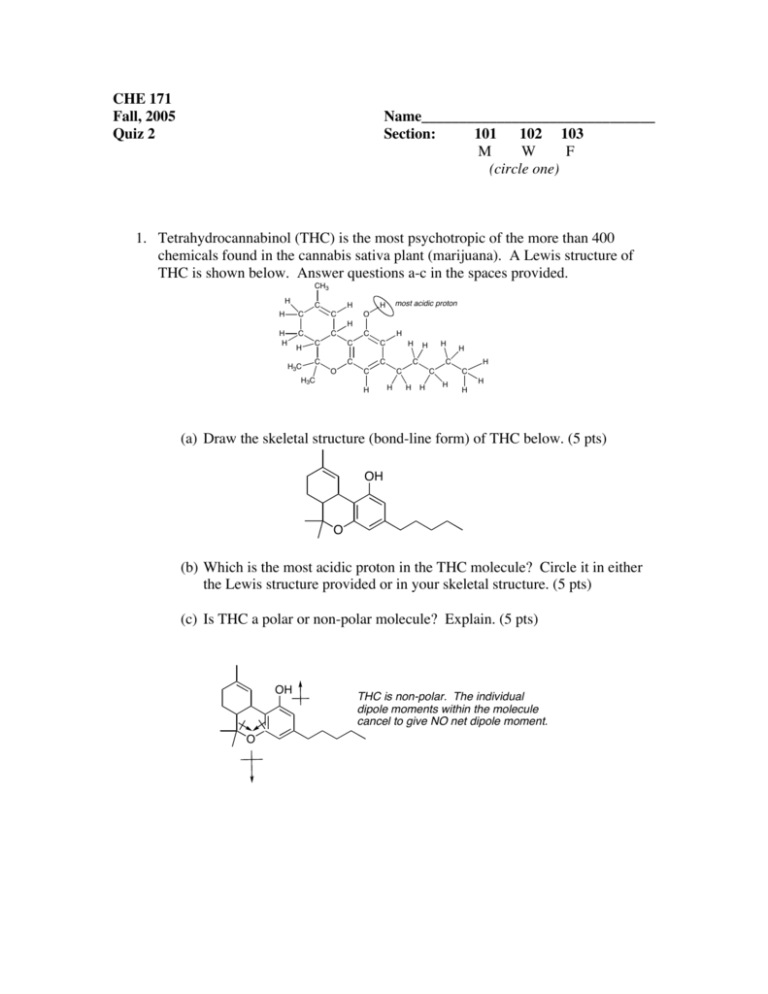
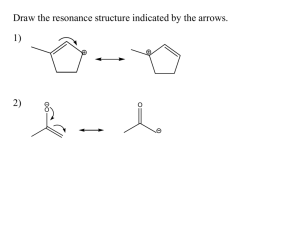
CHE 171 Fall, 2005 Quiz 2 Name_______________________________ Section: 101 102 103 M W F (circle one) 1. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the most psychotropic of the more than 400 chemicals found in the cannabis sativa plant (marijuana). A Lewis structure of THC is shown below. Answer questions a-c in the spaces provided. CH3 H C H C H H C H C most acidic proton H O H H H3C C C H C C C C C C O H C H 3C H H H C C H C H H C H H C H H H (a) Draw the skeletal structure (bond-line form) of THC below. (5 pts) OH O (b) Which is the most acidic proton in the THC molecule? Circle it in either the Lewis structure provided or in your skeletal structure. (5 pts) (c) Is THC a polar or non-polar molecule? Explain. (5 pts) OH O THC is non-polar. The individual dipole moments within the molecule cancel to give NO net dipole moment. 2. Draw the products of each of the following acid-base reactions and predict whether the equilibrium favors the starting materials or products (draw an arrow above the equilibrium arrows either towards products or reactants to show this; a pKa table is on the next page). Use curved-arrow notation to show electron flow. (5 pts each) O (a) O H O + O H + H2 (b) NH2 + H O NH3 + H2O + O (c) HO + H C C H C C H 3. Acetonitrile (CH3CN) has a pKa of 25, making it more acidic than many other compounds having only C-H bonds. Draw Lewis structures for acetonitrile and its conjugate base. Use resonance structures to account for the acidity of acetonitrile. (5 pts) See Smith Problem 2.16 H H C C N H + H H B C C NH C C N H H acetonitrile 4. In the reaction shown below, label the nucleophile and electrophile. Used curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs. (6 pts) H3C CH3 + H3C H Br CH3 nucleophile (Lewis base) H3C H3C electrophile (Lewis acid) H CH3 CH3 + Br 5. The pKa of three different C-H bonds is given below. (9 pts) (a) For each compound, draw the conjugate base, including all possible resonance structures. (b) Explain the observed trend in pKa. CH3CH2CH2-H CH3 H 2C C CH2-H pKa = 50 CH3CH2CH2 H 3C O C CH2-H pKa = 19.2 pKa = 43 CH3 H 2C C CH2 H 3C O C CH3 H 2C C CH2 H3C CH2 O C CH2 The most acidic compound has a conjugate base that is resonance stabilized, where the electron density is shared by the electronegative oxygen atom. See Smith Problem 2.39.