BIOLOGY REMEDIATION PORTFOLIO
advertisement

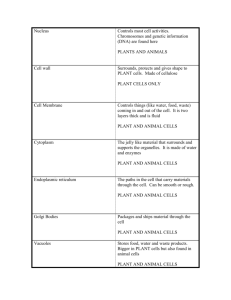
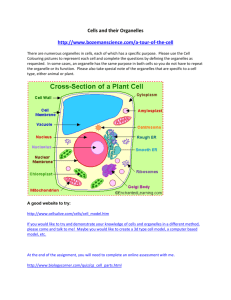
Objective 4a. Differentiate among plant and animal cells and eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. BIOLOGY REMEDIATION PORTFOLIO ©Angela Holley 9-12-11 ©Angela Holley 9-12-11 FOLLOW THIS “RECIPE” FOR SUCCESS: Check the box when you COMPLETE the activity. Follow these in their EXACT order. ☐1. READ THE ESSENTIAL QUESTION #1 and #2 BUT DO NOT ANSWER. ☐2. READ THE INSTRUCTIONS FOR ACTIVITY 1 (CELL FAMILY PHOTO ALBUM) ☐3. AFTER COMPLETING ACTIVITY 1(CELL FAMILY PHOTO ALBUM), YOU MUST HAVE YOUR TEACHER CHECK YOUR WORK. ☐4. COMPLETE THE ESSENTIAL QUESTION #1 DOUBLE BUBBLE ACTIVITY. ☐5. COMPLETE THE ESSENTIAL QUESTION #2 ☐6. THE TEACHER MUST CHECK BOTH ESSENTIAL QUESTION COMPLETIONS BEFORE YOU CAN MOVE ON. ☐7. THE TEACHER WILL GIVE YOU ACTIVITY 1 ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS TO COMPLETE. YOU CANNOT USE YOUR NOTES OR FRIENDS TO COMPLETE THIS. ☐8. THE TEACHER MUST CHECK YOUR ANSWERS ON THE ASSESSMENT WHEN COMPLETE. 8 OUT OF 10 MUST BE ANSWERED CORRECTLY TO MOVE ON TO ACTIVITY 2. BIOLOGY REMEDIATION PORTFOLIO SECTION 1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION #1: (ANSWER AFTER YOU COMPLETE ALL ACTIVITIES OF SECTION 1) 1. How can we compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? USE THE “WORD SPLASH” ON THE NEXT PAGE TO FILL THIS IN…WRITE THE ANSWERS IN THE APPROPRIATE “BUBBLE”…REMEMBER ALL ACTIVITIES MUST BE COMPLETE BEFORE YOU DO THIS. BOTH PROKARYOTIC EUKARYOTIC CELLS CELLS ©Angela Holley 9-12-11 NO ORGANIZED NUCLEUS Classified in Protist (Protista), Fungi, Plant and animal kingdoms MOST METABOLISM IS AEROBIC(WITH OXYGEN) CLASSIFIED INTO KINGDOMS OF ARCHAEBACTERIA AND EUBACTERIA Cell Are Variety of specialized membrane bound organelles like mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, etc. CONTAINS DNA WITH HISTONES ATTACHED ; FORMS CHROMOS OMES THIS PAGE GOES WITH ESSENTIAL QUESTION #1 MORE ORGANIZED STRUCTURES Metabolism is often anaerobic (without oxygen), or aerobic (with oxygen) Internal organelles surrounded by membranes MOSTLY UNICELLULAR (ONE-CELLED) Have an organized nucleus with nuclear membrane PRIMITIVE STRUCTURES Cells typically small Both unicellular and multicellular t Cells typically small Typically contain circular DNA strands called plasmids which do not contain histones Few specialized cell organelles (for example) ribosomes without their own membrane ESSENTIAL QUESTION #2: (ANSWER AFTER YOU COMPLETE ALL ACTIVITIES OF SECTION 1) 2. What is the relationship between the structure and function of the major cell organelles? COMPLETE THE CONCEPT MAP ON THE NEXT PAGE REMEMBER ALL ACTIVITIES MUST BE COMPLETE BEFORE YOU DO THIS. ©Angela Holley 9-12-11 Use this to answer Essential Question #2 Use this to answer Essential Question #2 Eukaryotic Cell Organelles Plant cell organelle Animal cell Function of organelle organelle Cell wall Cell membrane Cell membrane nucleus nucleus nucleolus cytoplasm ribosome \ Endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes Cytoplasm chloroplast lysosome Endoplasmic Golgi body mitochondria Golgi body mitochondria vesicle vacuole vesicle vacuole cytoskeleton ©Angela Holley 9-12-11 Function of organelle CELL “FAMILY SWAG” Photo Album ☐ ACTIVITY ONE DIRECTIONS: You are to create a Cell “family” photo album. The pictures in your photo album must contain captions to explain what they are representing. You can draw, cut and paste from magazines, use PowerPoint or another creative technology application to complete this activity. There are a few rules to follow and you will have 10 assessment questions to answer after you complete this activity. Rules: 1. You cannot use actual pictures of cells or cell organelles. You must find a real life, everyday picture that would be a creative representation of that type of cell and its organelles. I will give examples below, but you cannot use the examples I give. You will have a photo album for: i. FIRST PHOTO BOOK- a prokaryotic cell and its organelles (example: A race track for prokaryotic cell because it is free and open without much structure and example for DNA would be the tire marks left from spinouts because the DNA is typically circular in prokaryotic cells) ii. SECOND PHOTO BOOK-A eukaryotic cell 1. Plant cell and its organelles 2. Animal cell and its organelles 2. Use the rubric below to ensure you have the necessary components to complete the activity. 0 Points Cell and organelle pictures organelle descriptions 11 or more pictures are the actual organelles and not real life representations 11 or more organelle descriptions are the actual definitions and not real life representations 5 Points 15 Points 25 Points TOTAL POINTS POSSIBLE 6-10 pictures are the actual organelles and not real life representations 3-5 pictures are the actual organelles and not real life representations 0-2 pictures are the actual organelles and not real life representations _____/25 6-10 or more organelle descriptions are the actual definitions and not real life representations 3-5 or more organelle descriptions are the actual definitions and not real life representations 0-2 or more organelle descriptions are the actual definitions and not real life representations _____/25 Number of organelles represented 0 to 6 organelles represented 7 to 9 organelles represented 10-12 organelles represented 13 or more organelles represented _____/25 “swag” of photo album The pictures and descriptions are not clear and hard to read Less than half the pictures and descriptions are not clear and hard to read Half of the pictures and descriptions are not clear and hard to read All the pictures and descriptions are clear and easy to read _____/25 ©Angela Holley 9-12-11 Assessment Questions for Activity 1 1. What is the outermost structure that surrounds and supports plant and fungal cells? A) cell wall B) cytokinesis C) cytoskeleton D) cell membrane 2. In the image of the cell, letter C is the control center of the cell. Please identify this organelle. A) lysosome B) mitochondria C) nucleolus D) nucleus 3. Which organelle is the powerhouse of the cell, the site of cellular respiration? A) 2 – nucleus B) 5 - endoplasmic reticulum C) 6 - Golgi bodies D) 9 - mitochondria 4. Immature bone cells, or osteoblasts, manufacture a protein called osteoid as well as several hormones. Because of this, we would expect osteoblasts to contain numerous A) nuclei. B) ribosomes. C) lysosomes. D) Golgi bodies. 5. This part of the cell stores wastes, water or food. A) lysosome B) mitochondria C) ribosome D) vacuole 6. Which two structures are found ONLY in plant cells? A) vacuoles and ribosomes C) cell walls and chloroplasts B) chloroplasts and ribosomes D) endoplasmic reticulum and cell walls 7. ___________ digest and recycle the cell's used components by breaking down proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates. A) Vesicles B) Ribosomes C) Lysosomes D) Endoplasmic reticula 8. In a eukaryotic cell, DNA is found in A) a vacuole. B) a nucleus. C) a cytoplasm. D) an endoplasmic reticulum. 9. What is the function of a cell’s selectively permeable plasma membrane? A) It helps the cell to manufacture proteins. B) It regulates the amount of ATP the cell produces. C) It regulates what materials enter and leave the cell. D) It packages and stores most of the material in a cell. 10. Suppose that the cell is a city. What cell organelle would have a similar purpose to the roads throughout the town? A) ribosomes B) Golgi body C) chloroplasts D) endoplasmic reticulum