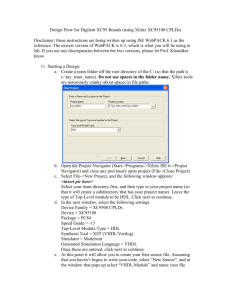
ENG560 Embedded Systems Design
advertisement
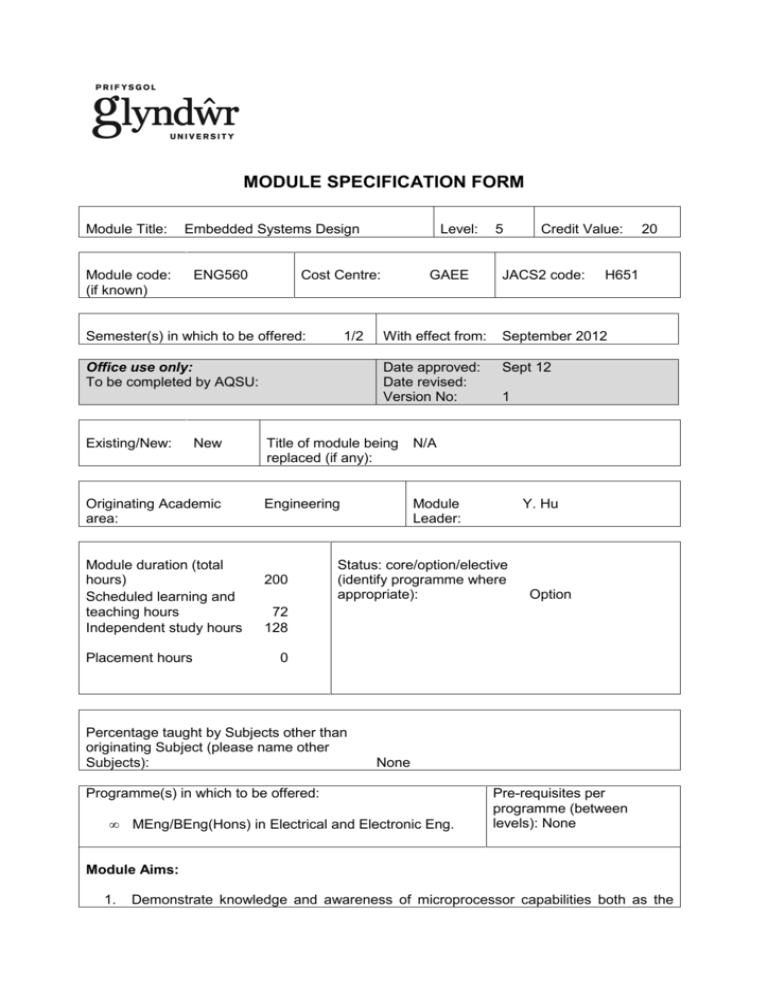
MODULE SPECIFICATION FORM Module Title: Embedded Systems Design Module code: (if known) ENG560 Cost Centre: Semester(s) in which to be offered: 1/2 Office use only: To be completed by AQSU: Existing/New: New Originating Academic area: Module duration (total hours) Scheduled learning and teaching hours Independent study hours Placement hours Level: GAEE JACS2 code: Date approved: Date revised: Version No: Sept 12 Engineering Module Leader: 20 H651 September 2012 N/A 1 Y. Hu Status: core/option/elective (identify programme where appropriate): Option 72 128 0 Percentage taught by Subjects other than originating Subject (please name other Subjects): None Programme(s) in which to be offered: • Credit Value: With effect from: Title of module being replaced (if any): 200 5 MEng/BEng(Hons) in Electrical and Electronic Eng. Pre-requisites per programme (between levels): None Module Aims: 1. Demonstrate knowledge and awareness of microprocessor capabilities both as the 2. central processing element in a computer system and as an embedded element in an electronic system; To develop previous studies into a knowledge and understanding of combinational and sequential circuit analysis and design using a range of current techniques, including modelling via VHDL (computer-based modelling using a Hardware Description Language). Expected Learning Outcomes At the end of this module, students should be able to: Knowledge and Understanding: 1. Demonstrate knowledge and awareness of microprocessor capabilities both as the central processing element in a computer system and as an embedded element in an electronic system; 2. Design appropriate hardware interfacing; 3. Design, test and evaluate assembly-level programs. 4. Design sequential and combinational logic systems using a range of established methods; 5. Apply circuit design to digital programmable devices technology; 6. Write VHDL programs and thus design digital systems using VHDL and EDA tools. Transferable/Key Skills and other attributes: 1. 2. 3. System analysis and design; Apply design; Apply Technology. Assessment: please indicate the type(s) of assessment (eg examination, oral, coursework, project) and the weighting of each (%). Details of indicative assessment tasks must be included. Assessment One: is by means of writing a correctly documented assembly-language programme to enable a microprocessor to respond to inputs from and control outputs to external hardware, for example to control a stepper motor speed and direction, including acceleration and deceleration profiles. It will cover outcomes 1 to 3. Assessment Two: is by means of a portfolio of practical exercises in the use of hardware programming, including a major programming exercise using VHDL. For example, to design a hardware multiplier. It will cover outcomes 4 to 6. *Derogations from Academic Regulations are in place for this module for some programmes. Please see the programme specification for further details and to check applicability. Word count (or equivalent if appropriate) Assessment number Learning Outcomes to be met One 1,2,3 Coursework 50% 2,000 Two 4,5,6 Portfolio 50% 2,000 Type of assessment Weighting Duration (if exam) Learning and Teaching Strategies: The module will be delivered through lectures, tutorials, and practical laboratory exercises. Case studies will be used to illustrate applications in the module content. Syllabus outline: Digital conventions: Bit, byte, word; binary, hexadecimal, octal; binary arithmetic, logical operations; Gray code, BCD, ASCII. System architecture: Clock, CPU, memory, interfaces, bus systems and controlling logic; CPU internal architecture; Van Neumann model - fetch/execute cycle; instruction set, timing. Pipeline and multi-processing architectures. Memory structures: Main memory address, access and structures; device types and parameters, memory map. Interfaces: Functional treatment of parallel ports, serial ports - UARTs etc, ADC/DACs. Dedicated interfaces eg to drive 'power' equipment. Memory-mapped I/O and I/Omapping. Communication: polling and interrupts. Bus systems e.g. VME, STE, I²C. Design, writing and testing: of assembly language programs for a microcontroller (eg PIC) or a personal computer processor. Development tools (editor, assembler, ICE), use of subroutines, functions, to carry out an engineering task. Digital system design process: Combinational simplification: tabular method. Sequential system design and analysis for components and circuits. D/A and A/D conversions Introduction to FPGA/CPLD: Hardware description language (HDL): VHDL basic concepts, main elements, top-down design, data types, subprograms, vhdl operators, concurrent and sequential assignments, etc. Hardware: structural description, behavioural description, design organization and parameterization Practical examples of VHDL design of digital systems Practical/IT session includes: comparison types of FPGA/CPLD, introduction to EDA software, VHDL coding practices, further programs, working towards digital system design assignment. Bibliography Essential reading: Bates, M. (2011) The PIC Microcontroller: An Introduction to Microelectronics, 3rd Edn., Newnes. Kafig, W. (2011) VHDL 101: Everything you Need to Know to Get Started, Newnes. Hughes, E. et al. (2012) Electrical and Electronic Technology, 11th Edn., Pearson. Wakerly, J.F. (2005) Digital Design: Principles and Practices, 4th Edn., Prentice-Hall. Recommended reading: Wilmshurst, T. (2009) Designing Enbedded Systems with PIC Microcontrollers: Principles and Applications, 2nd Ed., Newnes. Nilsson, J.W. and Riedel, S. (2010) Introduction to Multisim for Electric Circuits, 9th Edn., Prentice-Hall. Navabi, Z. (2007) VHDL Modular Design and Synthesis of Cores and Systems, McGraw-Hill. Morton, J. (2005) The PIC Microcontroller: Your Personal Introductory Course, 3rd Edn., Newnes. Katzen, S. (2005) The Quintessential PIC Microcontroller; 2nd Edn., London: Springer-Verlag. Smith, D.W. (2006) PIC In Practice: A Project –based Approach, Elsevier. Yalamanchili, S. (2003) Introductory VHDL From Simulation to Synthesis, Prentice-Hall. Key Website References: Microchip Technology Inc: http://www.microchip.com/; PIC Microcontrollers – Free online Book – mikroElektronika: http://www.mikroe.com/eng/products/view/11/book-pic-microcontrollers/; Xilinx, Inc: http://www.xilinx.com/university/index.htm. IEEE Xplore Digital Library (http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/guesthome.jsp) including: IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems.