Plant Parts Worksheet: Botany Definitions

Plant Parts Worksheet
Taproot- A straight tapering root growing vertically downward and forming the center from which subsidiary rootlets spring
Fibrous Root- Fine, threadlike or slender roots.
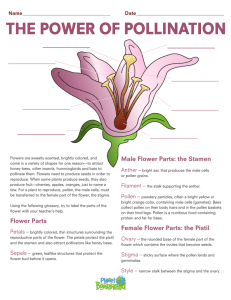
Petal- The segment of the flowers, usually colored.
Anther- The part of a stamen that contains the pollen
Filament- The slender part of a stamen that supports the anther
Stamen- The male fertilizing organ of a flower, typically consisting of a pollen-containing anther and a filament
Ovule- A part of a flower. Part of the female part of the flower and is an unpollinated, immature seed.
Once pollinated, the ovule will develop into seeds.
Sepal- the outermost parts of a flower which cover and protect the flower when it is in bud. They are usually green.
Receptacle- The part of a flower stalk where the parts of the flower are attached.
Ovary- the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
Style- the style is a structure found within the flower. It is a long, slender stalk that connects the stigma and the ovary.
Stigma- the receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower .
The stigma receives pollen at pollination and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germinates
Pistil- Female reproductive part of a flower
Blade- the broad portion of a leaf as distinct from the petiole
1. Petiole- the stalk that joins a leaf to a stem
Stipules-
Midrib- The central or principal vein of a leaf
Vein- the vascular tissue of the leaf
Small Netted Vein-
Stomata- One of the tiny openings in the epidermis of a plant , through which gases and water vapor pass. Stomata permit the absorption of carbon dioxide necessary for photosynthesis from the air, as well as the removal of excess oxygen.