Physics 11 Dynamics Practice Test
advertisement

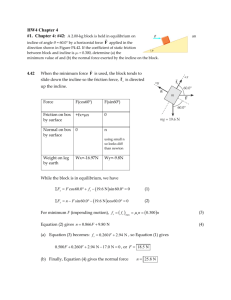
Fraser Heights Secondary Physics 11 Mr. Wu Practice Test (Dynamics) Instructions: Pick the best answer available for Part A. Show all your work for each question in Part B Part A: 1. Multiple-Choice Inertia is directly related to which of the following quantities? A. Mass B. Charge C. Velocity D. Position 2. The units N/kg are used for A. Displacement B. Velocity C. Acceleration D. Time 3. When an object is subjected to a constant positive net force it will experience a constant. A. Velocity. B. Friction. C. Acceleration. D. Displacement. 4. The block in the diagram below is being accelerated to the right across a rough surface by a force applied through the rope. Which of the following best represents a free-body diagram for the block? 1 5. If the net force on a falling object is zero, then the object has A. Constant speed. B. Constant altitude. C. Constant displacement. D. Constant time. 6. A 5.0 kg object is pulled at a constant speed by a horizontal 12 N force as shown in the diagram below. What is the coefficient of friction between the object and the surface? A. 0.24 B. 0.42 C. 1.0 D. 2.4 7. If the only forces acting on the object shown below are equal in magnitude, which of the following is not possible? A. The object is at rest. B. The object is accelerating to the left. C. The object is moving with constant velocity to the right. D. The object is moving with constant velocity towards the top of the page. 8. A 1200 kg trailer is accelerated from rest to 15 m/s in 5.0 s. The average force of friction acting on the trailer is 800 N. What is the pulling force applied to the trailer through the hitch? A. 800 N B. 2800 N C. 3600 N D. 4400 N 2 9. An 810 kg dragster is being decelerated by a parachute at 2.5 m/s2 as shown in the diagram. What is the tension in the cord at this moment? A. 0 N B. 2.0 ×103 N C. 5.9 ×103 N D. 7.9 ×103 N 10. A 1200 kg vehicle is accelerated from rest to 15 m/s over a distance of 85 m. What is the net force on the car during this acceleration? A. 1 600 N B. 3 200 N C. 6 800 N D. 10 000 N 11. A falling 0.60 kg object experiences a frictional force due to air resistance of 1.5 N. What is the object’s acceleration? A. 2.5 m / s 2 B. 4.4 m / s 2 C. 7.3 m / s 2 D. 12 m / s 2 12. A 6.0 kg object is projected directly upward with an initial speed of 15 m s. This object experiences an average air resistance force of 24 N. What is the maximum height reached by this object? A. 8.2 m B. 11 m C. 16 m D. 19 m 13. The 4.0 kg block shown below is accelerating downwards at 3.0 m / s 2 near the earth’s surface. What is the tension in the rope attached to it? A. 12 N B. 27 N C. 39 N D. 51 N 3 14. The free body diagram shown below is for a block being accelerated across a floor to the right by the force F. Which of the following represents the coefficient of friction for this situation? 15. The system of masses shown below is accelerating to the right at 2.0 m / s 2 . If the tension in the rope at point P is 70 N, what is the coefficient of friction between the masses and the surface? A. 0.15 B. 0.20 C. 0.43 D. 0.57 4 16. The mass shown below is accelerating to the right due to the two forces acting on it. What is the size of the force F ? A. 32 N B. 50 N C. 65 N D. 78 N 17. A 6.0 kg penguin in a zoo exhibit starts from rest and slides 5.0 m along a very slippery rock slope (ignore friction) into the water in 1.4s. What angle does the rock slope make with the horizontal? A. 21° B. 28° C. 31° D. 59° 18. A locomotive pulling a freight car accelerates at 0.50 m / s 2 as shown in the diagram. What is the tension in the coupling linking the locomotive and car? (Ignore friction.) A. 5 000 N B. 25 000 N C. 30 000 N D. 390 000 N 19. A 5.0 kg block is being pulled to the right by a 75 N force. What is the normal force on this block? A. 23 N B. 26 N C. 49 N D. 75 N 20. Two masses are connected by a string as shown in the diagram. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of these masses? (Ignore friction.) 5 A. 0.11 m / s 2 B. 0.19 m / s 2 C. 0.86 m / s 2 D. 1.1 m / s 2 21. The system of blocks shown in the diagram below is being accelerated to the right at 4.4 m / s 2 . What pulling force is applied by the hand? A. 0.3 N B. 1.0 N C. 1.3 N D. 2.3 N 22. What is the normal force on the block in the diagram below? A. 0.0 N B. 10 N C. 22 N D. 25 N 6 23. A 1.5 kg block slides down the incline at a constant speed. What is the net force on this block? A. 0 N B. 6.2 N C. 13 N D. 15 N 24. A block is launched up the frictionless incline in the diagram below with an initial speed of 5.5 m/s. What is the maximum displacement, d, of the block up the incline? A. 0.44 m B. 0.87 m C. 1.5 m D. 2.4 m 25. The block shown in the diagram below remains at rest. What is the friction force acting on the block? A. 0 N B. 3.1 N C. 3.8 N D. The friction force cannot be calculated. 7 26. If the tension in the line joining the two masses shown below is 12 N, what is the mass, m1 ? (Ignore surface friction.) A. 1.1 kg B. 1.4 kg C. 2.0 kg D. 10 kg 27. Two masses, one of 1.0 kg, the other of 3.0 kg, are suspended from the ends of a light string passing over a frictionless pulley. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of these masses? A. 2.5 m / s 2 B. 4.9 m / s 2 C. 7.4 m / s 2 D. 9.8 m / s 2 28. A 2.0 kg mass is suspended by a spring scale from the ceiling of an elevator. If the spring scale reads 25 N, then the acceleration of the elevator is A. 2.7 B. 2.7 C. 1.3 D. 1.3 m / s 2 upwards. m / s 2 downwards . m / s 2 upwards . m / s 2 downwards. 8 Part B: 1. Open Ended A 65 N force is applied to a 5.0 kg object as shown. The coefficient of friction between the object and the horizontal surface is 0.25. a) Draw and label a free body diagram showing the forces acting on the object. b) What is the acceleration of the object? 2. 3. A 2.2 kg can of paint is projected up an inclined plane with an initial velocity of 15 m/s as shown below. a) Determine the magnitude of the force due to friction which acts on the paint can as it slides up the incline. b) Determine the magnitude of the net force on the paint can as it slides up the incline. c) Determine how far the paint can slides up the incline before stopping. Determine the acceleration of the system of masses shown below when it is released. 9 4. A system of masses is connected by a light cord passing over a pulley as shown in the diagram. a) Draw a labeled free body diagram for mass m2. b) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the system of masses? 5. Identical blocks are placed on inclines as shown. The coefficients of friction between the blocks and the inclined surfaces are identical. Both blocks are then pushed to the top of each incline at the same constant speed. Using principles of physics, explain which block required more work to reach the top of the incline. 6. The diagram shows two objects connected by a light string over a frictionless pulley. Object m 2 is on a frictionless horizontal table. The tension in the string is 24 N. What is m2 if the system accelerates as shown? 10