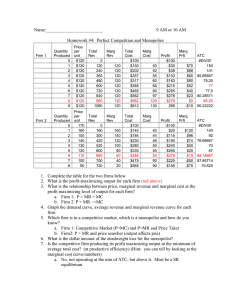
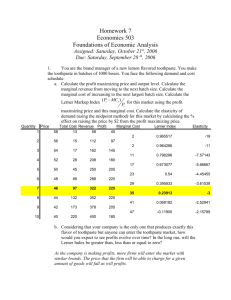
MATH REVIEW: Some Tools for E i A l i Economic Analysis Role of
advertisement

MATH REVIEW: Some Tools for E Economic Analysis i A l i Functions, Derivatives & Optimization Procedures But First, the Context Role of Math in Econ • An Integral Part of Economics – A Means to an End? – An End Unto Itself? • Math as: – An Analytic Framework – A Tool – A Way to: • Structure Complex Situations • Organize Information • Examine/Evaluate/Predict Economic Behavior Basic Premise in Economics: • Purposeful Behavior – Logic or Pattern to Actions – Discover, Model, & Use Info • Standard Economic Assumption: p “Optimizing” – MAXIMIZING BEHAVIOR • Households: Maximize Utility or Satisfaction • Firms: Maximize Profits; (Wealth; NPV) – MINIMIZING BEHAVIOR • Minimize Costs • Minimize Defects? 1 Justifications for Maximizing Assumption • Simple & Intuitive • Aids in Model Building – Optimization Techniques • Useful Approximation…”as if...” • Powerful and Flexible – Easily Extended – Can Introduce Complications Baseline Firm Objective: • "Maximize” Something • Simplest Case: Current Period Profits • Alternatives/Extensions – Long Run Profits – Shareholder Wealth/Value Shareholder Wealth/Value • NPV of Multi‐Period Profit Stream • Max Subject to Constraints – Unit or Dollar Sales Revenue • While Acknowledging Potential Problems: – – – – Hard to Specify Exact “Objective Function” Constraints: Legal, Social, Environmental, Behavioral Often Don't Know/Understand Constraints Often Difficult to Quantify Constraints Principles for Decision Making • Marginal and Incremental Analysis: – Examine Impact of Small Changes – "Decisions Made at the Margin" (or should be) • Difference Tied to Magnitude of Change – “Marginal” Small Change Derivative – Incremental Bigger Change (Same Principle) 2 Decision Making as an “Optimization Problem” • Optimizing Means Max or Min – Maximizing – Minimizing MARG BEN = MARG COST • We Need to Consider the Basic Mechanics: – The Set Up & Solve Process – Framework for Analysis of Critical Issues – (Can Soften/Adapt Prior to Implementation) Wrap Up: • Economics Assumes Purposeful Behavior • Economic Behavior Modeled Using Math Tools • Optimization Techniques (Max/Min) O i i i h i ( / i ) • Fundamental Principle: – “Decision Making at the Margin” – Marginal Benefits = Marginal Cost 3